Table of Contents
Introduction
- The Ostwald process is one of the most widely utilised procedures or chemical processes for producing nitric acid. Wilhelm Ostwald, a German scientist, invented the technique in the year 1902. In 1909, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for his research.
- The Ostwald method has grown in popularity over the years since it is the simplest way to manufacture nitric acid, which is utilised in a variety of applications including fertiliser manufacturing and the production of inorganic and organic nitrates or nitro compounds.
The Ostwald Process’s History
- Industrial nitrogen used to be nitrates that were processed with sulphuric acid to make nitrogen before the Ostwald Process.
- In addition to Haber’s nitrogen-fixing process, the Ostwald Process was primarily utilised during World War I. Later, when nitrogen use expanded, the process was employed for fertiliser production.
- Later in 1902, Ostwald patented and profited from the Process. Stainless steel was introduced to increase yield by increasing and supporting higher pressure.
The Basics of Primary Oxidation
- For the oxidation of ammonia, a catalytic chamber is employed, with platinum gauze as the catalyst and a temperature of 600 degrees. Nitric acid oxidation is both reversible and exothermic. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, lowering the temperature can accelerate the reaction. 95 per cent of ammonia is converted to nitric acid during initial oxidation.
- The nitric oxide gas produced by the oxidation of NH3 is hot, thus it is sent through a heat exchanger to lower the temperature to 150 degrees Celsius.
Haber’s Process and its Importance in the Ostwald Process
- Haber’s Process is the commercial synthesis of ammonia, which is a raw material in the Ostwald Process. With the use of ammonia, this process overcomes the difficulties of breaking down the energy in nitrogen and hydrogen, therefore aiding the Ostwald Process, as ammonia is the feedstock for this reaction.
Mechanism
- We may rapidly understand the idea or mechanism behind this Process before moving on to the various steps. The conversion of ammonia to nitric acid is merely the outcome of an oxidation reaction.
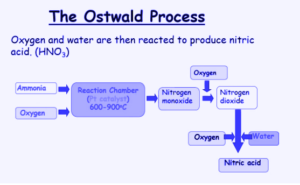
- This oxidation reaction provides us with the required nitric oxide. Furthermore, when nitric acid is oxidised, nitrous gases are produced, which can trap water molecules. We are in possession of We get nitric acid this way.
- Where ammonia will give rise to the desired product, catalytic oxidation with O2 is used. There are specific reaction chambers where ammonia is injected from one way and the air is fed through several paths while the process is being carried out.
FAQs
In the Ostwald Process, what catalyst is used?
In two phases, ammonia is transformed to nitric acid. It is oxidised by heating in the presence of oxygen in the presence of a platinum catalyst, which must be mixed with 10% rhodium fused with copper or nickel to generate nitric oxide. In the contact method, a vanadium oxide catalyst is also employed.
What is the significance of the Ostwald Process?
The Ostwald Process was first significant because the Germans need it for explosives during World War I. It can also be used to produce explosives on a big scale. The ammonium nitrate produced in this method is utilised as fertiliser for crops and lawns.
What is Nitric Acid's chemical formula?
The nitrogen atom is connected to a hydroxyl group and the remaining oxygen atoms by an analogous connection. It functions as a reagent as well as an aprotic solvent. It is also the nitrate conjugate acid. The molecule of nitric acid is made up of three oxygen atoms, one nitrogen atom, and one hydrogen atom. One oxygen atom is doubly bound to the nitrogen atom in the nitric acid molecule, while the second oxygen atom is attached to the hydrogen atom and the central nitrogen atom. The last oxygen atom in the nitric acid molecule has a charge of -1 and is singly linked to the central nitrogen atom.