Table of Contents
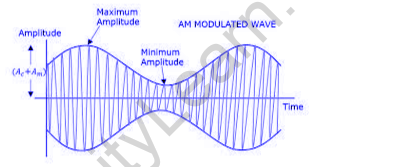
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic conversation, maximum usually for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude (sign electricity) of the wave is varied in share to that of the message sign, which includes an audio signal. This technique contrasts with attitude modulation, in which both the frequency of the provider wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its segment, as in section modulation.
AM become the earliest modulation approach used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It turned into development throughout the primary region of the 20 th century beginning with Roberto Landell De Moura and Reginald Fessenden’s radiotelephone experiments in 1900.[1] This original form of AM is occasionally called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM) due to the fact the standard technique produces sidebands on both sides of the service frequency.
Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to get rid of one of the sidebands and in all likelihood, the carrier sign, which improves the ratio of message electricity to general transmission electricity, reduces electricity managing requirements of line repeaters and permits higher bandwidth usage of the transmission medium.
AM remains in use in many varieties of communique further to AM broadcasting: shortwave radio, amateur radio, two-manner radios, VHF plane radio, citizens band radio, and computer modems within the form of QAM.
In electronics, telecommunications, and mechanics, modulation means various a few aspects of a continuous wave carrier signal with a records-bearing modulation waveform, which includes an audio sign which represents a valid, or a video signal which represents photographs. In this feel, the service wave, which has a much higher frequency than the message sign, incorporates the information. At the receiving station, the message sign is extracted from the modulated service using demodulation.
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude or strength of the radio frequency oscillations is varied. For instance, in AM radio communication, a non-stop wave radio-frequency sign has its amplitude modulated by way of an audio waveform before transmission. The audio waveform modifies the amplitude of the radio wave and determines the envelope of the waveform. In the frequency area, amplitude modulation produces a signal with strength focused on the service frequency and adjoining sidebands. Each sideband is equal in bandwidth to that of the modulating sign and is a mirror photo of the alternative. Standard AM is hence on occasion known as “double-sideband amplitude modulation” (DSBAM).
A drawback of all amplitude modulation techniques, not only preferred AM, is that the receiver amplifies and detects noise and electromagnetic interference in the same proportion to the signal. Increasing the obtained sign-to-noise ratio, say, by an element of 10 (a 10-decibel development), as a result, might require increasing the transmitter strength via an issue of 10. This is in comparison to frequency modulation (FM) and virtual radio in which the effect of such noise following demodulation is strongly reduced as long as the received signal is well above the threshold for a reception. For this purpose, AM broadcast is not desired for music and excessive-constancy broadcasting, but rather for voice communications and broadcasts (sports activities, news, speak radio, etc.).
An additional characteristic supplied with the aid of the provider in widespread AM, however that’s misplaced in either unmarried or double-sideband suppressed-service transmission, is that it gives an amplitude reference. In the receiver, the automatic benefit manages (AGC) responds to the provider so that the reproduced audio level stays in a set percentage to the unique modulation. On the opposite hand, with suppressed-carrier transmissions there’s no transmitted strength at some stage in pauses inside the modulation, so the AGC needs to respond to peaks of the transmitted electricity at some stage in peaks in the modulation. This commonly includes a so-referred to as fast attack, slow decay circuit which holds the AGC degree for a 2nd or more following such peaks, in among syllables or quick pauses within the program. This could be very perfect for communications radios, in which compression of the audio aids intelligibility. However, it’s miles undesired for track or regular broadcast programming, in which faithful replica of the authentic application, consisting of its various modulation ranges, is predicted.
An easy shape of amplitude modulation is the transmission of speech indicators from the traditional analogue phone set the usage of a common battery nearby loop.[2] The direct current supplied via the relevant workplace battery is a provider with a frequency of zero Hz, that is modulated with the aid of a microphone (transmitter) inside the phone set in keeping with the acoustic signal from the mouth of the speaker. The result is a various amplitude direct contemporary, whose AC issue is the speech signal extracted on the primary office for transmission to another subscriber.
An easy shape of virtual amplitude modulation that can be used for transmitting binary information is on-off keying, the best form of amplitude-shift keying, in which ones and zeros are represented by the presence or absence of service. On-off keying is also used by radio amateurs to transmit Morse code wherein it is known as a non-stop wave (CW) operation, even though the transmission isn’t strictly “non-stop.” An extra complex shape of AM, quadrature amplitude modulation is now greater commonly used with virtual information whilst making greater efficient use of the available bandwidth.
AM is likewise inefficient in energy utilization; as a minimum of two-thirds of the strength is concentrated inside the provider sign. The carrier sign includes not one of the authentic statistics being transmitted (voice, video, information, and so forth.). However, its presence affords a simple manner of demodulation the use of envelope detection, imparting a frequency and phase connection with extracting the modulation from the sidebands. In a few modulation structures based on AM, decrease transmitter strength is required via partial or overall removal of the provider aspect, but, receivers for those signals are extra complex due to the fact they need to offer a particular provider frequency reference signal (generally as shifted to the intermediate frequency) from a greatly decreased “pilot” provider (in decreased-service transmission or DSB-RC) to apply in the demodulation method. Even with the carrier removed in double-sideband suppressed-service transmission, provider regeneration is feasible using a Costas segment-locked loop. This does no longer paintings for unmarried-sideband suppressed-provider transmission (SSB-SC), main to the feature “Donald Duck” sound from such receivers while slightly detuned. Single-sideband AM is even though used broadly in novice radio and different voice communications as it has electricity and bandwidth efficiency (reducing the RF bandwidth in half of in comparison to conventional AM). On the opposite hand, in medium wave and quick wave broadcasting, fashionable AM with the total provider permits for the reception the usage of cheaper receivers. The broadcaster absorbs the extra energy cost to substantial growth the potential audience.
FAQ’s
What are amplitude modulation and its types?
There are 3 principal kinds of amplitude modulation. They are; Double sideband-suppressed service modulation (DSB-SC). Single Sideband Modulation (SSB). Vestigial Sideband Modulation (VSB).
Why is amplitude modulation used?
Amplitude modulation (AM) is also widely used to modify a carrier wave to transmit statistics. For instance, in AM radio, the voltage (amplitude) of a service with a fixed middle frequency (the station's channel) is varied (modulated) through the analogue audio signal. AM is likewise used for digital information.
What are the traits of amplitude modulation?
amplitude modulation (AM), a variant of the amplitude of a provider wave (generally a radio wave) according to the traits of a signal, which include a vocal or musical sound composed of audio-frequency waves.





