Table of Contents
Dynamic Equilibrium: Important Topic of Chemistry
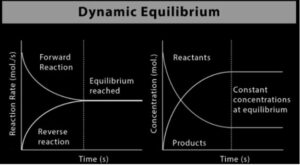
When one reversible reaction occurred, a dynamic equilibrium is established. There is no net effect because substances transit at the same rate between reactants and the products. The pace at which reactants and products are generated is that neither one of their concentrations varies. It is an example of a state that is in a steady-state.
A Brief Outline
When reactions occur at a rate that the composition of the mix does not vary over time, a closed-loop system is in thermodynamic equilibrium. Reactions certainly happen, sometimes violently, but rarely to the point where changes in the composition may be seen. The rate constants for reversible reactions could be used to express equilibrium constants.
With the interchange between the two states, two states (state 1 and state 2) are generated when the two opposing forces operate simultaneously and independently of one another. It’s said that the states are in dynamic equilibrium. The dynamic equilibrium “A ⇌ B” is commonly represented as a double-sided arrow.
Important Concepts
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the liquid phase of a new bottle of soda has a specific value. If half of the liquid is poured out and the bottle is sealed, carbon dioxide will exit the liquid phase at an increasing rate as the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the gas phase rises until an equilibrium is attained. A molecule of CO2 may exit the liquid phase at that point due to thermal motion, but another molecule of CO2 will transfer from the gas to the liquid in a very short time, and vice versa.
The rate of CO2 transfer from the gas to the liquid state is equal to the rate of CO2 transfer from the liquid to the gas phase at equilibrium. Henry’s law, which states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is exactly proportional to the fraction of that gas above the liquid, is used to calculate the equilibrium concentration of CO2 in the liquid in this example. This connection is written as
C=KP
K = temperature-dependent constant
P= partial pressure
C = concentration of the dissolved gas in the liquid.
Significance of Dynamic Equilibrium in chemistry in IIT JEE exam
The dynamic equilibrium in chemistry is a less important topic that requires a solid understanding of equations. They will only respond to questions based on equations. Around 1 to 2 questions will be asked on the IIT JEE exam, which accounts for 3.3 percent of the total.
FAQs
Only reversible reactions have a dynamic equilibrium. There is no net change in the case of dynamic equilibrium since both reactants and products transition at the same pace.
When you open a soda can and leave it out for an extended period of time, it becomes flat and no longer contains any bubbles. As a result, they lose dynamic equilibrium and continue to release gaseous carbon dioxide until no bubbles remain.
Static equilibrium is a state in which all chemical reactions in a system have ceased and all movement between reactants and products has ceased, resulting in the absence of any chemical reactions. Do you want to write a message about Dynamic Equilibrium?
Why may a reaction's equilibrium be shifted by temperature, pressure, or concentration?
What is the definition of static equilibrium?






