Table of Contents
Human Brain Diagram Class 10 Biology: The human brain serves as the command center of the nervous system and is an intricate organ responsible for controlling various bodily functions and cognitive processes. Understanding the labeled diagram of the human brain is essential for excelling in class 10 examinations. When it comes to studying the brain, it’s a fascinating subject in biology. In this article, we’ll see some easy steps of Human Brain Diagram Class 10, breaking it down into easy-to-understand bits.
Human Brain – Introduction
The human brain is one of the most intricate and fascinating organs in the body, responsible for controlling everything we think, feel, and do. At first glance, its structure may seem complex, but breaking it down simplifies its understanding. In this article we will have a look
A human brain diagram serves as a visual representation of the brain’s structure, depicting its various parts and functions. Typically, it’s divided into different regions, each with specialized roles that contribute to overall cognition, behavior, and bodily functions.
Human Brain Diagram Class 10 Biology
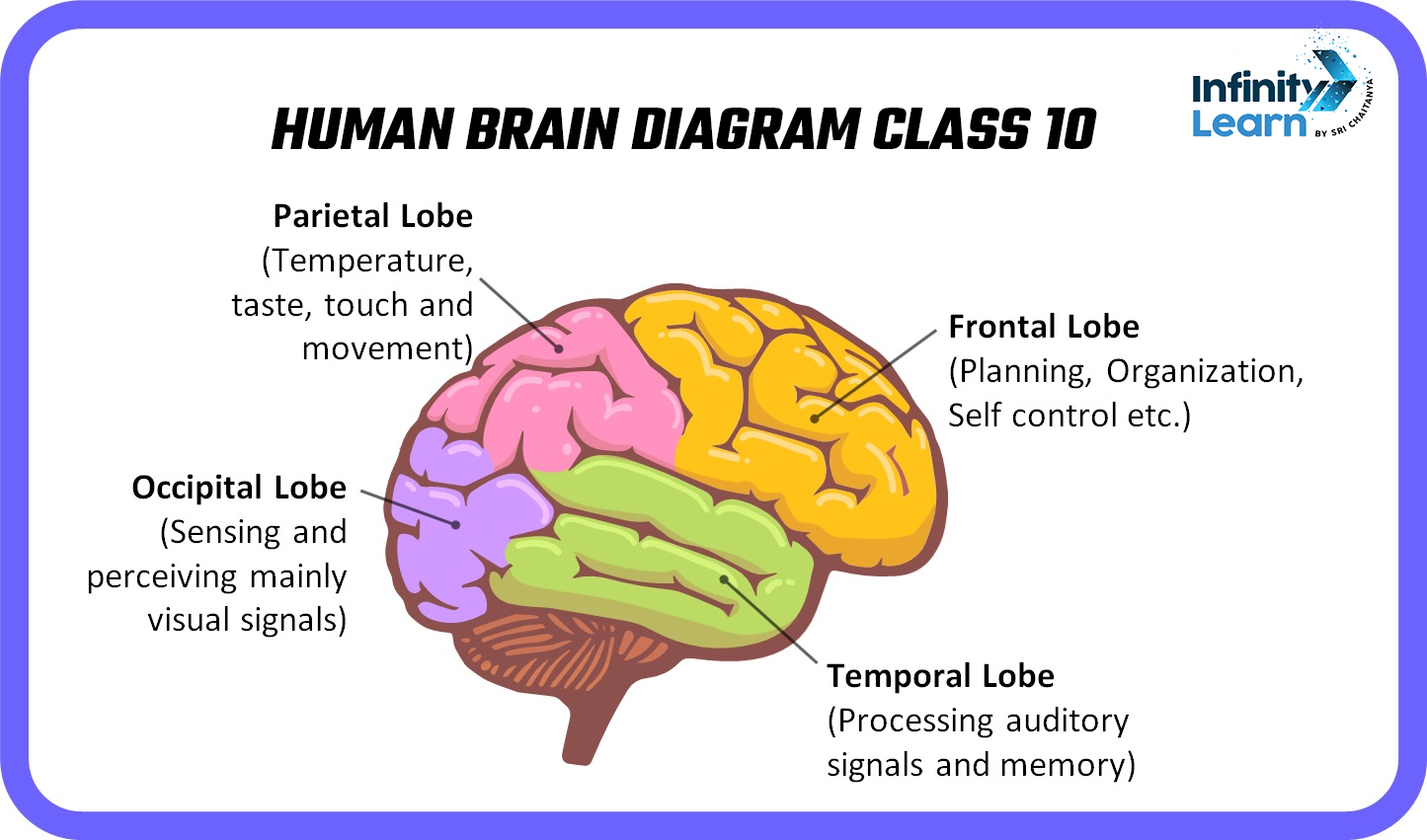
Parts of Human Brain
The human brain comprises three primary sections: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, each composed of various smaller components.
1. Forebrain:
Also known as the prosencephalon, the forebrain encompasses crucial regions such as the cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, and hypothalamus, playing a pivotal role in functions like learning and emotion regulation. Further divided into the diencephalon and telencephalon, it includes structures like the olfactory system, optic nerves, and cranial nerves. The cerebrum, the largest section of the brain, is primarily responsible for housing crucial components like the cerebral cortex and subcortical elements. Distinct lobes—frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal—divide it, each bearing its own set of functions such as speech, vision, and auditory processing.
2. Midbrain:
Referred to as the mesencephalon, the midbrain, though small, is significant, situated between the cerebral cortex and hindbrain. It comprises the tectum, cerebral peduncle, and substantia nigra, among others, governing functions like hearing, vision, and body temperature regulation. The substantia nigra, housing dopamine-producing neurons, is associated with Parkinson’s disease.
3. Hindbrain:
Known as the rhombencephalon, the hindbrain, located at the bottom rear of the brain, includes the cerebellum, pons, and medulla. The cerebellum, second in size, coordinates voluntary movements and maintains balance. The medulla oblongata regulates autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate, while the pons acts as a relay between different brain regions, controlling sleep cycles and facilitating sensory experiences.
Also Check: Brain Facts
Functions of Human Brain
The human brain serves as the central hub for processing information and orchestrating the body’s functions, acting as a sophisticated ‘command and control system’. It regulates both voluntary actions, such as movement, and involuntary processes like those of the lungs, heart, and kidneys. In addition to these vital functions, the brain also manages:
- Voluntary Movements: Controlling intentional actions and coordination.
- Balance of the Body: Maintaining equilibrium and spatial orientation.
- Thermoregulation: Regulating body temperature to ensure optimal functioning.
- Hunger and Thirst: Monitoring and responding to metabolic needs.
- Circadian Rhythms: Governing the body’s internal clock, influencing sleep-wake cycles.
- Endocrine Glands: Directing the activities of glands responsible for hormone secretion.
- Human Behavior: Influencing cognition, emotions, and responses to stimuli.
Human Brain Diagram Class 10: Essential Regions and Functions Explained
Here’s a simplified overview of the parts of the human brain:
- Cerebrum: This is the biggest part of your brain and is divided into two hemispheres: left and right. It controls things like thinking, memory, and emotions.
- Cerebellum: Found at the back of your head, this part helps with balance, coordination, and muscle movement.
- Brainstem: This connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls basic life functions like breathing, heart rate, and swallowing.
- Thalamus: It acts as a relay station, passing messages between different parts of the brain. It also plays a role in consciousness and sleep.
- Hypothalamus: This tiny but powerful part regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, and your sleep-wake cycle. It also controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
- Amygdala: The amygdala, situated deep within the brain, actively processes emotions, particularly fear and pleasure.
- Hippocampus: This part is crucial for forming new memories and organizing information so that you can recall it later.
- Pons: It helps in controlling sleep, breathing, and some aspects of facial movements.
- Medulla Oblongata: It regulates involuntary functions like heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Basal Ganglia: This group of structures is involved in voluntary motor control, procedural learning, and emotions.
Benefits of Human Brain Diagram for Class 10
- Easy Understanding: Brain diagrams are like treasure maps, but instead of finding gold, you’re exploring the amazing world inside your head. They show you how your brain is built, making it easier to understand.
- Discovering Functions: Just like different superheroes have unique powers, each part of your brain has its own special job. With brain diagrams, you can learn what each part does, from thinking and moving to feeling happy or sad.
- Seeing is Believing: Have you ever read a story and wished you could see the characters? Brain diagrams are like pictures in a storybook, helping you visualize what you’re learning. It’s like having a sneak peek into your own brain.
- Memory Boost: Imagine having a magic spell to remember things better. Brain diagrams can work like that spell, helping you recall information more easily. They create a mental picture that sticks in your mind.
- Real-life Connections: Ever wondered why you feel butterflies in your stomach when you’re nervous? Brain diagrams can help you connect what you learn in class to everyday experiences. You’ll understand why your brain reacts the way it does in different situations.
FAQs on Human Brain Diagram for Class 10
What is the structure of the human brain for Class 10?
The human brain comprises three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain includes the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The midbrain coordinates sensory information and motor responses, while the hindbrain consists of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata, regulating vital functions like breathing and coordination.
How does the brain function class 10?
The brain functions by receiving and processing sensory information, coordinating motor responses, regulating bodily functions, and controlling emotions and thoughts. Neurons, the brain's nerve cells, transmit electrical signals, enabling communication between different parts of the brain and the rest of the body.
How to draw a simple brain diagram?
To draw a simple brain diagram, start by outlining the basic structure of the brain, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. Then, add details such as the lobes of the cerebrum, the brainstem's components (medulla, pons), and the cerebellum's distinctive shape.
What are the three functions of the brain Class 10?
The three main functions of the brain are sensory processing (receiving and interpreting sensory information), motor coordination (controlling muscle movements and responses), and regulation of vital functions (such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion).
What is the function of hindbrain class 10?
The hindbrain, consisting of the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata, regulates essential bodily functions like breathing, heart rate, and coordination of voluntary movements. It also helps maintain balance and posture.









