Table of Contents
In chemistry, a cell is used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy or for the goal of energy conversion. Chemical processes take place inside the cells, and as a result, electrical current flows. In galvanic cells, chemical energy is turned into electrical energy, and electrical energy is changed back into chemical energy in electrolytic cells. These electrochemical cells are used for a variety of purposes.
Galvanic cells:
Galvanic cells are made up of two halves that transform chemical potential energy into electrical potential energy. It occurs as a result of a spontaneous chemical reaction. Each half-cell of a galvanic cell has an electrode immersed in an electrolyte. By producing a potential difference, the separation is necessary to prevent direct chemical interaction between the reduction and oxidation processes. Electrons generated during the oxidation reaction are routed through an external circuit before being utilized by the reduction reaction.
Electrolytic cells:
Electrolytic cells are similar to galvanic cells in that they require a salt bridge, two electrodes, and the passage of electrons from the anode to the cathode. Nonetheless, the two electrodes distinguish themselves from others in a variety of ways. For starters, the electrolytic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy rather than the other way around.
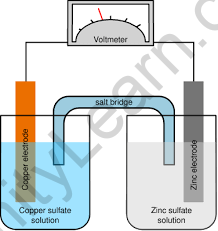
Difference between Galvanic cells and Electrolytic cells:
| Galvanic cells | Electrolytic cells |
| The chemical energy is converted to electric energy via spontaneous redox reactions. | Electric energy is converted to chemical energy via non-spontaneous redox processes. |
| Redox processes provide electric energy. | With the assistance of an external source, electric energy causes a chemical reaction. |
| The positive electrode is the cathode, while the negative electrode is the anode. | The positive electrode is the anode, while the negative electrode is the cathode. |
| The anode is responsible for oxidation, whereas the cathode is responsible for the reduction. | The anode is responsible for oxidation, whereas the cathode is responsible for the reduction. |
| Half cells are placed in various containers and are linked together by salt bridges. | In a molten or solution electrolyte, electrodes are retained in the same container. |
| The application is found in batteries. | Copper purification and electroplating are two applications. |
Based on the differences between galvanic cells and electrolytic cells discussed above, we can conclude that a galvanic cell generates electric current through spontaneous chemical reactions, whereas an electrolytic cell does the opposite, causing chemical reactions through the use of an electric current from an external source.
FAQs
What exactly is the purpose of a galvanic cell?
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell that is used to produce electrical current by executing a redox reaction in which electrons are transferred. Because such cells generate electrical energy through a chemical reaction, they are referred to as electrochemical cells. It is a device that transforms chemical energy into electrical energy. It is commonly used in electrochemistry.
How do you remember what cathode and anode are?
According to electrochemistry, the anode is where oxidation happens, while the cathode is where reduction occurs. Furthermore, the anode constantly draws negative anions, whereas the cathode always attracts positive cations. It occurs independently of the charges on the electrodes themselves.







