Table of Contents
Introduction:
Methane is the easiest of the soaked hydrocarbons with a substance equation CH4. It comprises four hydrogen particles and one carbon molecule and is the most straightforward alkane.
The point when regular methane arrives at the outer layer of the air is called environmental methane and can be found under the ocean bottom as well as beneath the ground.
It is scentless or has a sweet oil type smell and has no shading.
It is a combustible non-harmful gas. It is a tetrahedral particle that has four comparable C-H bonds. It is created by colonic anaerobes. Alessandro Volta an Italian physicist was quick to experimentally distinguish methane in the year 1776.
methane, dull, unscented gas that happens plentifully in nature and as a result of specific human exercises. Methane is the least difficult individual from the paraffin series of hydrocarbons and is among the strong ozone harming substances.
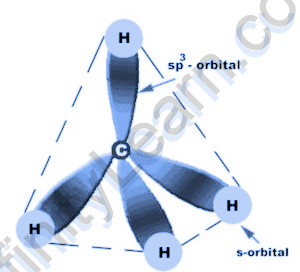
Hybridization of methane
The hybridization of methane, the focal particle carbon is sp3 hybridized. This is on the grounds that one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals in the valence shell of carbon join to frame four sp3 cross breed orbitals which are of equivalent energy and shape. Further, four H iotas likewise utilize these four sp3 cross breed orbitals of carbon to frame C-H sigma bonds which at last prompts the arrangement of the methane atom.
Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles of CH4
Deciding the CH4 atomic calculation will be simpler now as we have as of now talked about the bond development and the course of hybridization above. In methane, the four half breed orbitals are put in such a manner to limit the power of shock between them. Be that as it may, the four orbitals do repulse one another and get discarded at the edges of a tetrahedron. The state of the CH4 is tetrahedral. The sp3 half breed orbital holds a bond point of 109.5 degrees.
Properties of Methane
• Since methane is the least difficult alkane as well as the easiest sort of soaked hydrocarbons, it is basic to get its qualities. Coming up next are probably the main elements of methane:
• CH4 is the compound equation for methane.
• Methane gas has a particular gravity of 0.554, making it lighter than air.
• The Molar Mass of methane is 16.04 g/mol.
• It must be broken up in the water.
• Whenever methane is scorched, it creates a pale, glowing, and incredibly hot fire.
• Methane is quite possibly the main ozone harming substance.
• Due to its high energy thickness of 55.7 MJ/kg, unadulterated methane is likewise used for home warming and cooking.
• Methane has a limit of 161.50 degrees C. Methane has a liquefying point of 182.5 degrees C.
• Methane is the form corrosive of a methanide, which is one of its compound qualities.
• Methane is a petroleum derivative as well as a bacterial metabolite.
• Methane can detonate the compartment putting away it and the rocker whenever presented to fire or hotness for a drawn-out timeframe.
Significance of Methane
Methane (CH4) is a hydrocarbon that is an essential part of gaseous petrol. Methane is additionally an ozone harming substance (GHG), so its presence in the air influences the world’s temperature and environment framework. Methane is discharged from an assortment of anthropogenic (human-affected) and regular sources. Anthropogenic outflow sources incorporate landfills, oil and gaseous petrol frameworks, agrarian exercises, coal mining, fixed and versatile ignition, wastewater treatment, and certain modern cycles.
Methane is the second most plentiful anthropogenic GHG after carbon dioxide (CO2), representing around 20% of worldwide outflows. Methane is in excess of multiple times as intense as carbon dioxide at catching hotness in the air. In the course of the most recent two centuries, methane fixations in the environment have dramatically increased, generally because of human-related exercises. Since methane is both a strong ozone-depleting substance and brief contrasted with carbon dioxide, accomplishing critical decreases would have a fast and huge impact on air warming potential.
Uses of CH4 (Methane)
• It is utilized in cars, broilers and water radiators as a fuel
• It is utilized in the age of power
• It is utilized as rocket fuel in its refined fluid-structure
• It is utilized as a liquid catalyst fixing in businesses
• It is a generally expected fixing in compost
• It is utilized to clean items
• It is utilized in gas-terminated power stations
• It is utilized in gas cookers
• It is utilized in the testing of gas apparatuses
Health Hazard of Methane
Whenever taken in huge amounts, methane can contrarily affect the human body. A high amount of methane in encased spaces lessens oxygen levels, bringing about asphyxia, unsteadiness, migraine, heaving, loss of coordination, queasiness, and loss of awareness. Assuming the amount of methane in the air ascends by 5 to 14 per cent by volume, it becomes dangerous. Blasts of this nature are normal in coal mineshafts and collieries. Accordingly, prior to entering the mines, natural air is sent through to lessen the centralization of methane. Methane dangers can happen during the assembling, utilization, and transportation of methane. Despite the fact that we assimilate methane when we inhale, delayed openness to elevated degrees of methane is risky.
FAQs
Is methane gas unsafe for people?
Only methane is non-harmful yet can turn out to be dangerous when blended in with different gases. Methane dislodges oxygen to incite suffocation. It can cause wooziness and migraine side effects, however, these habitually go unrecognized until the mind cues the body wheezing for air.
What is the primary driver of methane gas?
Methane is delivered during coal, petroleum gas, and oil creation and transportation. Methane emanations are additionally brought about by domesticated animals and other cultivating exercises and the debasement of farming waste in metropolitan strong waste landfills.
For what reason is methane gas terrible for the climate?
For instance, on the off chance that methane spills up high prior to being utilized from a defective line - it ingests the hotness from the sun, heating up the environment. It's known as an ozone-depleting substance, similar to carbon dioxide, hence.
Is methane a petroleum derivative?
Non-renewable energy sources range from unpredictable materials with low carbon-to-hydrogen proportions (like methane) to fluids (like oil), to practically unadulterated carbon-made non-unstable materials, for example, anthracite coal. Methane can be seen as either alone, in the mix with oil, or as methane clathrates in hydrocarbon fields.