Table of Contents
Introduction
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material or a substance in a controlled atmosphere in simple terms. The temperature is usually controlled during the procedure. Calcination is used to alter the physical or chemical characteristics of a substance.
A brief outline
Calcination is commonly done in furnaces, retorts, or kilns, and materials are frequently racked over or agitated to ensure uniformity. The reverberatory furnace is among the most frequent calcination setups. The normal architecture and process are described in the following sections.
Important concepts
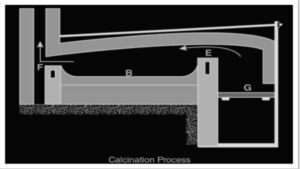
Reverberatory furnaces are built in a variety of ways, but the flames and hot gases from the fire always come into close contact with the material to be calcined; however, the fuel is isolated from it.
The fire is burning on the grate at G in the illustration above. The flames travelling over the bridge at E are now deflected downward by the furnace’s low sloping roof and pass directly and over the surface of the charge or calcination material on platform B. The fumes and heated gases subsequently escape into the chimney through the throat F. As a thin layer, the charge is stretched out uniformly on the bed.
Gypsum Calcination
Gypsum, also known as calcium sulphate dihydrate (CaSo4.2H2O), is a calcium mineral that is mined all over the world. Some coal-fired electric power stations produce it as a by-product of flue gas desulphurization. Gypsum comes in a variety of forms, which are listed below.
- Alabaster is a fine-grained, translucent white gypsum.
- Satin spar is silky gypsum with fibrous needle-like crystals.
- Selenite crystals are colourless and clear.
Calcination’s Purpose
Calcination is the method for determining a material’s thermal decomposition. It is attained by heating a component to a temperature higher than its melting point. This high-temperature heating aids in the removal of volatile chemicals while also oxidizing any quantity of the substance. As a result, calcination might be regarded a metal purifying process.
Gypsum is utilized in a variety of applications. The following is a list of some of the most popular domains.
- Construction of a building
- Conditioning the soil
- Additives to food
- Pharmaceuticals
- Medical equipment
Significance of calcination in IIT JEE exam
Calcination is topic that account for 2 to 3% of exam questions, encompass a wide range of topics. All you have to do is grasp the concepts of each topic. Based on the distribution of difficulty levels in previous years’ tests, we should expect 4 to 8 marks beneath the topic.
FAQs
What is the objective of calcination?
Since high-temperature warming of solids is utilized to dispense with unstable synthetics and other oxidizing segments of the mass, calcination is now and again alluded to as solids sanitization.
How does the calcination cycle work?
Heating a substance at a high temperature beneath its melding or liquefying focuses, causing oxidation or decrease, dampness misfortune, and disintegration of carbonates and different mixtures.
For what reason does the calcination response happen without air?
The calcination cycle is utilized to change over metal carbonates into carbon dioxide and metal oxides in the metal carbonates. There is no response except if the interaction is done within the sight of air.








