Table of Contents
Introduction
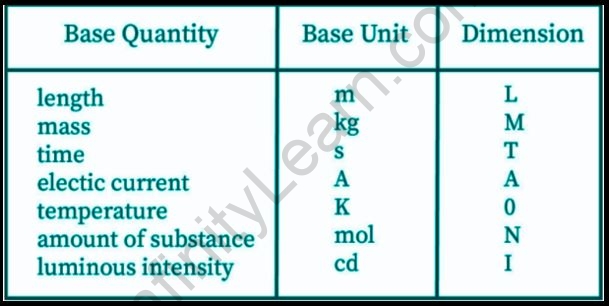
Fundamental quantities are those physical quantities that can be expressed without the use of any other physical quantity. To put it another way, these problems can’t be solved using any other physical quantity. As a result, fundamental quantities are sometimes referred to as basic physical quantities.
| S.NO | CONTENT |
| 1. | INTRODUCTION |
| 2. | BRIEF OUTLINE |
| 3. | IMPORTANT CONCEPTS |
| 4. | IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER |
| 5. | SIGNIFICANCE OF UNITS AND DIMENSIONS |
| 6. | FAQ’S |
A brief outline
Important concepts
Quantities, both fundamental and derived
Fundamental quantities are quantities that are not dependent on other quantities. Essential units are the units that are used to quantify these fundamental quantities. C.G.S., M.K.S., F.P.S., and SI are the four systems of measure.
The derived quantities are those that are derived from the basic quantities. Derived units are the units that are used to evaluate these derived quantities.
Important Points to Consider
- The wavelength of light is measured in angstroms, which is a unit of length. 1 m equals 10-10
- The Fermi unit of length is used to calculate nuclear distances. 1 Fermi is equal to 10-15
- The unit of length used to measure astronomical distances is the light year.
- 4605 * 1015 m is the distance travelled by light in a year.
- 5 * 1011 m is the astronomical unit for the distance between the sun and the earth.
- 084* 1016 m/parsec = 3.26 light-years
- A barn is a measurement unit for the dispersing cross-section of collisions. 10–28 m2 = 1 barn
- A chronometer and a metronome are time-keeping devices. Time is a quantity that has the same unit in all systems of measurement.
Significance of units and dimensions in the IIT JEE exam
Every aspect of a subject’s chapter should be approached holistically. Not only will it fully prepare you again for the exam, but it will also clarify your comprehension of each topic. It will assist you in passing the JEE exam’s conceptual questions. There would be one or two questions from chapter unit and dimensions, with a weightage of about four marks.
FAQs
“What are Dimensions, exactly?
The powers to which basic units are elevated to obtain one unit of a numeric value are called the dimensions of such a quantity.”
What are Dimensional Constants and How Do They Work?
answer-1= Dimensional constants are physical quantities that have dimensions and to have a fixed value. Examples have included gravitational constant (G), Planck’s constant (h), Universal gas constant (R), and the speed of light in a vacuum (C).
What are dimensional variables, and how do you use them?
Physical quantities with dimensions but still no set value are considered as dimensional variables. For example, velocity, acceleration, force, work, power, and so on.









