Table of Contents
Dimensions Of Gravitational Constant: Gravity is a universal phenomenon that exists throughout the universe. Gravity is an important factor in defining and maintaining the physical connection between space and matter. As we all know, gravitational force, along with nuclear and electromagnetic forces, is one of the fundamental forces that exist in the universe. The force of gravity governs the entire galaxy, including planets and stars.
Gravity, in other words, is the force that acts on all objects that have mass or energy. Gravity contributes to the weight of an object on the Earth’s surface. Gravity has an infinite range, and the effects of gravity weaken with increasing distance between the objects. It is represented by the letter ‘g.’ Sir Isaac Newton, a famous physicist, discovered gravity in 1687 to explain the motions of the planets and moons. After Newton’s death, Henry Cavendish coined the term “gravitational constant.”
Universal Gravitational Constant
The universal gravitational constant, the Cavendish gravitational constant, and the Newtonian constant of gravitation are all names for the gravitational constant. The letter ‘G’ represents the gravitational constant. The gravitational constant can be calculated in classical form using Planck’s length, mass, and time. It is derived from the electric force equation in the waveform.
The universal gravitational constant can be determined using the following formula:
G = 6.673 x 10-11 N m2/kg2
Three methods have been used to calculate the gravitational constant:
- The measurement of Earth’s attraction on a test mass using a laboratory balance.
- The comparison of a large natural mass’s pull with that of Earth
- In the laboratory, the force between two masses is measured directly.
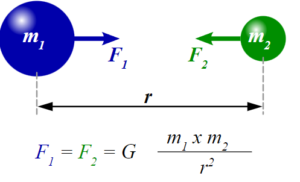
According to Newton’s law, any two objects with masses m1 and m2 (in kilogrammes), separated by a distance r (in metre), will have a gravitational force F (in Newton) between them.
This force is represented by:
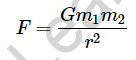
Dimensions Of Gravitational Constant
In Newton’s law of gravitation, the gravitational constant is the proportionality constant. It refers to the force of attraction between two masses separated by a distance. As a result, the dimensional formula is affected by the dimensions of force, mass, and distance.
The gravitational constant’s dimensional formula is given by,
M-1 L3 T-2
Where M stands for mass.
T = Time L = Length
According to Newton’s law of gravitation,
Force (F) = [GmM] × r-2
Gravitational Constant (G) = F × r2 × [Mm]-1 . . . . (1)
Force (F) = Mass × Acceleration = M × [LT-2]
The dimensional formula of force is = M1 L1 T-2 . . . . (2)
When we substitute equation (2) into equation (1), we get
Gravitational Constant (G) = F × r2 × [Mm]-1
G = [M1 L1 T-2] × [L]2 × [M]-2 = [M-1 L3 T-2].
As a result, the gravitational constant is represented in three dimensions as M-1 L3 T-2.




