Table of Contents
Introduction
Hybridization was presented by Pauling, to clarify the same idea of covalent bonds in a particle. It can likewise be characterized as the blending of various shapes and rough equivalent energy nuclear orbitals and rearrangement of energy to frame a new orbital, of a similar shape and similar energy.
- These new orbitals are called half breed orbitals and the peculiarity is called Hybridization. Consider an illustration of Be compound.
- On the off chance that it is framed without Hybridization, both the Be- – – Cl bond ought to have various boundaries and p- – – p bond strength > s- – – p bond strength.
- For all intents and purposes, bond strength and distance of both the Be- – – Cl bonds are something similar.
- This issue can be survived if the Hybridization of s and p orbital happens. Presently subsequent to thinking about s- – – p Hybridization in Beryllium Dichloride, Cl- – – – Be- – – – – Cl. Here in the principal bond from the left side p- – – sp Hybridization is available and in the second bond sp- – – p Hybridization, so here bond strength of the two bonds will be equivalent.
Normal for Hybridization
Hybridization is a course of blending orbitals and not electrons. Hence in Hybridization full-filled, half-filled, and void orbitals may participate.
- Some of the crossover orbitals framed is generally comparable to the number of nuclear orbitals which might participate during the time spent Hybridization.
- Every crossover orbital has two projections, one is longer, and the other is more modest. The bond will be framed from a huge flap.
- The quantity of half and half orbitals on the focal particle of an atom or particle = number of sigma bonds + solitary pair of electrons.
- The first connection between two molecules will be sigma. The other connection between similar two molecules will be a pi bond.
- The greatest two pi bonds might be available on a solitary molecule. The electron pair of an iota which doesn’t participate in bond development is known as a solitary pair of electrons.
One component can address numerous Hybridization states relying upon trial conditions, for instance, C appearance sp,sp2, sp3 Hybridization in its mixtures.
The repugnance between lp- – lp > lp- – – bp > bp- – – bp.
Half and half orbitals are separated as sp, sp2, sp3, and so forth The directional properties in a half and half orbital are more than nuclear orbitals.
Along these lines, crossover orbitals structure more grounded sigma bonds. The directional property of various crossover orbitals will be in the accompanying request.
sp < sp2 < sp3 < sp3 d2 < sp3 d3 . In dsp3 and d2 sp3 Hybridization, different quantum numbers are being utilized.
Assurance of Hybridization State
Technique 1: Count the accompanying pair of an electron around the focal particle:
- Count all unadulterated sigma fortified electron sets.
- Count all solitary sets of electrons.
- Count coordinate bond.
- Count negative charge.
Technique 2: Th anticipates Hybridization following formulae might be utilized:
Number of half breed orbitals = ½ ( absolute number of the valence electron in the focal particle + complete number of the monovalent molecule – charge on cation + charge on anion )
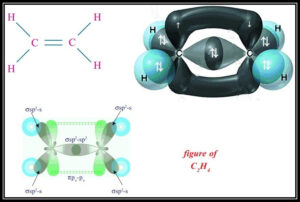
Hybridization of Ethene ( C2 H4 )
C2 H4 has an sp2 Hybridization process. In this Hybridization one ‘s’ and two ‘p’ orbitals are blended to give three new sp2 cross breed orbitals which all are in similar shape and comparable energies. These three sp2 half and half orbitals are at a point of 120 degrees and give a three-sided planar shape. Ethene has two 2CH atoms and 4H particles.
Carbon comprises 6 electrons and hydrogen has 1 electron. During the development of CH2 =CH2 , the electronic design of carbon in its ground state (1s2 2s2 2p1 2p1) will change to an energized state and change to 1s2 2s1 2px12py1 2pz1. In an invigorated state, carbon needs an electron to frame securities; one of the electrons from the 2s2 orbital will move to 2pz orbital to give four unpaired electrons.
Mathematical Structure of Ethene
Ethene is certifiably not an exceptionally mind boggling atom. The carbon molecules of ethene are doubly attached to one another separated from this carbon particle is likewise reinforced with two Hydrogen iotas. They consolidate to frame a sum of three bonds to every carbon iota, giving them a sp2 Hybridization. As a carbon molecule is framing three sigma bonds rather than four sigma bonds, so they additionally need to hybridize three of its external orbitals, rather than four orbitals. A carbon particle is framing three sigma bonds rather than four orbitals. These three orbitals are framed by 2s electrons and 2p electrons, shaping bonds in ethene.
Five Basic Shapes of Hybridization
The five essential states of hybridization are
- Straight
- Three-sided planar
- Tetrahedral
- Three-sided Bipyramidal
- Octahedral
FAQs
What is the Hybridization of Ethene?
Hybridization of ethene particles is sp2. The ethene particle is CH2 =CH2. The C particle has 3 holding spaces and 0 solitary sets of electrons. It goes through sp2 hybridization which brings about planar math.
What causes sp2 hybridization?
The sp2 hybridization is clarified in both the orbitals like the s and p which on blending prompts the advancement of an electron in the s orbital to that of 2p orbitals which is the primary explanation that produces sp2 hybridization.
What shape does ethene have?
As it is realized that Ethene or ethylene is the least complex alkene model and hence as a twofold bond is available and every carbon is appended to 3 molecules the math state of ethene has a three-sided planar shape which implies two covering triangles are available.
What number of single and twofold bonds are there in ethene C2 H4?
As we examine the Lewis design of C2 H4 it says that there are just four C-H bonds, one C=C bond, and no solitary sets on the last shells. There is just a solitary connection between a carbon molecule and a hydrogen iota. Also, there is just one twofold bond present in ethene C2 H4.
Clarify what number of bonds ethene has?
Ethene is certifiably not an exceptionally mind boggling atom. The carbon iotas of ethene are doubly clung to one another separated from this carbon particle is likewise reinforced with two Hydrogen molecules. All complete ethene structures three bonds to every carbon particle and hybridization present in ethene is sp2 hybridization.








