Table of Contents
Nitrous acid is a mildly acidic and unstable chemical. It can only be found in nitrate salt solutions. Nitrous acid is a combination of nitric acid and nitrous gas, but with a lower amount of oxygen than nitric acid. Scheele developed nitrous acid. It is made by distilling absolutely dry lead nitrate in a retort connected with a receiver. Nitrous acid is emitted as a liquid.
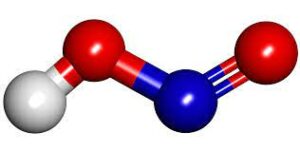
Structure of Nitrous Acid
- The formula of nitrous acid is represented as HNO2.
- Because it is an acid, the hydrogen molecule exits through one of the oxygen molecules. So we may place nitrogen in the centre, two oxygens on either side and hydrogen outside one of them.
- If we count the number of electrons, hydrogen has one, nitrogen has five, and each oxygen molecule has six, for a total of twelve. This provides us with a total of 18 electrons.
- With the exception of nitrogen, all of the atoms in the nitrous acid structure HNO2 have entire outer shells. Nitrogen and oxygen can form a double bond, which means each atom has a formal charge of 0.
Nitrous Acid Physical Properties
- Nitrous acid is exclusively present in liquid form, either dissolved in water or as a nitrate salt.
- The nitrous acid solution is pale blue in colour and is derived from N2O3, a blue solid that is acidic in nature.
- Nitrous acid has a density of around 1 g/mL and a weight of approximately 47.013 g/mol.
- The boiling point of nitrous acid is 158 degrees Celsius.
Nitrous Acid Chemical Properties
- Since Nitrous acid has only one hydrogen ion which it can donate to a base in case of a reaction between an acid and a base, it is known as a monobasic acid. It can release only one proton, i.e., H+ in solution.
- Nitrous acid is very unstable in nature, hence it is generally found in liquid form. Every time it is used, it must be newly made.
- Because nitrous acid is a weak acid, it does not entirely dissociate in water.
- Because the oxidation number of the N in HNO2 is 3+, it may serve as both an oxidizing and reducing agent.
- Nitrous acid oxidizes hydrogen sulphide to create sulfur:
H2S+2HNO2→2H2O+2NO+S
- Reaction With Bases: Since nitrous acid is acidic in nature, it interacts with bases to generate salts. It frequently produces nitrite salts, such as sodium nitrite.
Nitrous Acid Applications
- Used in the synthesis of diazonium salts from amines and the synthesis of azo colours via the Sandmeyer reaction.
- Sodium azide, a potentially explosive chemical, is treated to eliminate its hazardous characteristics.
- Also used as an oxidizer in liquid fuel rockets
FAQs
Is nitrous acid considered a strong or weak acid?
Nitrous acid is an extremely weak acid. Nitric acid, on the other hand, is a very acidic substance. This is because the conjugate base of nitric acid is substantially more stable than the conjugate base of nitrous acid.
What causes nitrous acid to be unstable?
Nitric oxide (chemical formula: NO) and nitric acid are formed when nitrous acid is broken down (chemical formula: HNO3). It can react as an oxidising or reducing agent: the nitrogen atom can acquire or lose electrons in interactions with other chemicals.






