Table of Contents
Introduction
Alkali (NH3 ) is sp3 hybridized, or more specifically, the focal iota of smelling salts, nitrogen. We’ll take a gander at how to sort out assuming NH3 is hybridized in this article.
Smelling salt is a dreary synthetic that is used in manure creation. It’s a steady hydride with one nitrogen and three hydrogen iotas in it. The synthetic has a solid scent. Tolerating a proton permits it to turn into an NH4+ particle. This part post will cover the Lewis dab structure, electron math, and atomic calculation of this article.
Lewis Structure
Lewis structures, otherwise called Lewis point structures, Lewis point structures, electron point constructions, or Lewis electron point structures (LEDSs), hold connections between particles inside an atom and all solitary combines that can be gifted. It is an outline to show. All covalently reinforced atoms and coordination mixtures can be addressed by the Lewis primary recipe.
Gilbert N. Lewis named the Lewis structure after himself subsequent to presenting it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule. Lewis structures add lines between iotas to address shared sets in a compound bond, expanding the idea of the electron speck outline.
Lewis structures utilize substance images to address every iota and its spot in the particle’s construction. Between iotas that are connected together, lines are drawn (sets of spots can be utilized rather than lines). Solitary sets of overabundance electrons are displayed as sets of spots close to the molecules.
Albeit fundamental gathering components in the subsequent period and past regularly respond by procuring, losing, or sharing electrons until they have a total octet of (8) electrons in their valence shell electron arrangement, hydrogen (H) can shape securities that share two electrons.
Hybridization
When nuclear orbitals consolidate to produce another nuclear orbital, this is known as hybridization. The new orbital can oblige a similar number of electrons as the old ones. The new, hybridized orbital attributes and energy are the ‘normal’ of the first unhybridized orbitals.
Hybridization was proposed as the best clarification for why all C – H bonds in particles like methane are indistinguishable.
Electron Geometry
The course of action of electron bunches is called electronic math. Whenever an electron that isn’t associated with a solitary pair of electrons or one more particle is found in the atom, the state of the particle changes, not the state of the electron.
The electron math and sub-atomic calculation are something very similar in the event that all the electron bunches are reinforced and there are no solitary sets.
Hybridization of NH3 (Ammonia)
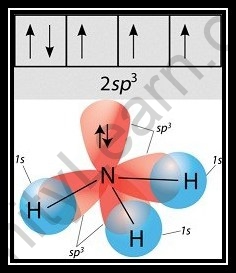
- To appreciate alkali hybridization, we should explore the environmental factors encompassing Nitrogen. The nuclear number of nitrogen is 7, and its ground state is 1s2, 2s2,2p3 as per its nuclear number.
- One 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals of nitrogen blend during the development of alkali to create four mixture orbitals with identical energy, which is alluded to as a sp3 sort of hybridization.
- Besides, assuming we take a gander at the NH3 particle, we can see that nitrogen’s three half-filled sp3 orbitals make bonds with the three hydrogen molecules. The fourth sp3 orbital, then again, is a nonbonding pair of hybridized orbitals that is for the most part utilized to keep the solitary pair intact.
- It is a generally expected nitrogenous misuse of sea-going animals and a significant part of earthbound species’ wholesome necessities. Besides, assuming that put away in adequate amounts, smelling salts is viewed as destructive as well as unsafe.
FAQs
Q: How to Calculate the Hybridization?
Ans: To start with, we need to compose the Lewis construction to find out about the design of a particle and holding design. We can utilize the valence idea to do as such. The further advance is to compute the sigma (σ) bonds include in that sub-atomic design. From that point forward, observe the solitary pair numbers on a given particle by utilizing the recipe,
- Number of solitary sets = {(v-b-c) ∕2}
- Where v = number of valence electrons in the concerned molecule in a free state
- c = charge on the iota
- b = number of bonds shaped by a concerned iota
We can compute the steric number as,
Steric number = number of σ-bonds + number of solitary matches and afterwards founded on the steric number Assign hybridization and state of a particle
Q: What are the valence electrons in the Hybridization of NH3 (Ammonia) – Lewis Structure and Electron Geometry?
Ans: Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in an iota’s peripheral shell, i.e., free electrons. These valence electrons take part in bond development by either retaining or giving valence electrons from another particle.
The valence electrons fundamentally act in this manner on the grounds that every iota endeavours to lay out a steady state by finishing its octet.
Besides, in light of the fact that the core’s hang on the peripheral shell is most vulnerable on the grounds that it is the uttermost away, the valence electrons respond to the presence of encompassing valence electrons.
Q: For what reason do Hybrid Orbitals Form Stronger Bonds?
Ans: The half and half orbitals have indistinguishable energy. They additionally contain more electron thickness in a specific projection contrasted with the other flap. The unadulterated nuclear orbitals contain uniform charge thickness all through the orbital.
- The half breed orbital covers the focal iota with the nuclear orbital of the fortified particle bringing about a more grounded bond contrasted with the cross-over of two unadulterated nuclear orbitals.
- For instance, an sp3 hybrid orbital has 75% of electron thickness in a projection and 25% in the other flap. The 75% electron thickness projection cross-over with a nuclear orbital of the reinforced particle brings about the arrangement of a solid bond due to the enormous covering area.
Q: What is the Geometrical Structure of Ammonia (NH3)?
Ans: The hydrogen-nitrogen-hydrogen molecules (H-N-H) have a 107° bond point. Clearly, the mathematical design of NH3 will be mutilated.
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) hypothesis expresses that the presence of a solitary pair on the nitrogen molecule makes the whole construction of NH3 twist, bringing about a bond point of 107°.









