Table of Contents
Introduction
A chemical link known as a polar bond is a form of a chemical bond. It is the boundary between the development of a pure chemical bond and the formation of an electrovalent bond. A polar chemical bond, on the other hand, is a link that exists between two atoms and is made up of electrons that are irregularly distributed.
A brief outline
The many forms of covalent bonds are mostly determined by electronegativity. An atom’s tendency to attract a shared pair of electrons to itself is known as electronegativity. It doesn’t have any units. A polar chemical bond is defined as a chemical bond formed by two atoms in a molecule with an electronegative difference.
Important concepts
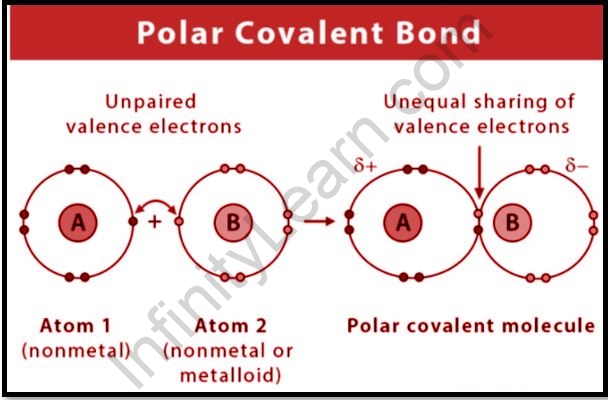
Polar covalent bonds arise when two nonmetal atoms with differing electronegativities come together. Consider A and B, who share a chemical bond and have an electronegativity difference that is not equal to zero. The electrons that establish a connection between A and B migrate towards the electronegative B.
Then B receives a partial charge and achieves ‘A.’ As in H – Cl, A becomes partially charged, with two charges. The shared pair of electrons in this molecule moves towards a chlorine atom with a strong electronegative charge. The H-atom gains a partial positive charge, whereas the Cl atom gains a partial negative charge, resulting in the formation of a dipole.
The following sections go through some of the properties of covalent bonding.
- Covalent bonds are extremely strong chemical connections between atoms.
- Covalent bonds do not generate additional electrons. Only electrons are paired in the bond.
- Covalent bonds are extremely rare to break spontaneously after formation.
- Covalent bonds are directional, meaning that the atoms that are bonded have definite orientations in relation to one another.
Significance of polar covalent bond in IIT JEE exam
Because the weighting for chemical bonding and molecular structure in the chapter is usually consistent between years, we may estimate that the weighting for Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure is about 6-7 per cent. As a result, the total number of questions from this chapter is estimated to be around 2.
Also Check: Non Polar Covalent Bond
FAQs
Question 1: What is the difference in electronegativity between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds?
Answer 1: A polar covalent bond is one where the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 0.4 and 1.7. A polar covalent bond is one in which the atoms have uneven electron attraction and hence do not share electrons equally.
Question 2: What is a polar covalent bond and how is it explained?
Answer 2: A polar covalent bond is a chemical relationship in which two atoms exchange one pair of electrons unevenly. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) molecules, for example.
Question 3: What distinguishes polar covalent bonds from other types of bonding?
Answer 3: The bonding electrons are shared unevenly between the two atoms in a polar covalent bond (b), and the electron distribution is asymmetrical, with the electron density being greater near the more electronegative atom.









