Table of Contents
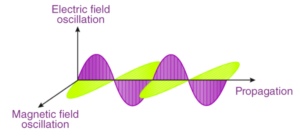
Electromagnetic waves, also known as EM waves, are a type of electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic radiations are composed of electromagnetic waves produced when an electric field collides with a magnetic field. Electromagnetic waves are also defined as an oscillating combination of electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic waves solve Maxwell’s equations, which are the fundamental equations of electrodynamics. In general, a charged particle generates an electric field.
This electric field has an effect on other charged particles. Positive charges move in the direction of the field, whereas negative charges move in the opposite direction. A moving charged particle generates the magnetic field. This magnetic field has an effect on other moving particles.
Because the force acting on these charges is always perpendicular to their velocity, it only changes the direction of the velocity rather than the speed. As a result, an accelerating charged particle generates the electromagnetic field. Electromagnetic waves are nothing more than electric and magnetic fields travelling through free space at the speed of light c. A charged particle is said to be accelerating when it oscillates around an equilibrium position. If the frequency of oscillation of the charged particle is f, it produces an electromagnetic wave with frequency f. The wavelength of this wave is given by λ= c/f. Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy transfer that takes place in space.
Solved Solutions
Question: Demonstrate that the displacement current![]() has the same direction as an electric current.
has the same direction as an electric current.
Solution:
Dimensions of displacement current ![]() is given as:
is given as:
![]()
![]()
Also, dimension of the electric current ![]() dimension of
dimension of
∴ Displacement current and electric current are the same.
Question: A point charge moves in a straight line at constant velocity v. Consider a small area A perpendicular to the charge’s motion direction. Calculate the displacement current through the area when the charge is x distance away. Because x is small, the electric field at any given instant is essentially given by Coulomb’s law.
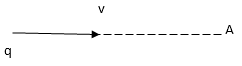
Solution:
By Columb’s law,
![]()
Also, we know,
![]()
![]()
Question: The food is kept in a plastic container in a microwave oven, and the microwaves are directed towards the food. The food is cooked without the plastic container melting or igniting. Explain.
Solution:
The natural frequency of water is the same as the frequency of microwaves. This is why food containing water must be cooked. The natural frequency of the plastic container does not correspond to the frequency of the microwave. As a result, the plastic container is undamaged.
Question: Can an electric or magnetic field deflect an electromagnetic wave?
Solution:
An electromagnetic wave cannot be deflected by either an electric or magnetic field. This is due to Maxwell’s theory, which states that an electromagnetic wave does not interact with the static electric and magnetic fields. Even when we consider the wave’s particle nature, the photon is electrically neutral. As a result, it is unaffected by static magnetic and electric fields.
FAQs
Name the property of an electromagnetic wave that is affected by the medium through which it travels.
The velocity of an electromagnetic wave is a property that depends on the medium through which it travels. Other properties of the wave, such as frequency, time period, and wavelength, are determined by the source of the wave.
What are the seven different types of electromagnetic waves?
From longest to shortest wavelength, the electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, optical, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma-rays.




