Table of Contents
Chemicals in Food Preservatives: Phytochemical preservatives are substances or chemicals used to help corrupt products like packaged foods, bottled drinks, maquillages/varnishes, biological samples from living organisms, beauty, and other different types of products.
Preservation is done in two modes, chemical and physical, individually. Chemical protection deals with adding chemical composites to the product. Physical conservation deals with processes like refrigeration or drying up of products.
Chemical Food Preservatives:
There are three groups of chemical preservatives usually used in foods
- Benzoates (like sodium benzoate),
- Nitrites (like sodium nitrite),
- Sulfites (sulphur dioxide).
How does food preservation work?
Food preservation is one of the manners to secure food from unwanted microbial growth. After the food is produced, we store and confirm it by covering the rice and curry with lids to keep covers and other insects down. By this, we’re watching it for any infection caused by them. It’s a short-term condition. Food preservation aims to maintain food for a more extended period.
Preservatives are chemical agents which serve to slacken, hamper or mask undesirable changes in food. A preservative refers to a substance added to food to delay, inhibit, or stop the growth, similar to bacteria, fungi, and fungi, and mask the signs of corruption. Still, it doesn’t include salt, sugar, energy, glycerol, alcohol, spices, essential canvases, etc.
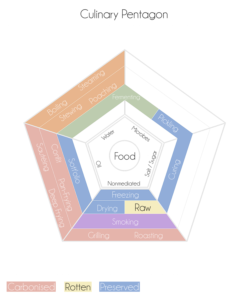
Food Preservation Definition:
- Food preservation is the system to help food corruption, food poisoning, and microbial impurity in food.
- According to the Prevention of Food Adulteration (PFA) Act (1954) and Food morals and Safety Act (FSSA) of 2006, a preservative means a substance that, when added to food, is equal to inhibiting, breaking, or arresting the process of unrest, acidification or other corruption of food.
Preservation of food by canning
The food contents are sealed in a previous holder at high temperatures. Meat, fish, and fruits are saved by canning. Canning includes cooking food, sealing it in sterile drums or pots, and boiling the holders as a system of sterilization to destroy or weaken any remaining bacteria. Foods with varying degrees of natural corruption protection may bear the final step in a pressure cooker.
No preservatives are added to High-acid fruits like strawberries, and only a short boiling period, while borderline fruits similar to tomatoes bear extended boiling and other acidic factors. Feeding stuff with low acidities requires canning pressure vegetables and flesh.
Food saved through canning or bottling is at immediate threat of corruption after opening the can or bottle.
Canning is a system of food preservation in which food is reused and sealed in a watertight vessel ( jars like Mason jars and sword and drum barrels). Canning provides a shelf life that generally ranges from one to five times, although it can be much longer. Under specific circumstances, Aa cold-driedformulaic product, similar to canned, dried lentils, could last as long as 30 times in a comestible state.
In 1974, samplers of ceased food from the wreck of the Bertrand, a steamboat that devolved in the Missouri River in 1865, were sampled by the National Food Processors Association.
Drying food for preservation
Drying is one of the most ancient methods of food preservation which reduces water exertion enough to help bacterial growth.
The original curing was dehydration or drying, used as early as BC. Smoking and salting perfect the drying process and add antimicrobial agents to save. Smother deposits several pyrolysis products onto the food, including syringol, guaiacol, and catechol. Salt accelerates the drying process using osmosis and inhibits the growth of several common strains of bacteria. Recently, nitrites have been used to cure meat, contributing to a characteristic pink colour.
Food drying is a food preservation system that is dried ( dehydrated or desiccated). Drying inhibits the growth of bacteria, motivations, and mould by removing water.
Home drying of vegetables, fruit, and meat can be carried out with electrical dehydrators ( ménage appliances), sun-drying, or wind. Preservatives similar to potassium metabisulfite, BHA, or BHT may be used but aren’t needed.
Salting Food Preservation
Salting is the preservation of food with dry eating salt. It’s related to pickling in general and, more specifically, to bringing, also known as raising ( preparing food with Neptune, salty water), and is one form of curing. It’s one of the oldest styles of maintaining nutrition. Two historically significant swab-cured foods are interspersed fish ( generally dried and wreathed cod or interspersed herring) and salt-cured meat ( like bacon). Vegetables similar to runner sap and cabbage are also frequently saved in this manner.
Salting is used because utmost bacteria, fungi, and other potentially pathogenic organisms can not survive in a primarily salty terrain due to the hypertonic nature of swabs. Any living cell in such terrain will become dehydrated through osmosis and die or be temporarily inactivated.
Salting is a food treatment to make it last longer. Salting is comparable to pickling. In pickling, food is treated with Neptune.
Conclusion
Preservatives and preservation methods help prevent foods from spoiling and snappily, allowing grocery manufacturers to distribute foods across the country and the globe without impacting food safety or quality. Microbes and oxidation are two significant factors affecting foods going bad snappily. Microbes that beget spoiling are undesirable bacteria, fungi, and provocations that grow in our food products. These microorganisms feed off the food’s nutrients and can generate serious detriment to humans if consumed. Without preservatives, bacteria like listeria and botulism can foray into our foods and, if ingested by humans, can beget us to come critically ill. Minor dangerous bacteria, fungi, and provocations will grow on foods making them indigestible. Food preservation has been around for centuries. It began in ancient times with swabs on flesh and fish. Humans started pickling vegetables and using sugar to save food for the future. While all those older methods are OK in moderation, today’s new chemical means of preservation are growing more abundant and harmful to our bodies. There are many benefits to food preservation, such as the ability to prevent deterioration and spoilage from yeast, botulism, and other means of food poisoning. Conservation also reduces food costs and extends shelf life.
FAQs
Describe the purpose of food preservation.
Food preservation involves preserving foods safely and nutritionally for an extended period. Conservation involves refrigerating, freezing, canning, and drying food products.
What does the term food chemical mean?
Chemicals are necessary to structure blocks for everything in the world. All living matter, including people, creatures, and works, consists of chemicals. All food is formed up of chemical substances.
Question: Which are the five most effective methods of preserving food?
Answer: Food preservation methods fall into five categories:
- Canning
- Freezing.
- Drying.
- Fermenting.
- Pickling.









