Table of Contents
Introduction
In rotating motion, the moment of inertia plays the same role as mass does in translational motion. To put it another way, the moment of inertia is a measurement of the body’s resistance to a change in rotational motion. The greater the body’s moment of inertia, the more difficult it is to rotate it. The greater the body’s moment of inertia, the more difficult it is to stop its rotating motion.
Area Density is a concept that is used to describe how dense an area is.
Selecting and defining a narrow strip of mass with varied width yields Area Density. Write an expression for the area density of the entire cube, followed by the little strips of differential widths. Integral Calculus is used to add all of the separate strips. Area density, defined as mass divided by area, is an intense quality, meaning that it is independent of the amount of material used and that, as long as the mass is uniform, its area density is the same whether the complete or a tiny strip of differential width is chosen.
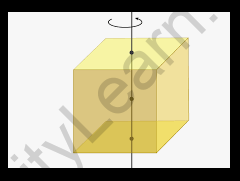
Derivation of the Cube’s Moment of Inertia
We’ll suppose the solid cube has mass m, height h, width w, and depth d to calculate its moment of inertia as its axis passes through the centre. The cube’s moment of inertia is now similar to that of a square object with a side centred on an axis. In addition, we’ll assume that the lamina’s area density is. The element of the lamina in the plane with cartesian coordinates x, y will thus be dx -dy. As a result, its mass is equal to dxdy.
Helpful Hints
- Understand the Syllabus and Purchase the Required Materials: Make sure you have all of your study materials as soon as possible. Specific books are vital since they aid in determining which topics are necessary for the exam and which aren’t worth the time, which is crucial during preparation. Popular JEE books are meticulously designed to assist students in comprehending the pattern and scope of the assessment sections. While those reference books are vital, many students believe that NCERT isn’t as significant, despite the fact that it is the book that aids in the formation of a sound foundation. Solving all of the NCERT examples and exercises lays the groundwork for higher-order issues.
FAQs
What is a Cube's Moment of Inertia?
The moment of inertia is a feature of a rigid body's mass that defines the total net torque required to achieve a desired or required angular acceleration along a rotational axis. A solid cube's mass moment of inertia (axis of rotation at the centre of a face) is proportional to the length of its side.
What is the significance of the Moment of Inertia?
In Physics, rotational inertia is important because it involves a mass in rotating motion. It is used to calculate angular momentum, which also helps us to understand how rotational motion changes when mass distribution changes (by conservation of angular momentum).
Which of the following shapes has the smallest Moment of Inertia?
Because any moment of inertia through another axis would add mr2 to the result, the moment of inertia through the centre of mass of that body will be the smallest for any given shape.






