Table of Contents
Urinary System Diagram: The urinary system is a crucial part of the human body, responsible for removing waste, balancing fluids, and maintaining overall health. In this blog, we’ll break down the urinary system diagram, explaining each part and its functions in a clear and simple way. Whether you’re a student, healthcare professional, or just curious about how your body works, this guide will help you understand the urinary system’s anatomy and physiology.
What is the Urinary System?
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, is a collection of organs and structures that work together to filter blood, remove waste, and regulate bodily fluids. It consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in maintaining homeostasis. Let’s explore these parts in detail, using a detailed urinary system diagram for reference.
Urinary System Diagram
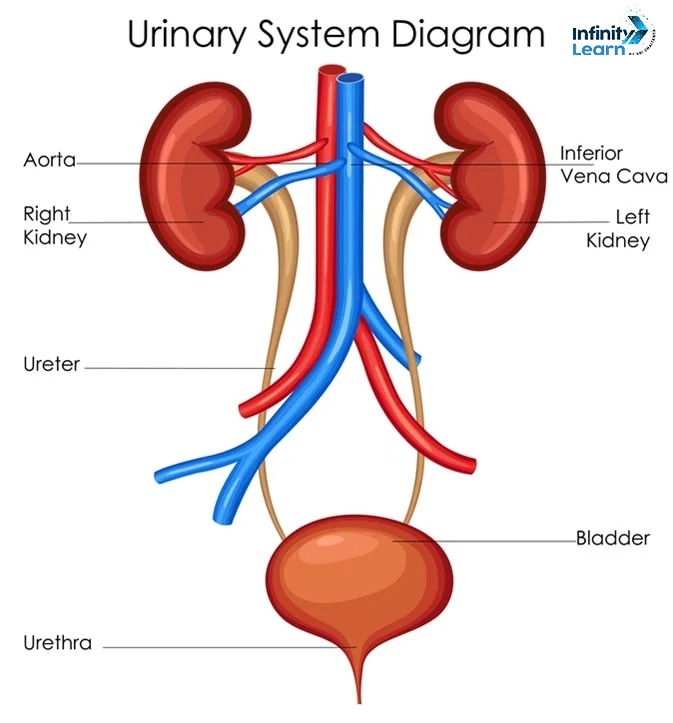
Components of the Urinary System Diagram
Here’s a breakdown of the urinary system diagram, explaining each component’s structure and function:
1. Kidneys: The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back, one on each side of the spine. The kidneys are vital organs that filter blood to remove waste and excess substances, which are subsequently expelled from the body as urine. They also contribute to regulating blood pressure, maintaining electrolyte levels, and secreting hormones that support red blood cell formation.
2. Ureters: The ureters are two thin tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. They are around 10-12 inches long and use smooth muscle contractions, called peristalsis, to move urine downward.
3. Bladder: The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ located in the pelvis. It stores urine until it’s ready to be excreted from the body. The bladder expands as it fills with urine and contracts to release urine through the urethra during urination.
4. Urethra: The urethra is a passageway that transports urine from the bladder to the external part of the body. In males, the urethra also carries semen. It is shorter in females and longer in males, and it plays a key role in the urinary process.
Don’t Miss:
- Animal Cell Diagram
- Nitrogen Cycle Diagram
- Plant Cell Diagram
- Nephron Diagram Class 10
- Neuron Diagram
- Nucleus Diagram
- Human Brain Diagram Class 10
- Autoclave diagram
- Block Diagram of Computer
- Human Excretory System Diagram
- 8085 Pin Diagram of Microprocessor
How to Draw the Urinary System Diagram
- Draw the Kidneys: Start with two bean-shaped structures on either side of the spine, slightly below the ribcage.
- Add the Ureters: Draw two thin tubes extending downward from each kidney to the bladder. Position them so they angle slightly towards the bladder.
- Sketch the Bladder: Draw a rounded, balloon-like structure at the lower end of the ureters. Place it centrally between the ureters.
- Draw the Urethra: Extend a short, narrow tube from the bottom of the bladder downward to indicate the urethra. This tube should be slightly thicker than the ureters.
- Label the Structures: Add labels for each part: Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra.
- Include Arteries and Veins (Optional): Draw a short artery and vein connecting to each kidney to represent blood flow. Label these as Renal Artery and Renal Vein.
- Highlight the Path of Urine: You can use arrows to show the direction of urine flow: from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder, and then out through the urethra.
How Does the Urinary System Work?
Understanding how the urinary system works can help you appreciate its importance in maintaining health. Lets have a look on each of its functions.
- Filtration: Blood enters the kidneys through the renal arteries. Inside the kidneys, blood is filtered through structures called nephrons. The nephrons remove waste products, excess salts, and water, creating a fluid called filtrate.
- Reabsorption: As the filtrate moves through the kidney’s tubules, essential substances like glucose, amino acids, and certain ions are reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
- Secretion: Additional waste products are secreted into the filtrate from the blood, helping to fine-tune the body’s balance of fluids and electrolytes.
- Excretion: The final product, urine, flows from the kidneys into the ureters. The ureters carry the urine to the bladder, where it is stored until it is eliminated from the body through the urethra.
Why is the Urinary System Important?
The urinary system plays several vital roles in maintaining overall health:
- Waste Removal: It filters out toxins and waste products from the bloodstream, preventing them from accumulating in the body.
- Fluid Balance: It regulates the body’s fluid levels, ensuring that we neither retain excess water nor become dehydrated.
- Electrolyte Balance: It maintains the proper levels of essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and calcium.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: It helps control blood pressure through the release of renin and the regulation of blood volume.
- Hormone Production: The kidneys release hormones like erythropoietin that promote the production of red blood cells.
Common Urinary System Disorders
Understanding the urinary system diagram also means being aware of common disorders that can affect it:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections that can affect any part of the urinary system, causing pain and discomfort.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits of minerals and salts that can form in the kidneys and cause pain and blockages.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A chronic condition in which the kidneys progressively lose their ability to function over an extended period.
Conclusion
The urinary system is a complex yet essential part of human anatomy. By understanding the urinary system diagram and learning about the functions of each component, you gain insight into how your body maintains balance and health. From the kidneys filtering blood to the urethra expelling urine, every part plays a specific role in the process.
By keeping this information in mind, you can better appreciate how your body works and recognize the importance of keeping your urinary system healthy. Regular check-ups and staying hydrated are simple ways to support this vital system.
FAQs on Urinary System Diagram
What does a typical urinary system diagram show?
A typical urinary system diagram displays the main organs and structures involved in urine production and excretion. It usually includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, along with blood vessels like the renal arteries and veins.
How can I use a urinary system diagram for study purposes?
A urinary system diagram helps you visualize and grasp the arrangement and functions of the organs involved in urine production and excretion. It helps in memorizing the parts of the system and their interactions, which is useful for exams and practical applications.
What are the key components labeled in a urinary system diagram?
Key components typically labeled in a urinary system diagram include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, renal arteries, renal veins, and nephrons. These labels help in identifying the structures and understanding their roles.
Are there different types of urinary system diagrams for various educational levels?
Yes, there are different types of urinary system diagrams for various educational levels. Basic diagrams may focus on the main organs, while more detailed diagrams might include structures like nephrons and blood vessels, suited for advanced studies.
What are common mistakes to avoid when studying a urinary system diagram?
Common mistakes to avoid include misidentifying the organs, confusing the flow of urine, and overlooking the role of each component. Make sure you understand how urine moves through the system and the functions of each organ.







