Table of Contents
Proteins are larger polypeptides or polypeptides that contain more than one polypeptide. That is, proteins seem to be linear polymers formed by the amide bond, also known as the peptide bond, which connects the alpha carboxyl group of one amino acid to the alpha-amino group of another amino acid—the joining of two amino acids to form the dipeptide results in the loss of one water molecule.
The equilibrium of this reaction is determined by the hydrolysis side but not by the synthesis side. As a result, free energy input is required for the biosynthesis of peptide bonds. Kinetically, these peptide bonds are quite stable, and in the absence of a catalyst, the lifetime of the peptide bond in an aqueous solution approaches 1000 years.
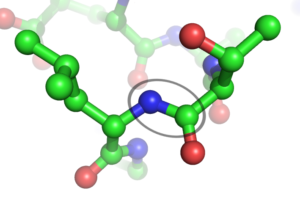
A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed by the joining of two amino acids. Peptide bonds are used by many living things to create long-chain amino acids or proteins. The proteins are required for the formation and operation of all living cells and viruses. Protein accounts for nearly half of a cell’s dry weight. It is a high-molecular-weight organic molecule made up of a biopolymer of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
Overview:
A peptide bond is created among two molecules when a reaction occurs between the carboxyl group of one molecule and the amino group of another molecule, and a water molecule is released as a result of this reaction.
This reaction usually occurs between amino acids and is a dehydration synthesis reaction. Polypeptides are formed by the chaining of amino acids, and proteins are formed by the combining of polypeptide molecules.
The polypeptide’s N terminal contains a free amino group. On the other end, there is a free carboxyl group known as the C-terminal group. The codons direct the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides.
Peptide bond
Proteins are essential for the structure and function of all living cells and viruses. Protein makes up roughly half of the dry weight of cells. It is a high molecular weight organic substance that is a biopolymer of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
A peptide bond is a type of chemical bond formed between two molecules when one’s carboxyl group reacts with the amino group of the other, releasing a molecule of water (H2O). This is treated as a dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction) that occurs most commonly between amino acids.
The arising CO-NH bond is known as a peptide bond, and the molecule is known as an amide. The four-atom functional group -C(=O)NH- is known as an amide group or a peptide group (in the context of proteins). Polypeptides and proteins, like PNA, are chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
Peptide bond formation
At the molecular level, dehydration synthesis or reaction, also known as condensation reactions, creates peptide bonds. The presence of amino acids is a distinguishing feature of the process. After removing oxygen and two hydrogen molecules, two amino acids are more likely to connect.
They add the carboxyl group to the process while depleting the hydroxyl group. Proteins with amino groups derived from different amino acids have a lower hydrogen content. Following that, the substitution of nitrogen for the hydroxyl group results in the formation of a peptide bond. As a result, peptide bonds are amide connections that have been substituted.
After the reaction, the amino acids used in the peptide bond formation process are referred to as residues because they lose many atoms and become covalently bound to one another as a result of the formation of a peptide bond.
The nitrogen-carbon link formed by the peptide bond is noticeably different from the nitrogen-carbon bonds formed by the various other molecule sections.
On the carboxyl bond side, nitrogen has a positive charge, whereas oxygen has a negative charge. Given the minor nature of the negative and positive charges, this interaction results in nitrogen and carbon sharing more electrons than they do. The entire operation results in the formation of an electric dipole.
The bond becomes a double bond with the addition of extra electrons, which is very rigid and cannot spin. A peptide group is a six-molecule unit that can be found in the form of a flat plane or a ball. Peptides can be found in all living things.
The carbons in the centre of amino acids can spin freely, in addition to having four equal bonds. When a peptide bond forms between several amino acids, a chain of unbending atom planes forms around it to provide structural support.
Carbon’s flexible bonds properly connect it. Because of this environment, peptide chains can bend and spin, resulting in highly sophisticated creations with the ability to catalyse chemical pathways. As a result, the resulting CO-NH bond is known as a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is known as an amide (CO-NH).
Peptide bond structure
The peptide bond is said to be a planar, transverse, and rigid structure. It also depicts a character with a partial double bond. The peptide bond’s coplanarity refers to the resonance or partial sharing of two pairs of electrons between the amide nitrogen and carbonyl oxygen.
The peptide bond’s atoms C, H, N, and O are in the same plane as the hydrogen atoms of the amide group and the oxygen atoms of the carboxyl group, which are trans to each other. The scientists who discovered that peptide bonds are rigid and planar are Linus Pauling and Robert Corey.
FAQs:
What is a peptide bond?
A covalent bond established by combining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another while removing a water molecule is known as a peptide bond, and it is also known as peptide linkage.
How do you identify a peptide bond?
A peptide bond is considered a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule interacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a water molecule.
Is a peptide bond polar?
Polar covalent bonds seem to be covalent bonds in which the atoms have unequal electron attraction, and thus, the sharing is unequal. Because it holds two amino acids together, the peptide bond is a nonpolar covalent bond.







