Table of Contents
Introduction
The energy delivered to or from an item by force applied and generating a displacement is referred to as work. In its most basic form, it is often shown as the product of force and displacement. A force is considered to do positive work if it has a component in the path of the displacement of the application site.
A brief outline
Work is directly tied to energy. A rise in the kinetic energy of a rigid body is induced by an equal amount of positive work produced on the body by the force acting on it, according to the work-energy principle. The resultant force does an equal amount of negative work, resulting in a decrease in kinetic energy.
Important concepts
The application of the Work-Energy theorem is that it is extremely useful in determining circumstances when a stiff body should move under many forces. A rigid body can only have kinetic energy due to its rigid construction, which prevents it from storing potential energy in its lattice. The rigid body work-energy equation is based on the fact that the work done by any force acting on a rigid body eventually constitutes the change in its kinetic energy.
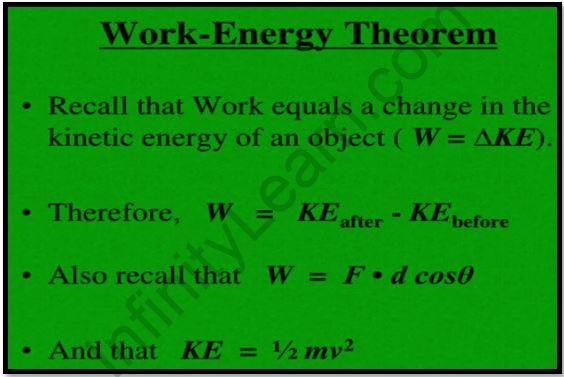
Work is based on the notion of energy.
The work and kinetic energy idea state that all forces acting on an object accomplish the same amount of work, resulting in the same change in the particle’s kinetic energy. In other words, the resultant force’s work W on a particle matches the change in the particle’s kinetic energy Ek.
Significance of Hc Verma Solutions Class 11 Chapter 8 Work energy in IIT JEE exam
Work, Energy, and Power account for almost 4% of the total number of queries addressed over the last 33 years. Work, Energy, the Work-Energy Theorem, Power, and Collisions are all important sub-topics in the Work, Energy, and Power textbook. The most important chapter in modern physics is given a 13.3 per cent weighting, whereas the other chapters are given 3.3 per cent and 6.6 per cent, respectively.
FAQs
Q. What is the primary distinction between conservative and non-conservative forces?
Ans: The conservative force is defined as the effort expended in moving a component from one place to the next that is independent of the direction taken. The power of a non-conservative force is defined as one in which they work or active energy is dependent on a variety of conditions.
What is the work-energy theorem, and how does it work?
The work-energy theory is also known as the kinetic energy hypothesis or the principle of work. The hypothesis states that the effort done by all powers going to follow up on a component results in the adjustment of the component.
What are the benefits of the work-energy theorem?
The work-energy theorem has the advantage that the work done on an item may be computed by integrating the area that is applied as a force and multiplying it by the work done if it moves from point A to point B.









