Table of Contents
What is Hysteresis?
The significance of hysteresis is “lagging”. Hysteresis is portrayed as a slack of attractive transition thickness (B) behind the attractive field strength (H).
All ferromagnetic materials show the peculiarities of hysteresis. To provide you with a superior comprehension of the idea, we will take a case where a ferromagnetic substance is put inside a current-conveying curl. Because of the attractive field that is available the substance gets polarized. In the event that we invert the course of the current, the substance gets demagnetized, this cycle is known as hysteresis.
Frameworks that show hysteresis is typically nonlinear. So this can be numerically difficult for some hysteretic models, for example, the Preisach model and the Bouc-Wen model. Furthermore, there are models, for example, phenomenological models for explicit peculiarities, for example, the Jiles-Atherton model that is utilized to portray ferromagnetism.
Sorts of Hysteresis
There are two kinds of hysteresis;
Rate-subordinate hysteresis: In this kind of hysteresis there is a slack among information and result. We can take the case of a sinusoidal information X(t) bringing about a sinusoidal result Y(t).
Rate-free hysteresis: This hysteresis found in frameworks will quite often have a determined memory of the past that actually stays even after the drifters have vanished.
Hysteresis Loop
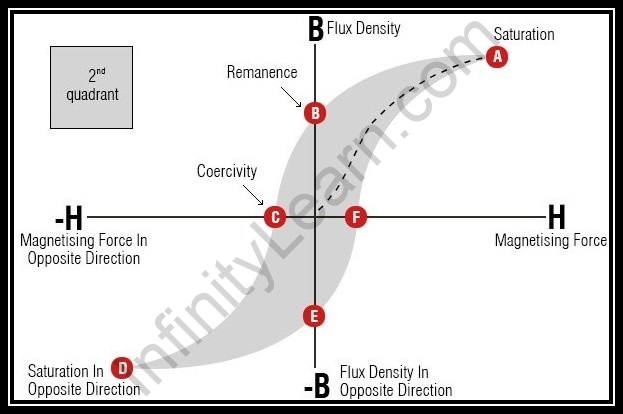
The hysteresis circle shows the connection between the attractive transition thickness and the charging field strength. The circle is produced by estimating the attractive motion emerging from the ferromagnetic substance while changing the outer charging field.
- The attractive transition thickness (B) is expanded when the attractive field strength(H) is expanded from 0 (zero).
- With expanding the attractive field there is an expansion in the worth of attraction lastly arrives at point A which is called immersion point where B is steady.
- With a diminishing in the worth of the attractive field, there is a decline in the worth of attraction.
- However, at B and H are equivalent to nothing, substance or material holds some measure of attraction is called retentivity or remaining attraction.
- Whenever there is an abatement in the attractive field towards the negative side, attraction additionally diminishes. At point C the substance is totally demagnetized.
- The power expected to eliminate the retentivity of the material is known as Coercive power (C).
- The other way, the cycle is proceeded with where the immersion point is D, retentivity point is E and coercive power is F.
- Because of the forward and inverse course process, the cycle is finished and this cycle is known as the hysteresis circle.
Benefits of Hysteresis Loop
1. A more modest district of the hysteresis circle is demonstrative of less loss of hysteresis.
2. Hysteresis circle furnishes a substance with the significance of retentivity and coercivity. In this manner, the method for choosing the right material to make a super durable magnet is simplified by the core of machines.
3. Remaining attraction can be determined from the B-H diagram and it is, in this manner, easy to pick material for electromagnets.
Retentivity and Coercivity
Whenever a ferromagnetic material is polarized by applying the outer charging field, after polarization assuming that we eliminate the outside polarizing field the material won’t unwind back to its zero charge position.
Retentivity;
How much charge is present when the outer polarizing field is eliminated is known as retentivity.
It is a material’s capacity to hold a specific measure of the attractive property while an outside polarizing field is taken out.
The worth of B at point b in the hysteresis circle.
Coercivity
How much converse(- ve H) outer polarizing field is expected to totally demagnetize the substance is known as coercivity of substance.
The worth of H at point c in the hysteresis circle.
Hysteresis Applications
Hysteresis can be generally found in Chemistry, Physics, Engineering, Economics and Biology. Normal models further incorporate attractive hysteresis, ferroelectric hysteresis, superconducting hysteresis, mechanical hysteresis, optical hysteresis, electron shaft hysteresis, adsorption hysteresis, financial hysteresis, and so forth Regardless, we will check out a portion of the significant purposes of hysteresis.
- A few uses of hysteresis are found in ferromagnets. It is for the most part used to hold a memory, for instance, hard plates, attractive tape, and Visas.
- Hysteresis is applied in numerous fake frameworks, for example, in indoor regulators and Schmitt triggers which are intended to forestall undesirable regular or undesirable fast exchanging.
- A hysteresis is at times purposefully made part of PC calculations.
- Hysteresis can be seen while diminishing the approach of a wing after slowing down, in regards to the lift and drag coefficients.
- The presence of the air pocket shape hysteresis has significant outcomes in interfacial rheology tests including bubbles.
- In Biology, it is found in Cell science and hereditary qualities, Immunology, Neuroscience, Respiratory physiology, Voice and discourse physiology, Ecology and Epidemiology.
- Generally, hysteresis is experienced in various areas of science and has a lot of purposes.
Energy Loss because of Hysteresis
- A transformer is the best instance of concentrating on energy misfortune because of hysteresis, as we probably are aware that during the course of polarization and demagnetization energy is required.
- During the pattern of charge and demagnetization of attractive substances, energy is spent and this is burnt through effort shows up as hotness. This heat misfortune is known as hysteresis misfortune.
- The deficiency of energy per unit volume of the substance is equivalent to the region of the hysteresis bend
- In transformers because of the consistent course of polarization and demagnetization energy is lost as hotness constantly, because of this energy misfortune proficiency of the transformer gets diminished.
- To stop this energy misfortune delicate iron centre is utilized in transformers on the grounds that the energy misfortune or hysteresis misfortune on account of delicate iron is a lot more modest than different materials.
FAQs:
Clarify Magnetization and Demagnetization?
The technique for fostering the attractive properties inside an attractive substance is called charge; any of the attractive substances can be polarized utilizing an electric flow or by contracting with a solid magnet.
Are there any benefits of the hysteresis circle?
Indeed, the hysteresis circle makes long-lasting magnets more conspicuous. The more modest the hysteresis circle region of an attractive material, the less is the hysteresis misfortune. The hysteresis circle region for silicon steel is tiny thus, silicon steel is utilized in the assembling of transformer centres.
How are delicate and hard magnets unique in relation to one another?
Delicate and hard magnets vary as far as their qualities. A delicate magnet can be framed by warming and afterwards cooling steadily while a hard magnet is shaped by warming and cooling abruptly. Delicate magnets are brief magnets however the hard ones are super durable magnets.








