Table of Contents
Boric acid has the chemical formula H3BO3 and is a monobasic Lewis acid.
It is an acid with four oxygen atoms, one phosphorus atom, and three hydrogen atoms. Boric acid also goes by the names hydrogen borate, boracic acid, and orthoboric acid. It is a weak acid that is antiviral, antifungal, and antiseptic.
Boric acid is water-soluble and does not have a distinct odour. Under normal circumstances, this chemical occurs as a colourless crystal or as a white powdered substance. Boric acid may be made by combining borax with hydrochloric acid. Wilhelm Homberg was the first one to create boric acid from borax.
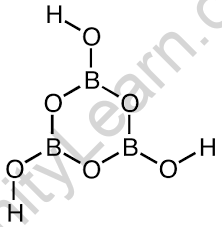
Boric Acid Crystal Structure
Because of the three oxygen atoms surrounding the boron, it possesses trigonal planar geometry. The length of this bond is 136pm for B-O and 97pm for O-H.
Boric Acid Preparation
- Boric acid is produced by reacting borax with mineral acid (or hydrochloric acid).
Na2B4O7.10H2O + 2HCl →4B(OH)3 + 2NaCl + 5H2O
- By Hydrolysis of Diborane – Boric acid is generated as a byproduct of diborane hydrolysis. The reply is detailed below.
B2H6 + 6H2O → 2B(OH)3 + 6H2
- By Trihalide Hydrolysis – Boric acid is produced as a byproduct of the hydrolysis of boron trihalides. The reply is detailed below.
BX3 + 3H2O → B(OH)3 + 3HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
Boric Acid Properties
Boric acid’s physical properties are as follows:
- At room temperature, it is a colourless or white crystalline solid.
- It has a molecular mass of 61.83 g/mol.
- It has a melting point of 170.9°C.
- It has a boiling point of 300°C.
- It dissolves in water.
The following are the chemical properties of boric acid:
- Boric acid, when heated, produces metaboric acid. The reaction at 170°C is shown below.
H3BO3 → HBO2 + H2O
- At 300°C, it produces tetraboric acid. The reaction is shown below.
4HBO2 → H2B4O7 + H2O
- It produces boron trioxide when heated over 330°C. The reaction is shown below.
H2B4O7→ 2B2O3 + H2O
- Boric acid interacts with alcohol to form borate esters. The reaction is shown below.
B(OH)3 + 3ROH → B(OR)3 + 3H2O
- It also dissolves in anhydrous sulfuric acid. The reaction is shown below.
B(OH)3 + 6H2SO4→ B(HSO4)4– + 2HSO4– + 3H3O+
FAQs
Is boric acid synonymous with borax?
In truth, borax and boric acid are the same thing and are commonly used to make homemade laundry soap. Boron is present in all of these materials. Borax is often extracted and purified from tourmaline, kernite, and colemanite. Boric acid is used to extract the mineral sassolite.
Is acetone soluble in boric acid?
Boric acid is a lethal toxin. It is soluble in acetone, water, glycerol, ether, alcohol, methanol, and liquid ammonia, as well as moderately soluble in acetone. Boric acid can be made from borax or by hydrolyzing boron halides or hydrides. Boron oxide crystals are somewhat soluble in cold water and completely soluble in hot water.
What is the purpose of boric acid?
Boric acid is also employed as an antiseptic, pesticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, and precursor in many chemical compounds.







