Table of Contents
Dimensions Of Coefficient Of Viscosity: Put some drops of water on one aspect on a slanting floor and a few drops of honey on the alternative. Come again and study the float of each beverage. You would be aware that the slowness of water became very short while honey become no longer that easily movable. For this situation, honey is viewed as Viscous.
So, viscosity is defined as the ratio of the pressure required to make adjoining layers of the liquid move over each other.
Let’s take an instance,
there may be a version in each horizontal layer of the liquid that is happening because of the presence of a few inner frictions (viscosity) among the layers of the fluid passing through two plates.
The idea has sizeable significance for competitive exams like JEE and NEET. So the faculty at Infinity Learn have holistically protected the topic retaining in thoughts the want of each scholar. So in this text, we shall be gaining knowledge of about –
What is a Viscous Gradient?
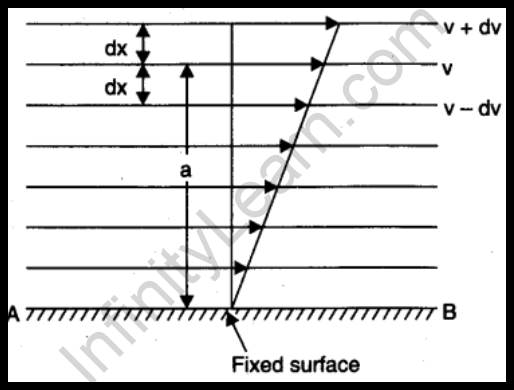
The viscous gradient is the distinction in the pace between the adjacent layer of the fluid. If more pressure is implemented by way of the upper layer to move forward the more can be the viscous gradient. It is represented by v/x, in which v is the speed distinction and x can be the difference of distance between the two layers. So, the higher the value of v/x, the extra will be the viscous gradient.
Coefficient of Viscosity:
The ratio of the shearing stress to the rate gradient of the fluid is known as the coefficient of viscosity η.
Hence the coefficient of viscosity is given using,
η = F . D / A .ⅴ
Where F is the tangential pressure required to maintain a unit speed gradient between parallel layers of liquid of unit area.
ⅴ is the speed.
A is the place
d is the distance among the 2 layers of liquid skidding over each other.
The difference inside the movement of speed among the adjoining layers of the fluid is measured within the pace gradient.
The viscosity of fuel is much less than the liquid viscosity.
SI Unit of Coefficient of Viscosity:
Every liquid has its particular viscosity and the degree of this attribute is known as the coefficient of viscosity.
The coefficient of viscosity η is described because the tangential pressure F is required to maintain a unit velocity gradient between parallel layers of liquid of unit area A.
The SI unit of η is Newton-second in keeping with rectangular meter (Ns. M – 2) or
Pascal-seconds (Pa .S)
Hence the coefficient of viscosity is the degree of the resistance of the fluid to deformation at a given charge because of internal friction.
Unit of Coefficient of Viscosity:
The centimetre-gram-2nd or CGS unit of coefficient of viscosity, η is
dyne-sec/ cm 2 that is equal to Poise.
Where one poise is precisely zero.1 Pa·s.
The meter-kilogram-second or MKS unit is: Kilogram according to a meter in step with 2d or
Kg m -1 s -1.
Coefficient of Viscosity Unit and Dimension:
Since, the method for the coefficient of viscosity is given by means of,
η = F . D/ A .ⅴ = MLT−2 . L / L2 . LT −1
On solving we get,
Dimensional components for η = ML−1T−1ML−1T−1 and its miles equal to Kg m -1 s -1The Viscosity of Water in SI
Units:
The coefficient of viscosity of water can be determined by using the usage of Poiseuille’s law.
Poiseuille’s equation for the glide of liquid determines the extent of the liquid flowing via a capillary tube in a unit of time.
Poiseuille’s components are given by using,
Ⅴ = π P ໗ 4 / 8 η l
Here, the fee of the flow of the viscous liquid thru a tube of period ‘l’ and radius ‘໗’ is proportional to the implemented stress P.
The price of the float of the viscous liquid is proportional to the fourth power of the inner radius of the tube and inversely proportional to the viscosity of the liquid and the length of the tube.
The formula for the coefficient of viscosity of water is given with the aid of,
η = π P ໗ 4 /8 Ⅴ l
Here, Ⅴ is the rate of go with the flow of the extent of liquid.
P is the pressure that could be implemented to the liquid.
໗ is the internal radius of the capillary tube.
L is the period of the capillary tube.
SI unit of viscosity of water is Ns.M-2 or Pa.S.
Do You realize?
The dynamic viscosity of water at room temperature 250C are having various values cited below:
In the SI unit, the value of viscosity is eight. Ninety × 10 – 4 Pa·s.
In the CGS unit, the value of viscosity is eight.90 × 10 – 3 dyn·s/cm 2 or zero.890 cP.
Hence, water has a consistency of 0.0091 balance
Viscosity and density are two specific terms wherein viscosity is the thickness of fluid and density refers to the distance among its particles.
FAQs:
Q. Who discovered viscosity?
Ans: Jean-Louis-Marie Poiseuille discovered viscosity by setting up experiments where he tested the flow of liquids through varying-sized narrow tubes in the year 1929.
He was a French physicist and physiologist whose interest in the circulation of blood in the human body led him to discover viscosity
Explain how heat affects viscosity?
When the liquid is heated, the particles gain entropy. Consequently, the active energy created debilitates the intermolecular powers between the particles prompting the detachment between the atoms which diminishes the thickness of the fluid as consistency is the state of fluid being thick and sticky. Hence, the viscosity of the liquid also decreases.









