Table of Contents
The process of converting energy from one form to the next is known as energy transformation or energy conversion. Energy is a quantity in physics that has the competence to implement work or create heat.
A Brief outline
Many sources of energy can be employed in natural processes or to provide social services such as heating, refrigeration, lighting, or mechanical labour to operate machines. To heat a home, for example, a furnace burns fuel, converting chemical potential energy into thermal energy, which is subsequently transferred to the air in the home to raise the temperature.
Important Concepts
The investigation of how energy is transformed from one state to another is known as thermodynamics. Energy cannot be generated or destroyed; instead, it can only be converted from one state to another. This is sometimes referred to as the law of energy conservation or the law of energy transfer.
Energy Transformation Examples
The following are some instances of energy conversion sets in machines.
Coal fire power plant:
- A coal-fired power plant is a type of power plant that uses coal to generate electricity.
- The chemical energy in coal is transformed into thermal energy during the burning process.
- The thermal energy of the exhaust gas is then transformed into the thermal energy of steam via the heat exchanger.
- The thermal energy of steam is then turned into mechanical energy in the turbine.
- Finally, mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy with the help of a generator.
Automobiles
- The chemical energy in the fuel is transformed into kinetic energy of the expanding gas during combustion.
- The expanding gas’s kinetic energy is then transferred into linear piston action.
- The linear piston motion is then translated to rotational crankshaft motion.
- The automobile’s linear motion is converted from the rotational movement of the drive wheels.

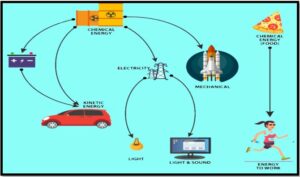
The Law of Conservation of Energy
In physical science, the law of conservation of energy is the principle that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be converted from one form to another. The law of conservation of energy is one of the most fundamental principles in physics.
The law of conservation of energy was first proposed by the French physicist Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century. He showed that the total amount of energy in a closed system is always conserved. This means that the total amount of energy in the system cannot change. It can only be transferred between the different forms of energy.
The law of conservation of energy is supported by a large amount of experimental evidence. It has been tested in many different situations, and has been found to be accurate.
The law of conservation of energy is important because it helps us to understand the fundamental nature of energy. It also helps us to understand how energy is transferred between different forms.
We know that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant. Let us now concentrate on the most common types of energy in physics.
- Kinetic Energy is the energy that a body/object has as a result of its motion.
- Because of the object’s position, this energy is seen as potential energy.
Significance of types of energy transformations in the IIT JEE exam
The IIT JEE is a very important exam for students aspiring to study engineering at the prestigious Indian Institutes of Technology. The exam is conducted in two parts- JEE Main and JEE Advanced. The JEE Main is the preliminary exam while the JEE Advanced is the final exam.
The JEE Main is a paper-based exam while the JEE Advanced is an online exam. The JEE Main is conducted in both Hindi and English while the JEE Advanced is conducted only in English.
The JEE Main is a three-hour exam while the JEE Advanced is a two-hour exam. The JEE Main is conducted in pen-and-paper mode while the JEE Advanced is conducted in computer-based mode.
The JEE Main is a multiple-choice question (MCQ) exam while the JEE Advanced is a subjective question (SQ) exam. The JEE Main is conducted in both Hindi and English while the JEE Advanced is conducted only in English.
The JEE Main is a three-hour exam while the JEE Advanced is a two-hour exam. The JEE Main is conducted in pen-and-paper mode while the JEE Advanced is conducted in computer-based mode.
The JEE Main is a multiple-choice question (MCQ) exam while the JEE Advanced is a subjective question (SQ) exam. The JEE Main is conducted in both Hindi and English while the JEE Advanced is conducted only in English.
Work on the chapter, energy, and power are worth fewer points and require less effort. The topic of energy transformation or conversion accounts for only 6.66 percent of the exam, with only 2 to 3 questions asked. Physics is a conceptual discipline that demands practice and comprehension.
FAQs
What is the most energy-efficient form?
Renewable energy is among the most efficient kinds of energy when measured in terms of efficiency.
Is it possible for energy transformations to be 100 percent efficient?
Energy transitions are 100 percent efficient, as per the law of thermodynamics. It means that the energy output to input ratio is always one. An electric heater, for example, has an energy input of electricity and energy output of heat.
What is Renewable Energy, and how does it work?
Renewable energy is defined as energy derived from renewable resources which are continuously regenerated by nature after use and consumption.






