Table of Contents
A conservative force is one in which the total work required to move a particle between two places is unaffected by the path followed. Friction transfers some of the energy from the bodies’ large-scale motion to small-scale movements in their interiors, making it appear non-conservative on a large scale.
A Brief Outline
As a force is conservative, the energy stored of an object may be given a numerical value at any place, whenever an object is moving from one position to another, the force modifies the object’s potential energy by an amount that is independent of the path followed. Non-conservative forces can occur in classical physics despite total energy conservation owing to ignored degrees of freedom or time-dependent potentials.
Important Concepts
When an object is moved from one position to the other by applying force, work is done. This movement could be in a straight line or along a non-straight path. So, if an object does not travel in a straight line, the amount of effort done is determined by the overall path travelled by the object. The force used for such operations is referred to as non-conservative force. Friction, air resistance, viscosity, non-elastic material stress, water drag on a large boat, and other non-conservative forces are examples. In some other cases, though, the work done is independent of the object’s path. It is solely dependent on the object’s original and final positions.
The force used in this case is termed the conservative force. The gravitational force, elastic spring restoring force, buoyancy force, and electrostatic force are all examples of conservative forces. The mechanical energy consumed in work done with non-conservative forces is dissipated into other kinds of energy such as heat, sound, or any other form. Non-conservative forces are also called dissipative forces because of this. The produced energy can only be used in a limited number of ways.
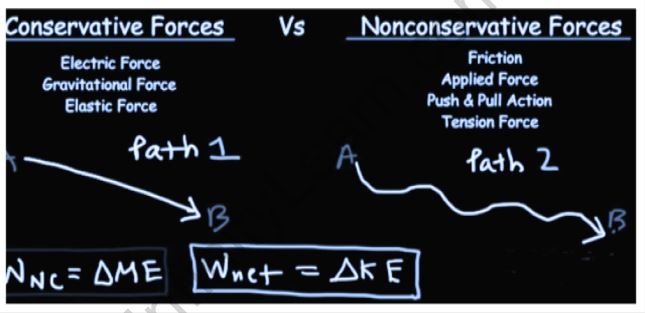
Force in an elastic spring, electrostatic force amongst two electric charges, and magnetic force between two magnetic poles are all instances of conservative forces. Friction and non-elastic material stress are examples of non-conservative forces.
Significance of conservative and nonconservative forces in IIT JEE exam
We may predict that the conservative and nonconservative forces are roughly 3% since the weighting for the law of motion in the chapter is usually similar between years. As a result, the total number of questions from this chapter is estimated to be around 2.
FAQs
Q. Energy conservation is a state statute.
Ans: “In a closed system, i.e., a system that is secluded from its environment, the total energy of the system is preserved,” says the law of conservation of energy.
Q. What does it mean to be a non-conservative force?
Ans: Working for a non-conservative force is dependent on the path. As a result, knowing where the object begins and ends is critical.
Q. Give some non-conservative forces examples.
Ans: Air drag, friction, and rope tension are examples of non-conservative forces.






