Table of Contents
Alcohols, phenols, and ethers are created by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with hydroxyl groups (OH) and alkoxy groups (R-O). These are a very important class of compounds that we see all around us and use on a daily basis. Another type of organic compound is aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. In this section, we will look at various important reactions such as the Cannizzaro reaction, aldol condensation, Gattermann-Koch reaction, and so on.
In our daily lives, we see a variety of important real-life applications. Some of them are as follows:
- Wine and beer are made from alcoholic beverages.
- When ethanol is burned as a fuel, it produces carbon dioxide and water.
- The use of ethanol as a fuel has the advantage of producing less pollution.
- Acetone is used to remove nail polish.
The functional group of alcohol is the hydroxyl group, abbreviated as OH. The general formula ROH is used to denote alcohols. They are formed by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with one OH group in alkanes. Secondary alcohol, R2CHOH, of 2°, has the OH group on a carbon atom that is attached to two other carbon atoms; and tertiary alcohol, R3COH, of 3° has the OH group on a carbon atom connected to three other carbon atoms.
Alcohols’ boiling points rise when compared to hydrocarbons of comparable molar mass due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds. Furthermore, alcohols can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, and those with nearly four carbon atoms are soluble in water.
Alcohols
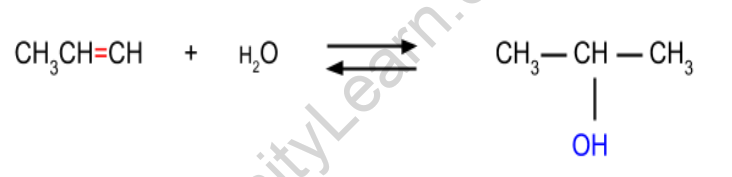
Alkenes from alcohol when reacting with water in the presence of acid. The alcohol is formed by following MArkovnikov’s rule in the case of unsymmetrical alkenes.
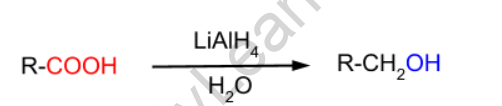
LiAlH4 is a very strong reducing agent derived from carbonyl compounds. This reagent is used to convert carboxylic acids to primary alcohols.
The OH group has a large influence on the properties of alcohol.
(a) Boiling point- The lower members have higher boiling points, such as methanol, ethanol, and 1-propanol.
(b) Water solubility: Lower alcohols are highly soluble in water, but as the size of the alkyl group increases, solubility decreases.
Phenols
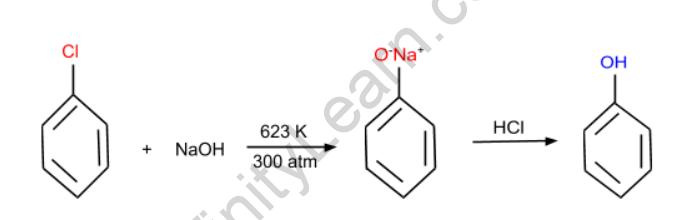
Chlorobenzene is used in this reaction to react with NaOH at high temperatures and pressure, yielding sodium phenoxide. After that, the phenoxide is acidified to produce phenol.
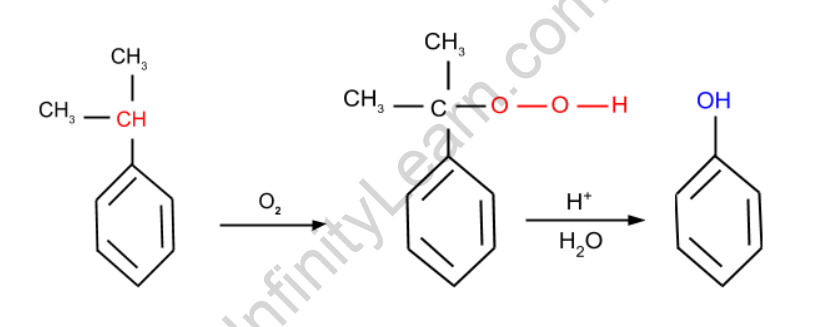
Cumene is oxidised in the presence of air in this reaction, resulting in cumene hydroperoxide. This hydroperoxide is now treated with dilute acid, which produces phenol.
Phenols’ Physical Properties
Phenol is a colourless solid with an m.p. of 41C and a b.p. of 182C. When exposed to air, it turns colour. It is moderately soluble in water.
FAQs
Is oxygen present in organic compounds?
Organic compounds are molecules made up of carbon atoms that are covalently bonded to hydrogen atoms (C-H bonds). This means that all organic compounds have carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms in common. Furthermore, various organic compounds can contain oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and other elements.
What do you call organic compounds that contain oxygen?
The two oxygen-attached alkyl groups are listed alphabetically, with spaces between the names, and are followed by the word ether. If both alkyl groups are the same, the prefix di- is used. The suffix -anal is used to name aldehydes instead of the suffix -ane.








