Table of Contents
Dimensions Of Gas Constant
The layered recipe of Universal Gas Constant is M1 L2 T-2 K-1
Where,
- M indicates the Weight(mass)
- L indicates the length
- T indicates the taken time
Inference of Gas Constant
Since Pressure × Volume=Total moles × Temperature × Gas Constant
- In this manner, we work out the element of the general gas consistent with the utilization of the accompanying:
- Gas Constant=Pressure× Volume× Total Moles× Temperature
- Total Moles × Temperature-1 . . . . (I)
- The layered equation of temperature and volume = M0 L0 T0 K1 and M0 L3 T0 . . .(ii)
- Since Pressure=Force×Area-1
- P=M× a Area-1 =M×LT-2 ×L-2
- Subsequently, the elements of strain = M1 L-1 T-2. . . (iii)
- On subbing condition (ii) and (iii) in condition (I) we get,
- Gas Constant=Pressure×Volume×TotalMoles×Temperature-1
- Or on the other hand, G= M1 L2 T-2K-1.
- In this way, the general gas steady layered recipe is addressed as M1 L2 T-2K-1
Wonderful Gas Equation of General Gas Equation and Specific and Universal Gas Constant
We know that,
- As indicated by Gay Lussacc’s regulation, P is straightforwardly relative to T… … … (I)
- As indicated by Charle’s regulation, V is straightforwardly relative to T… … … … ..(ii)
- Joining both the conditions, PV is straightforwardly relative to T or PV= Constant * T
- In the event that the mass of the gas is estimated in kg or gm, the consistent utilized is ‘k’, then, at that point,
- PV= KT (Ideal Gas Equation)
- Here, k is a gas consistent relying on the mass of a gas.
- For 1 kg of gas, K is known as a particular gas consistent assuming the mass of gas is 1 kg-mole or 1 gm-mole, then, at that point, steady k will be equivalent to the incentive for all gases.
- In this way, K is supplanted by R, known as the all-inclusive gas consistent.
- Accordingly, PV = RT- – – – – – – – (iv)
- It is the overall gas condition.
- R= (Mass∗Length2 ) / (Amount∗ Temperature∗ (time)2)
- R=8.314462618…kg.m2 .s-2 .k-1 .mol-1
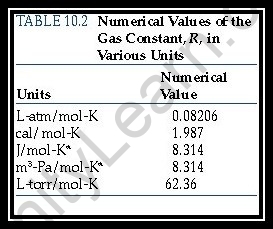
What is Universal Gas Constant?
Widespread Gas Constant is otherwise called the molar gas consistent, optimal gas steady, or general gas consistent. It is signified by the image R. It is identical to the Boltzmann consistent and can be communicated in units of energy per temperature per mole.
PV= nRT or PV= mRT
N is the number of moles and M is the mass
All-inclusive Gas steady is named so in light of the fact that it is no different for all gases. It can likewise be gotten from another hypothesis called the minute motor hypothesis, as it was accomplished (obviously autonomously) by August Krönig in the year 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in the year 1857.
Assurance of Universal Gas Constant
Right off the bat, the exploratory worth of Boyle’s regulation not entirely set in stone with the assistance of the result of strain P and volume V for a steady temperature T and a decent mass m of air. In the wake of knowing these qualities, the all-inclusive gas regulation consistent R is determined from the situation PV = nRT.
What is Specific Gas Constant?
The particular gas consistent with gas or for a combination of gases (RSpecific)
is addressed by the molar gas consistent isolated by the molar mass (M) of the gas or blend.
(RSpecific=R/M )
Otherwise called the molar gas consistent and the ideal gas steady, the general gas consistent is meant by the image R. It is communicated in units of energy per temperature per mole and is comparable to the Boltzmann Constant. It is addressed as follows –
PV = nRT where n is the number of moles or PV = mRT where m is the mass.
It is known as the “All-inclusive” Gas Constant since it is steady across all gases. The infinitesimal motor hypothesis additionally assists us with determining the general gas steady. This was accomplished by August Kronig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857.
FAQs
Q. What is the Dimensional Formula of Gas consistent?
Ans: The layered equation of Universal Gas Constant is given as – M1 L2 T-2K-1
Where, M = Mass, L = Length and T = time.
How would we Memorize these Formulae and Equations?
At the point when we get material science as a subject, we encounter numerous conditions and formulae which we are then expected to apply to take care of different actual issues which likewise structure a significant piece of the last inquiry paper!







