Table of Contents
X rays, which had been first founded in 1901, have revolutionized contemporary medicine. An X-ray is a painless, fast exam that creates pictures of the interior additives of your body, notably your bones. X -rays are electromagnetic radiation that may see via someone’s skin and offer photographs of the bones below it. Technology advancements have led to extra powerful and focussed X-ray beams, in addition to a developing number of packages for these mild waves.
Types of X-rays
There are two forms of X-ray spectrum:
Continuous – while high-velocity electrons collide with an excessive-atomic-wide variety goal material, X-rays are created. The majority of the power of the electrons is used to warm the target cloth in the creation of X-rays.A few speedy-transferring electrons penetrate deep into the indoors of the target material’s atoms and are attracted to their nuclei by using their nuclei’s attraction forces. The electrons are thrown from their initial course because of those forces. As a result, electrons gradual down, and their power reduces over time. The X-rays have a non-stop frequency range as much as a maximum frequency max or a minimum wavelength min. This is known as Continuous X-rays. The minimum wavelength depends on the anode voltage. If V is the capacity distinction among the anode and the cathode
eV = hνmax = hc / λmin
The minimum wavelength of the given radiation is,
λmin = hc /eV
in which h is Planck’s regular, c is the speed of light and e, the fee of the electron. Substituting the regarded values within the above equation.
λmin = 12400/V A0
For the given operating voltage, the minimum wavelength is identical for all metals.
Characteristic X-ray – Characteristic radiation is a type of electricity emission this is important inside the creation of X-rays. When a fast-transferring electron collides with a K-shell electron, the electron inside the K-shell is ejected (if the incident electron’s strength is greater than the K-shell electron’s binding energy), leaving a ‘hole’ behind. An outer shell electron fills this hole (from the L-shell, M-shell, and so on) with the emission of an unmarried X-ray photon with a strong degree equal to the electricity stage difference between the outer and internal shell electrons engaged in the transition.
What is an X-ray?
You probably recognize someone that has had a medical X-ray examination. You might also have even had one yourself. However, have you ever stopped to wonder how this invisible source of electricity is created? In this lesson, we will discuss different sorts of X-rays: non-stop X-rays and characteristic X-rays. We’ll mainly take a look at the production and houses of each. Before we begin this comparison, allow first evaluation of precisely what an X-ray is.
To recognize X-rays, you should remember the fact that this form of strength is just a sort of mild. This would possibly make you believe you studied seen light (mild that may be seen with the human eye). In technology, mild is a great deal more than simply visible light. Light is synonymous with the electromagnetic spectrum, that is a group of waves of various strength levels. The electromagnetic spectrum is most often visible as a chart that tiers from radio waves to gamma rays. On the electromagnetic spectrum, X-rays are ordered adjacent to gamma rays (on the excessive power facet of the spectrum). So, while you pay attention to the phrase X-ray, simply consider high electricity mild.
Here we are going to discuss continuous X-ray, non-stop X-ray manufacturing, characteristic X-rays and non-stop X-rays, continuous X-ray spectrum definition.
Continuous X-rays
Continuous X-rays are created while free moving electrons electromagnetically interact with nuclei, while characteristic X-rays are shaped in the course of the electron transition methods that occur while an internal shell electron is released from an atom.
Bremsstrahlung transitions generally tend to create a phenomenon of non-stop X-rays whereas the everyday function X-rays are produced by internal-shell transitions. The Bremsstrahlung mechanism may be viewed when a target fabricated from metallic suffers electron bombardment. The atoms of the target steel scatter the electrons, whose alternation in acceleration causes a phenomenon of radiation in them.
Continuous and Characteristic X -Rays
Characteristic X-rays are discharged from the heavy factors when the electrons make transitions among the lower atomic power stages. X-ray manufacturing normally entails bombarding a metal gate in an evacuated X-ray tube with high-velocity electrons which have been increased with the aid of tens to hundreds of kilovolts of capacity. The bombarding electrons can eject electrons from the internal shells of the atoms of the target metallic, typically tungsten or molybdenum. This void can be speedy crammed up by using the electrons falling from higher stages, emitting X-rays with clearly defined frequencies related to the distinction among atomic electricity levels of the goal atoms as they do.
Continuous radiation, or Bremsstrahlung, is the spectrum of electromagnetic emission when the bombarding electrons are of sufficient power, and outcomes from the electrons being rapidly decelerated by the goal. The generated X-ray wavelengths might be distributed over a range, which might also or may not consist of the feature ones, depending upon the strength of the bombarding electrons.
When we point out the function X-ray, it measures X-ray photons that have a strength equivalent to the difference of strength in digital stages of an atom. The most important reason why it’s widely called the characteristic is that each of the factors has a particular difference in electricity. Since the strength ranges are discrete (brief purpose, an outcome of quantum mechanics and chance distributions), they’re normally X-rayed with very unique electricity that depends on the detail which you see in the diagram below as a vertical line.
Those K-alpha, and greater, represent the electricity difference between the K degree and top stages.
As for the continuous X-ray, this is generated via some other method, and it’s far called Bremsstrahlung radiation or braking radiation. When an electron passes close to the nucleus, the nucleus exerts a pressure on it that modifies its direction and slows it down (for this reason the braking). That trade-in route implies a little energy is lost, and to preserve momentum and power, one photon is emitted. And because the power of the photon relies upon how the electron was from the nucleus, you come with a non-stop spectrum.
As you could see from this case, depending on how much the electron is deflected, you have got photons with specific energies.
If we test the mixed spectrum of the X-ray inside the graph, we typically will see something like this:
As you may see, you’ve got the continuous X-ray corresponding to Bremsstrahlung and the discrete lines which represent the characteristic X-ray radiation (the area once more, relies upon the detail).
Reason for Continuous X-ray Radiation
Continuous X-ray radiation is for the fact that the trade within the velocity which causes the emission of a good deal of the radiation in a tube that’s used as a radiography source is a random procedure that emits photons at specific energies. If we have a look at the spectrum of an X-ray tube it normally has a large lump due to this Bremsstrahlung emission. Whenever the tube voltage could be very low (below 60 kV) we ought to be capable of seeing some sturdy peaks due to the characteristic radiation of emission from the goal (anode) material. To watch those function peaks it, in reality, facilitates, as though the tube has home windows and very little filtering. A medical X-ray supply commonly has a few filters within the form of a metal sheet to dispose of almost all of the low strength photons from the beam so that this tube is sort of only emitting Bremsstrahlung.
A thrilling exception is a tube used for a mammogram set; those have a tendency to be Mo anodes run at approximately 50 kV. These will generate a large amount of Mo k alpha radiation. This decreased energy (circa 15 keV) radiation is nicely ideal for the examination of breast tissue, while the higher electricity Bremsstrahlung from a tube strolling at a hundred or two hundred kV can be more appropriate for searching at bones. The dental X-ray sets use approximately 70 kV at the tubes that are partway between the two.
On the other hand, a radioactive photon supply that emits gamma rays is constantly on, it can not be turned off. It emits photons with nicely-described energies. For example, Co-60 emits lines one at approximately 1.1 MeV and one at 1. Three MeV. This is only because the gamma photons are generated while an excited nucleus makes changes between the 2 states. In this example, the excited kingdom of the Ni-60 daughter emits the photons.
FAQs:
Q. What takes place under an X-ray? What happens to an X-ray?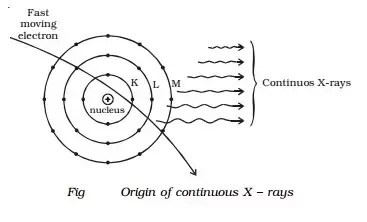
Ans: Our frame is located through a technician to gain the right views. To help you in preserving your posture, he or she may make use of pillows or sandbags. To hold the photo from blurring at some stage in the X-ray exposure, you must stay calm and every now and then keep your breath.
An X-ray technique can take as low as a couple of minutes for an easy X-ray or as an awful lot as an hour for greater complicated remedies using contrast material. An X-ray has no sensation.
Q. Write the purpose of an X-ray?
Ans: An X-ray can be ordered by your doctor to:
Examine a painful or uncomfortable location in your body.
Keep the song of the development of a condition, including osteoporosis.
Examine the efficacy of a given remedy.
The following conditions may additionally necessitate an X-ray: bone cancer, breast tumours, enlarged heart, blocked blood vessels, situations affecting your lungs, digestive troubles.





