Table of Contents
Introduction
The capacitive reactance is defined as the reactance that is generated by capacitive components (Capacitors). It can be expressed as. The capacitive reactance is a voltage opposition across a capacitive device that is used to temporarily store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. The capacitive reactance causes the current and voltage to be out of phase.
The current leads the voltage in a capacitive circuit. The voltage is led by the current in an ideal capacitive circuit. Because of capacitive reactance, the power factor of the system or circuit improves.
What Is the Difference Between Reaction and Resistance?
1. Reactance is an impedance component, whereas resistance is a DC component of Resistance.
2. The value of reactance is always a complex number, but resistance must always be a real number.
3. The resistance in a completely inductive or capacitive circuit is zero, and the reactance in a fully resistive circuit is zero.
4. As a result of reactance, both the amplitude and phase of current will vary. The current and voltage will always be in phase due to resistance.
5. The value of reactance is affected by the frequency of supply, but the value of resistance is unaffected by the frequency of the supply.
6. The inductive reactance for a DC supply must be 0, but the capacitive reactance must be unlimited. The resistance for DC supply will stay the same.
7. Reactions are denoted by the letters and. The term “resistance” is used to describe a person’s ability to resist something
8. Because of the reactance aspect, the power factor in reactance is either leading or trailing. When the reactance is zero, the power in Resistance is unity.
Electrical Reactance
It is defined as a flow in the electrical circuit that flows in the opposite direction of the current flow. The smaller the current for that supplied voltage, the stronger the reactance. In magnetic and electrical fields, reactance behaves differently. In the magnetic field, reactance opposes changes in current, but in the electrical field, it resists changes in voltage.
Inductive Reactance
Denoted by the symbol XL, it is formed when an inductive element, such as an inductor, is present. An inductive element may be used to store electrical energy in the form of a magnetic field, which is one of its applications. The direction of the current produced due to inductive reactance is clearly opposite the direction of the main current, according to Lenz’s law. This might result in a power lag between the voltage and current waveforms.
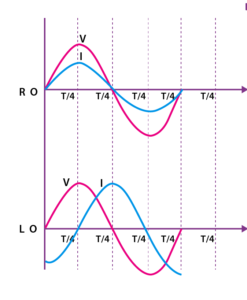
Capacitive Reactance
Denoted by the symbol XC, it is formed when a capacitive element, such as capacitors, is present. Unlike the inductive element, the capacitive element aids in the storage of electrical energy in the form of an electric field. The opposition of voltage across the capacitors causes capacitive reactance. There is also a lag between current and voltage as a result of this. In an inductive circuit, the optimal lag is 90 degrees, while in a capacitive circuit, the ideal voltage lead by the current is 90 degrees.
Also read: HC Verma Solutions Class 11 Chapter 5 Newtons Law Of Motion
FAQs
What Is An Electrical Reactance, And What Does It Mean?
Because of its inductance and capacitance, an electrical reactance is described as a flow in a circuit element that flows in the opposite direction of the current. For the same applied voltage, if the reactance is higher, the current will be lower. Although reactance is quite similar to electric resistance, it varies in a few areas. When an alternating current passes through an electric circuit or element, both the phase and amplitude of the current change. In addition, the energy is stored in the reactance-containing element.
Do inductive and capacitive reactance have different formulas?
This consequence is known as REACTANCE, and it is denoted by the letter X and stated as X = XL XC or X = XC X L. In a circuit with 50 ohms inductive reactance and 25 ohms capacitive reactance in series, the net reactance, or X, is 50 ohms 25 ohms, or 25 ohms inductive reactance.