Table of Contents
Phosphorous acid, commonly known as phosphonic acid, is a colourless phosphorus oxyacid.
The slow-burning of phosphorus results in the formation of phosphorous acid, which is a white volatile powder. Its salts are known as phosphites. It is easily produced by reacting phosphorous trichloride with water. PCl3 is sprayed into steam at 190°C and the heat of the reaction is employed to distil out the hydrogen chloride and surplus water vapour.
H3PO3 structure
Phosphorus acid, H3PO3, has one covalent link and the term trihydroxy ortho phosphorus acid implies that it has three OH groups, which are three hydrogen bond acceptors. Phosphorus acid has a pseudo tetrahedral shape. One oxygen atom forms a double bond with a phosphorus atom, while three OH groups are directly connected with the phosphorus atom.
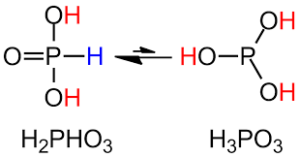
The molecular formula HPO(OH)2 can be used to more precisely describe the structure of H3PO3. Phosphorous acid is tetrahedrally coordinated in the solid-state by one P-H and PO bond and two longer POH links. It is in equilibrium with the tautomer form, which has three POH bonds. The one with two hydroxyl groups is called phosphonic acid, whereas the one with three hydroxyl groups is called phosphorous acid. The name ending in ‘ous’ indicates that it is in its abbreviated form.
Physical Properties of Phosphorous Acid
- It has a foul smell.
- It is a deliquescent white solid.
- It is water-soluble and may accept three hydrogen bonds.
Chemical Properties of Phosphorous Acid
- Because phosphoric acid has high reducing characteristics, it is easily transformed into phosphoric acid. When dry phosphorous acid is heated, it disproportionates to generate phosphine and phosphoric acid.
H3PO3 + 3H3PO3 → PH3 + 3H3PO4
- When phosphoric acid combines with a basic, such as sodium hydroxide, it produces sodium phosphate and water.
H3PO3 + 3NaOH → Na3PO3 + 3H2O
Uses of Phosphorous Acid
- Basic lead phosphonate PVC stabiliser, amino methylene phosphonic acid, and hydroxyethane diphosphonic acid are all products of this process.
- Also used as a powerful reducing agent.
- Used in the manufacture of phosphorous acid raw materials, synthetic fibres, and organophosphorus insecticides, among other things.
- Amino trimethylene phosphonic acid is a water treatment agent that is highly efficient.
FAQs
What makes phosphorous acid more potent than phosphoric acid?
Because hydrogen does not attract electrons as strongly as oxygen, a portion of the molecule is more positive, resulting in a higher dipole moment in phosphoric acid. Phosphorous acid has a greater acidity constant, which corresponds to a lower pKa value, and is hence more acidic than phosphoric acid.
What are the negative consequences of phosphoric acid?
Lips, tongue, throat, and stomach will become red and swollen. Nausea, vomiting, stomach pains, and diarrhoea are all possible symptoms. It is possible that irreparable harm will happen. Long-Run (Chronic) Exposure effects: After skin contact, low concentrations might produce dry, rough, cracking skin (dermatitis).
What type of acid is H3PO3?
H3PO3 is often referred to as orthophosphorous acid or phosphorous acid. It is a kind of phosphorus oxygenic acid.







