Table of Contents
Introduction
A mirror is something that reflects light and creates either a real or a virtual picture. When an object is located in front of a mirror, the mirror reflects the image of the same object. The incident rays are emitted by the object, and the image is generated by the reflected rays. The visuals are characterized as either genuine or virtual based on how light interacts with them. A true image is created when light rays truly connect, but virtual images are created when light rays appear to diverge from a point.
A brief outline
Ray diagrams assist us in tracing the path of light for someone seeing a point on an image of an item. The incident and reflected rays are represented by lines with arrows in a ray diagram. It also aids us in determining the direction of travel of light.
Spherical Mirrors vs. Plane Mirrors
For various purposes, mirrors are shaped in various ways. The following are two of the most common types of mirrors:
- Plane Mirrors
- Spherical Mirrors
A plane mirror is a reflective surface that is flat and smooth. A plane mirror always creates an upright virtual image that is the same shape and size as the thing it is reflecting. A spherical mirror is one with a constant radius of curvature and a consistent curve. A spherical mirror can produce either real or virtual pictures. There are two types of spherical mirrors:
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
Concave Mirror Characteristics
- When light strikes and reflects back from the concave mirror’s reflecting surface, it converges at a point. As a result, it’s also called a converging mirror.
- A magnified and simulated picture is generated when the concave mirror is put very close to the item.
- When the distance between the item and the mirror is increased, however, the size of the image decreases, and a true image is generated.
- The concave mirror can produce a little or huge picture, which can be real or virtual.
Important concepts
Before beginning the experiment, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with a few terms related to concave mirrors:
- Curvature’s centre: The centre of curvature, C, of a curved mirror can be defined as the centre of a hollow glass sphere, of which it is a component.
- The radius of curvature is defined as: The radius of curvature, R, of a curved mirror, can be described as the radius of the hollowed glass sphere of a spherical mirror.
- The imaginary line going through the pole and the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror is known as the principal axis.
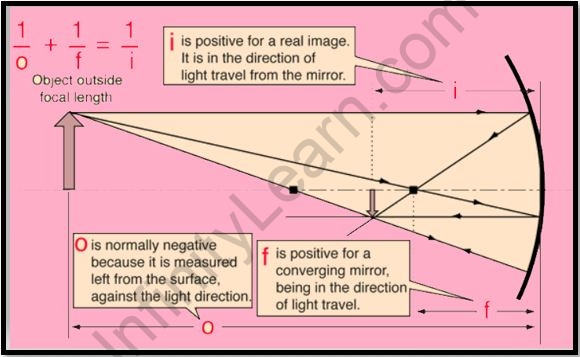
- For the spherical mirror, the principal focus is defined as the point where the reflected rays meet or appear to meet. The primary focus of a concave mirror is in the front, while the primary focus of a convex mirror is in the back.
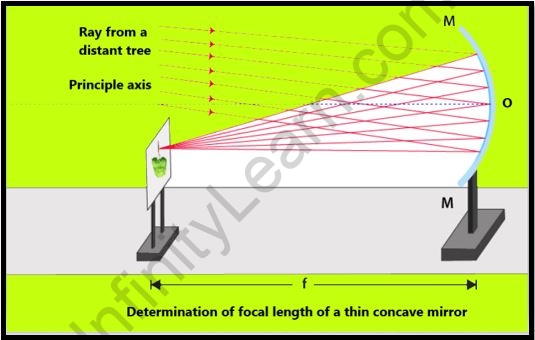
The experiment below shows how to calculate the focal length of a concave mirror
Aim: To determine the focal length of the mirror with a concave surface
Hypothesis:
- The central length of the concave mirror can be acquired in the accompanying ways:
- A concave mirror is a circular mirror with an internally bent reflecting surface that observes the laws of light reflection.
- Light beams from a distant article can be considered corresponding to each other.
- The equal beams of light meet the point before the mirror on the off chance that the image produced is real, altered, and tiny in size.
- The image made by the curved focal point is genuine and might be seen on a screen.
- The contrast between the essential pivot P and the center F of the curved mirror is indicated by the letter f.
Procedure
- The distance between the distinct objects chosen should be greater than 50 feet.
- The concave mirror is put on the mirror stand, and the distant object and the concave mirror should face each other.
- The mirror’s reflecting surface should be positioned in front of the screen. The screen should be adjusted to achieve a clean, sharp image.
- The distance between the concave mirror and the screen can be measured using a meter scale. The distance is equal to the focal length of the concave mirror in question.
- To calculate the average focal length, repeat the method three times.
Calculation
The average focal length of a concave mirror is as follows:
f1 + f2 + f3 cm/3 = 10cm
Result
The concave mirror’s focal length is 10 cm.
 Significance of focal length of the concave mirror in IIT JEE exam
Significance of focal length of the concave mirror in IIT JEE exam
The chapter on optics is essential for the IIT JEE exam, as well as future reference and competitive test preparation. You could not afford to neglect a few essential points in this Chapter. Light reflection, convex and concave mirrors, and other topics are covered in this chapter. This chapter’s exam questions include numerical and definitional difficulties. Ray Optics has been asked roughly 5% of the total questions in the past eight years’ question papers, as per the chapter-by-chapter weighting allocation for the IIT JEE test.
FAQ’s
Q. For a mirror, what is the law of reflection?
Ans:
- The law of reflection for a mirror is as follows:
- The incident reflected, and normal rays are all in the same plane.
- The incidence angle and reflection angle are the same
What exactly are concave mirrors, and how do they operate?
A concave mirror's intelligent surface is twisted internally and away from the light source. Internally, curved mirrors reflect light to a single center point. In contrast to elevated mirrors, a sunken mirror's image changes depending on the distance between the thing and the mirror.
Can you identify the difference between concave and convex mirrors without touching them?
When an object is placed in front of a concave mirror, it generates an enlarged image when it is kept close to the mirror, and an inverted image when it is kept farther away. A convex mirror reflects the object in a small, erect image all of the time.