Table of Contents
Atoms are referred to as the “basic building blocks of matter.”
- It is the lowest component unit of matter that possesses chemical element qualities. Atoms do not exist in isolation; instead, they combine to create ions and molecules, which then combine in enormous numbers to form the matter we see, feel, and touch.
- It is the smallest particle of an element, which may or may not exist independently but is always present in a chemical process.
- It is the smallest unit that preserves an element’s characteristics. An atom is made up of subatomic particles, which cannot be created or destroyed.
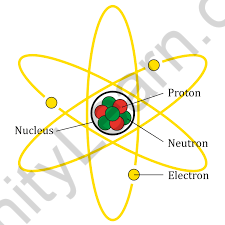
- Protons, electrons, and neutrons are the three primary types of particles that make up an atom. Neutrons and protons have almost the same mass, however, the mass of an electron is insignificant. A proton is positively charged, a neutron is neutrally charged, and an electron is negatively charged. Because an atom has an equal amount of protons and electrons, it has no charge. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged because it only contains protons and neutrons.
The nucleus is the core of the atom. The nucleus includes neutrons and protons, which are responsible for an atom’s weight and positive charges. A neutron has a mass of one unit and no charge. A proton has a single positive charge and a mass of one unit. An element’s atomic number is equal to the number of protons or positive charges in its nucleus. The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus is used to calculate an element’s atomic weight. A single negative charge is carried by an electron. To have zero charges, an element’s atom must have the same number of electrons as protons. These electrons are organized in orbits around the atom’s nucleus, similar to the layers of an anion.
Size of an Atom
An atom’s size is exceedingly tiny, considerably smaller than human imagination. When millions of atoms are packed together, a layer of one atom, the thickness of a thin sheet of paper, is created. Because it is difficult to detect the locations of electrons surrounding the nucleus, measuring the size of an isolated atom is impossible.
However, the size of an atom may be calculated by assuming that the distance between neighbouring atoms is half its radius. The radius of an atom is typically measured in nanometres.
1m = 109 nm
FAQs:
What happens when atoms combine to form molecules?
Chemical bonds hold atoms together when they combine to form molecules. These bonds occur as a result of the atoms sharing or exchanging electrons. Only the electrons in the outermost shell are ever active in bonding.
What is an atom's structure?
Atoms are made up of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The protons (positively charged) and neutrons are found in the nucleus (centre) of an atom (without charge). The outermost parts of the atom are known as electron shells, and they contain (negatively charged) electrons.





