Table of Contents
Elementary Idea of Antioxidants:
What is an Elementary idea of Antioxidants? How do they work and what are its benefits? An Elementary Idea of Antioxidants is a chemical compound that is added to certain foods, natural and synthetic rubbers, gasoline, and other substances to slow the process by which these substances combine with oxygen in the air at room temperature.
- Reducing autoxidation postpones the appearance of undesirable qualities such as rancidity in foods, loss of elasticity in rubbers, and gum formation in gasoline. Organic compounds such as aromatic amines, phenols, and aminophenols are the most commonly used antioxidants.
- Autoxidation has been discovered to be a chain reaction, that is, a reaction that consists of a series of successive steps that occur in repetitive cycles, each of which regenerates intermediate products known as chain carriers. As long as the chain carriers exist, such a reaction will occur.
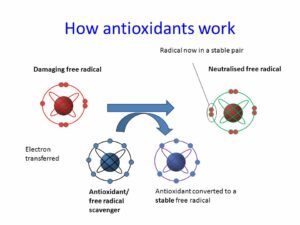
- The chain carriers in autoxidation are free radicals, which are electrically neutral molecular fragments containing unpaired electrons. Thermally excited molecules, free radicals, metal catalysts, or light can all start the chain.
- Antioxidants stop the oxidative chain reaction by reacting with chain carriers. The rancidity of fats, oils, and fatty foods is an example of autoxidation that is of great commercial concern.
- Rancidity is caused by the breakdown of the fat molecule in the presence of oxygen, resulting in a mixture of volatile aldehydes, ketones, and acids. Exposure to light or the presence of trace amounts of metals that act as catalysts can start the reaction.
- Organic antioxidants, such as tocopherol, propyl gallate, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), or butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are commonly used to delay the development of rancidity. By donating hydrogen atoms, these compounds react with chain carriers.
- In most countries, the use of antioxidants in food is strictly regulated. Specific restrictions are typically imposed on the type and quantity of antioxidants that may be used.
Overview on Elementary Idea of Antioxidants
- Antioxidants are compounds that prevent oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals and chain reactions that harm the cells of organisms. Antioxidants such as thiols and ascorbic acid may inhibit these reactions (vitamin C).
- To balance oxidative stress, plants and animals maintain complex systems of overlapping antioxidants such as glutathione.
- Vitamins A, C, and E are the only dietary antioxidants. Industrial chemicals added during manufacturing to prevent oxidation in synthetic rubber, plastics, and fuels, or as preservatives in food and cosmetics, are also referred to as antioxidants.
- Antioxidants are substances that, when present in food, delay, control, or inhibit oxidation and food quality deterioration. Antioxidants are substances that prevent oxidation. An antioxidant is a substance that, when present in low concentrations relative to oxidizable substrates, significantly delays or inhibits oxidation of that substrate. Antioxidants have been utilised in food accidentally since antiquity, especially by civilizations living in hot climes like India.
- Herbal antioxidants protect against oxidation and free radical damage. The term “antioxidant” comes from the Greek anti, which means “against,” and the English oxidant, which means “a substance that can cause oxidation or is oxidising in action.”
- Antioxidants are substances that neutralise free radicals, which are implicated in cancer, heart disease, and a variety of other diseases. Free radicals are highly reactive chemicals that have the ability to destroy cells. When a molecule or an atom loses or gains an electron, they form. The body produces free radicals in response to radiation or environmental stresses.
- Antioxidants are commonly found in two forms: artificial and natural. Some plant-based foods are thought to be rich in antioxidants, and plant-based antioxidants are thought to be a type of phytonutrient.
- The human body also produces a few antioxidants, which are known as endogenous antioxidants, whereas antioxidants that come from outside the human body are known as exogenous antioxidants.

Antioxidants benefits
- These are found in many fruits and prevent other molecules in our bodies from oxidising.
- Antioxidants are extremely beneficial to human health. Antioxidants prevent the cascade of reactions triggered by free radicals in our bodies, which can cause illness and many chronic diseases if they are left unchecked.
- Antioxidants benefit different sections of the body in different ways.
- For example, beta-carotene is good for our eyes, lycopene is good for prostate health, and proanthocyanidins are good for the urinary tract.
- Antioxidant consumption should promote the proper functioning of our bodies in today’s polluted world because our bodies cannot create the number of antioxidants required. Minerals, vitamins, and enzymes should all be included in our regular diet.
- They may be useful in the prevention of cancer. According to some research, antioxidants may be able to prevent some of the damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to cancer. However, more research is needed to determine whether antioxidants found in foods can help reduce people’s risk of cancer.
Use of antioxidants
- Antioxidants are widely used in dietary supplements and are critical for the prevention of many diseases, including cardiac disorders and cancer. Other applications for antioxidants include reaction control in industry, food preservatives, and cosmetics.
- Antioxidants are used as food additives to help prevent food spoilage. Because oxygen and sunlight are the two main causes of food oxidation, food is preserved by keeping it in the dark, sealing it in containers, or even coating it in wax, as with cucumbers. However, because oxygen is required for plant respiration, storing plant materials in anaerobic conditions results in unpleasant flavours and unappealing colours.
- Antioxidants are used as food additives to help protect against food poisoning. Antioxidant polymer stabilisers are commonly used to prevent the degradation of polymers such as rubbers, plastics, and adhesives, which results in a loss of strength and flexibility.
- Natural rubber and polybutadiene, for example, are particularly prone to oxidation and ozonolysis due to the presence of double bonds in their main chains. Antiozonants can keep them safe. As the material degrades and the chains break, solid polymer products begin to crack on exposed surfaces.
Antioxidant fruit
- Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts all contain a complex mix of antioxidants, so eating a variety of these nutritious foods will help ensure that you are getting enough of these disease-fighting nutrients. Here are some ideas for incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your diet:
- Every meal should include at least one fruit or vegetable.
- Choose fruits and vegetables that are rich in colours such as blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, and green because they contain the most nutrients and antioxidants
- Smoothies are an excellent way to reap the antioxidant benefits. Combine dark-coloured berries like blueberries or blackberries with citrus fruits, pineapples, apples, or pears.
- Grain products contain antioxidants as well. Oats, in particular, are an excellent source of antioxidants to include in your daily diet. Oatmeal and oat bran are both nutritious foods.
- Consume your legumes. Antioxidants are abundant in red beans, kidney beans, black beans, and pinto beans.
- Cooking with herbs and spices such as dried oregano, turmeric, cinnamon, cloves, and ginger provides high levels of antioxidants.
Also Read: Elementary Idea of Primary Structure
FAQs:
How do antioxidants function
Antioxidants are molecules found in your body that combat free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that can harm the body if there are too many of them. Antioxidants are molecules that neutralise free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can harm cells
Do antioxidants help your body detox
Antioxidants and their benefits Your body has a natural way of detoxifying, or removing the contaminants it is exposed to on a daily basis. Antioxidants act as cleaning and protective agents within the body, combating free radicals that cause illness and disease.
Which fruit contains the most antioxidants
Most fruits are high in antioxidants, vitamin content, and have a variety of health benefits. Cranberries, red grapes, peaches, raisins, strawberries, red currants, figs, cherries, pears, guava, oranges, apricots, mango, red grapes, cantaloupe, watermelon, papaya, and tomatoes are some examples.






