Table of Contents
The moment of inertia of a rigid body, otherwise called the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, the second moment of mass, or, all the more definitively, rotational dormancy, is an amount that decides the force expected for an ideal precise speed increase about a rotational hub, similarly, that mass decides the power expected for the ideal speed increase.
A Brief Outline
It depends on the mass dissemination of the body and the pivot picked, with higher minutes requiring more force to influence the pace of turn. It is a lengthy (added substance) property: the mass of inertia for a point mass is basically the mass times the square of the opposite distance to the revolution pivot.
Important Concepts
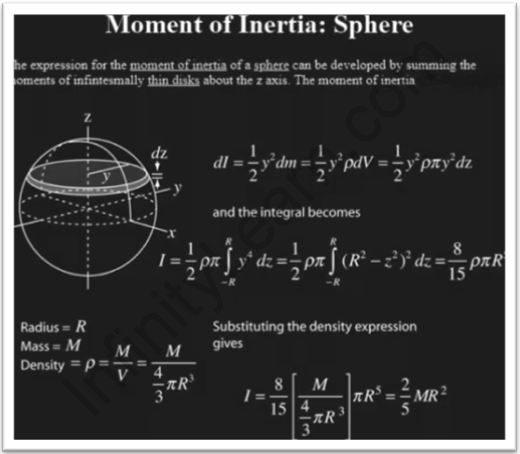
The moment of inertia of a sphere is calculated by adding the products from the total mass of all associated elements of the entity and multiplying them by the square of the particle’s distance from the center.
The sphere’s moment of inertia is usually stated as;
I = (⅖) MR2
The radius and mass of the sphere are represented by R and M, respectively. Students must remember that we are discussing the moment of inertia of a solid sphere as it rotates around its central axis. Furthermore, the moment of inertia of the sphere about its axis on the surface can be stated as;
I = (7/5) MR2
Spherical expression’s moment of inertia can be calculated in two ways.
- To begin, we slice the solid sphere into infinitesimally thin solid cylinders.
- Then, from left to right, we must add the moments of extremely small thin discs in a given axis.
The moment of inertia can often be determined in an exact closed-form expression for simple objects having geometric symmetry. This happens most of the time when the mass density is constant, but it can also happen when the density varies across the object.
Significance of moment of inertia of a sphere in IIT JEE exam
One of the most significant chapters in mechanics is rotation, which necessitates a thorough comprehension of the moment of inertia. They will only answer queries that are based on equations. The IIT JEE exam, which contributes for 6.6 percent of the total, will have around 2 to 3 questions.
FAQs
A solid sphere of mass M and radius R has a moment of inertia of (2/5) MR2. What is a solid sphere's moment of inertia if it has mass M and a radius R?
Q. Which of the following has the greatest inertia moment?
- a) Any of the diameters of a disc
- b) A ring that is the same diameter as any of its diameters
- c) Any of the diameters of a solid sphere
- d) Any of the diameters of a hollow sphere
Ans: d) Any of the diameters of a hollow sphere
Q. What are the factors which affect the Moment of Inertia?
Ans:
- The material’s density.
- The body’s shape and size
- Rotational axis






