Table of Contents
Chemists play an important role in everyday life. Chemical substances are used to meet the most basic needs, such as shelter, food, clothing, and medicines. Pharmaceutical chemistry is concerned with organic, analytical, physical, inorganic, and biological aspects. Chemistry affects every aspect of our lives, both directly and indirectly. From the air we breathe to the food we eat, the homes we live in, and the emotions we all feel, chemistry plays an important role in our daily lives. Pharmacists create the medications that people take when they are ill. Chemical principles underpin natural phenomena such as digestion, leaf browning, and ice floating on water. Cleaning agents, also known as hard-surface cleaners, are substances (typically liquids, powders, sprays, or granules) used to remove dirt from surfaces, such as dust, stains, bad odours, and clutter. Cleaning agents are used for a variety of purposes, including health, beauty, odour removal, and preventing the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can both kill bacteria (e.g., door handle bacteria) and clean (e.g., bacteria on worktops and other metallic surfaces). Others, known as degreasers, contain organic solvents that aid in the dissolution of oils and fats.
Soap and detergent are chemicals that, when dissolved in water, can remove dirt from surfaces such as human skin, textiles, and other solids. If detached oil droplets and dirt particles did not become stable and evenly dispersed in the detergent solution, they would flocculate or coalesce into aggregates large enough to be redeposited on the cleansed surface. Small oil droplets or fine, deflocculated dirt particles are more easily carried through interstices in fabrics and similar materials than relatively large ones. The detergent’s action in keeping the dirt in a highly dispersed state is thus critical in preventing the fabric from retaining detached dirt.
Overview
Soap and detergents are examples of cleaning agents. In everyday life, detergents and soaps are frequently used to remove dirt from clothing. Chemicals are used in the production of soap and detergent. The term “detergent” is derived from the Latin word “detergere,” which means “to scrub or clean.” Synthetic detergent, on the other hand, is now referred to as detergent. Agents of cleaning Soaps and synthetic detergents improve water’s cleansing properties. These aid in the removal of fats that cling to the fabric or skin. They are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids, such as stearic, oleic, and palmitic acids, and are used in cleaning. Only sodium and potassium soaps are water soluble and used for cleaning.
Potassium soaps are generally gentler on the skin than sodium soaps. These can be made by substituting potassium hydroxide solution for sodium hydroxide. Only sodium and potassium soaps are water-soluble and used for cleaning. Potassium soaps are generally gentler on the skin than sodium soaps. These can be made by substituting potassium hydroxide solution for sodium hydroxide. Soaps with sodium salts are made by heating fat (a glyceryl ester of fatty acid) with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. Saponification is the name given to this reaction. Esters of fatty acids are hydrolyzed in this reaction, and the resulting soap is colloidal. Sodium chloride is used to precipitate it from the solution. After removing the soap, the solution contains glycerol, which can be recovered through fractional distillation.
Synthetic detergents are another type of cleaning agent. These are exactly like soaps in that they have all of the properties of soap. They do not, however, contain any soap, and their chemical structure is completely different from that of soaps. One of the most significant advantages of detergents over soaps is that they can be used in any situation. They can work in both soft and hard water. In hard water, they do not form scum. Some detergents can even be used in ice-cold water. Detergents, like soaps, are long chains of molecules. Hydrocarbons, which are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms, are one type of molecule. These hydrocarbons are derived from fats, oils, and fatty acids, among other things.
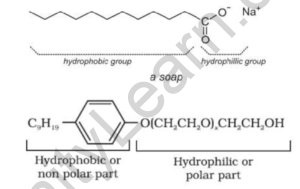
Cleansing agents soaps and detergents
Cleansing agents are substances that we use to remove stains, dust, foul odours, dirt, and other contaminants from surfaces. These are the chemicals we use to reduce surface tension on planes so that water can do its job properly. Cleaning with only water is ineffective because the surface tension is too high for cohesive forces to be effective.
Soaps are a common type of detergent. They are the most widely used type of cleaning agent. Soaps are typically created by reacting a liquid alkali (such as sodium hydroxide) with naturally occurring fats or fatty acids derived from animals and plants. Saponification is the name given to this process. Soaps have a molecular structure that is made up of long chains of molecules. The hydrophobic end (the tail) of the hydrocarbon chain is at one end. These molecules repel water and cling to the oils and grease. Then there’s the water-loving, or hydrophilic, chain, which is made up of anionic molecules at the top of the chain. Surfactants are surface-active agents found in soaps. They essentially lower the surface tension of the water. Surfactants attach to the water molecules on one end, allowing the water to better wet the surface. Surfactants, on the other hand, adhere to oils and dirt. Overall, they allow the water to clean the surface more effectively.
Detergents are amphipathic molecules with charged hydrophilic or polar groups at the end of long lipophilic hydrocarbon groups. The charged hydrophilic group is referred to as the head, and the long lipophilic hydrocarbon group is referred to as the tail. Detergents are also known as surfactants because they have the ability to reduce water’s surface tension. Synthetic detergents are products that are formulated with sodium salts of alkyl hydrogen sulphates or sodium salts of long chain alkyl benzene sulphonic acids. Detergents are classified into three types.
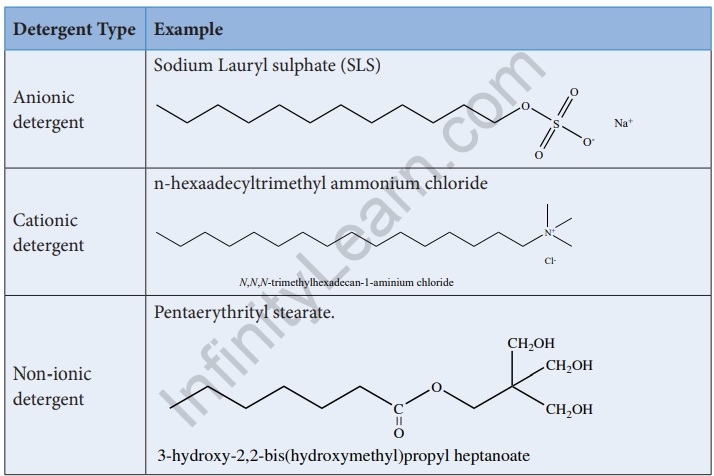
Detergents outperform soaps because they can be used in hard water and acidic environments. Laundry detergents have a similar cleansing action to soap.
Natural cleansing agents
One of the project’s goals is to raise awareness about environmental issues like air pollution in schools and homes. We decided to take action and improve the indoor environmental quality because it is important to be proactive. That is why the school Eco group has created some cleaning agents and is holding workshops for other students. Aside from the health benefits (cleaner air and less exposure to potentially toxic chemicals), non-toxic cleaning agents can help us protect the environment while also saving money.
Baking soda can be used for a number of different things. To clean the floors (with a scrubbing brush and a little water), and to clean the oven (combine 100g of baking soda with 40g of salt and 40g of water and leave in the oven overnight). Baking soda is also excellent for cleaning your HOB; simply apply it with a damp sponge. Baking soda can also be used to clean your bathtub and sinks. To remove tough stains, combine with a little vinegar and apply directly to the stain, wiping away grime with a damp cloth.
To clean your fridge, combine vinegar and water (it does not work as well on stainless steel). Vinegar is also great for cleaning glass, so use it to clean your windows. These natural ingredients make an excellent toilet cleaner when combined! Pour 40g of baking soda and 120g of vinegar into the bowl, let it settle, and scrub with a brush.
FAQs
What is the soap's cleansing agent?
Soaps are a common type of detergent. They are the most widely used type of cleaning agent. Soaps are typically created by reacting a liquid alkali (such as sodium hydroxide) with naturally occurring fats or fatty acids derived from animals and plants. Saponification is the name given to this process.
What is the most effective cleaning agent?
Acid cleaners are the most potent cleaning agents and should be used with caution. Acid cleaners can be extremely poisonous and corrosive if not properly diluted.







