Table of Contents
Moment Of Inertia Of A Circle: In simple terms, this is the fundamental concept. It can be assumed that inertia is proportional to a body’s mass. When a body begins to rotate around a fixed axis, every element in the body travels in a loop with linear velocity, implying that each particle travels with angular acceleration. Yes, the proper definition of inertia is the tendency of a body to resist angular acceleration. It is the total mass of each particle in the body multiplied by the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
Join Our Courses: JEE Class 11 Students | JEE Class 12 Students | JEE Dropper
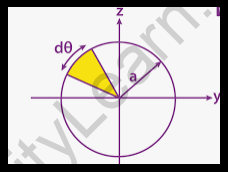
Derivation of Moment of Inertia of a Circle
Do you know how to calculate the moment of inertia of a circle? To understand this, we must first comprehend the derivation of a circle’s moment of inertia, which is discussed below. With this derivation, it will be easy to grasp how to get the moment of inertia of a circle.
Click Here To know: How to Calculate Moment of Inertia
According to the derivation of moment of inertia of a circle, the circular cross-section will be determined using the radius and an axis passing through the centre. This explanation will include the following steps:
- Give an explanation of the coordinate system.
- Find out where the difference is.
- Finally, put it all together.
Inertia manifests itself in a variety of ways.
- The inertia of Rest: The inability of a body to change its state of rest on its own is referred to as inertia of rest. When a car starts, a person in the passenger seat falls rearward. The lower section of the car begins to move due to the inertia of rest, while the top portion attempts to remain still.
- The inertia of Motion: The inability of the body to change its state of motion on its own is referred to as inertia of motion. When a person in a car, for example, hits the brakes, he or she falls forward. The lower portion of the car comes to a halt due to inertia of motion, while the upper portion continues to move.
- Directional inertia is the inability of a body to change its motion direction on its own. A person sitting inside a car is thrown outwards to maintain his direction of motion due to inertia of motion.
Make your IIT Dream come true with Infinity Learn.

JEE Foundation Class for 10
JEE Foundation Class for 10 enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
FAQs
Do you have a good understanding of the idea of inertia?
A moment of inertia is a quantitative measure of a body's rotational inertia—that is, the body's resistance to having its rotational speed modified by the application of torque—in physics (turning force).
What is the circle's inertia?
The moment of inertia of a circle, also known as the second-moment area of a circle, is commonly calculated using the formula I = R4 / 4. The radius is R, and the axis passes through the centre. When we represent this equation in terms of the circle's diameter (D), it becomes I = D4 / 64.
Could you give any additional examples of inertia?
The lift began abruptly. We take a step back. The satellite continues to move in a circular manner due to the inertia of motion. Even after you've stopped stirring, swirl the milk.
Infinity Learn App
Now you can find answers to all your subject queries & prepare for your Exams on our Ultimate Learning App for CBSE and K-12 – Infinity Learn.






