Table of Contents
Introduction:
Millions of species live on our planet, but did you know that they are divided into five separate kingdoms? Some, like animals and plants, are visible to the naked eye; but some, like bacteria, can only be seen under a microscope. Let’s dive deeper into the world of the five natural worlds and discover more about them.
Early in its history, scientists began to classify living things into different categories. Some biologists distinguish living things from plants and animals. Ernst Haeckel, Robert Whittaker, and Carl Woese are biologists working on a comprehensive classification system. Among these, Robert Whittaker’s Five Kingdom Classification was proposed and widely used. Whitaker suggested that living things should be broadly divided into empires, based on specific characteristics such as cell structure, nutrition, source of nutrition, relationships, body composition, and reproduction.
What is a Kingdom in Biology?
The system of biological realms is the way science distinguishes living things from their descendants during the evolutionary period. This means that all the species that make up these five major groups – some of the most recent theories divided into six or seven – have similar ancestors and therefore share some of their genes and are part of one family.
Along with the biological realms, there are other taxonomic categories within the same classification system, such as domain, phylum, class, order, family, genre, and species. They all follow the hierarchical order and depend on each other, so some categories include others. In this way, the domain includes the state, the state phylum, phylum class, and so on.
Classification of Living Things into Five Kingdoms:
The first man to divide the species into five superpowers was North American naturalist Robert Whittaker. The researcher proved in 1959 that fungi were not the plant organisms – previously thought to be – and ten years later proposed the formation of a fungal kingdom to separate them from plants.
ANIMAL KINGDOM:

The kingdom of Animalia is the most populous and divided into two major groups – vertebrates and invertebrates. These animals have many cells, heterotrophic eukaryotes with aerobic respiration, sexual reproduction, and the ability to move. This kingdom is one of a variety and includes mammals, fish, birds, reptiles, amphibians, insects, molluscs, and annelids, among others.
PLANT KINGDOM:

Trees, plants, and other plant species form part of the Plantae kingdom – one of the oldest and characterized by its immaturity, multicellular, and eukaryotic nature. These autotrophic compounds, whose cells contain cellulose and chlorophyll, are essential for life on earth as they release oxygen through photosynthesis. As for their reproductive system, this may be sexual or sexually explicit.
Also read: FIVE KINGDOM
FUNGI KINGDOM:
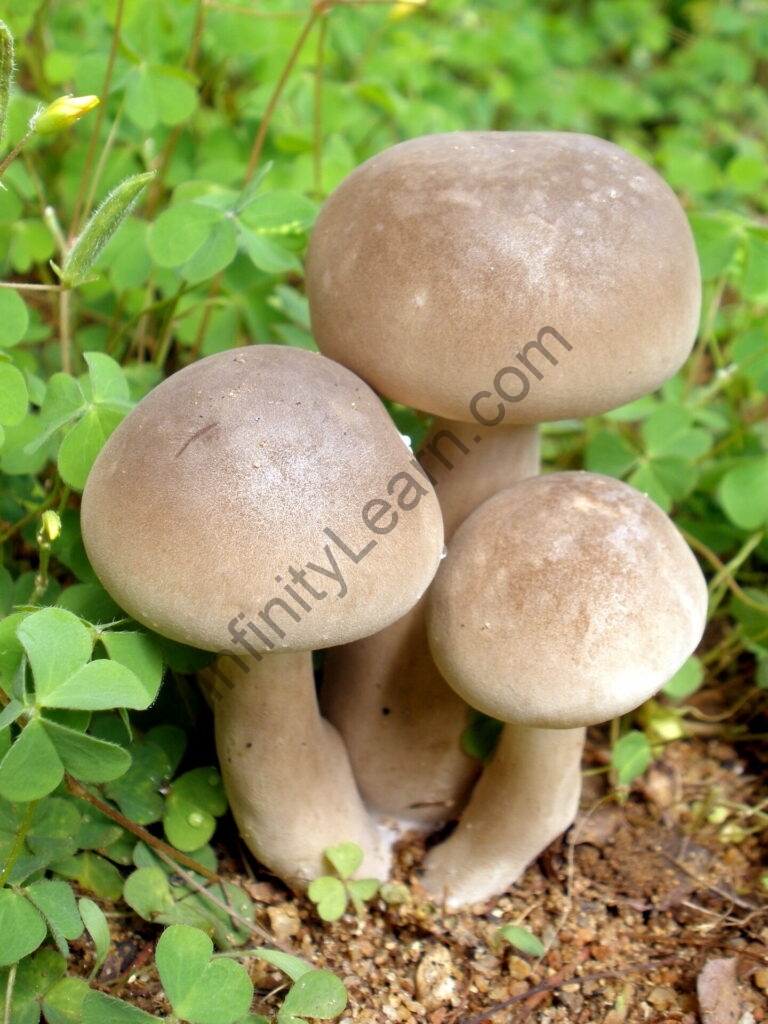

The term is used to describe a fungal state that includes yeast, mold, and all kinds of mushrooms and insects. These multicellular aerobic heterotrophic eukaryotes contain chitin on the walls of their cells, eat other organisms, and reproduce seeds.
PROTISTA KINGDOM:

Plasmodium is a protist spread by female Anopheles mosquitoes
This group is the oldest in the eukaryotic family and all the others are its descendants. The Protista state is paraphyletic – it contains one ant but not all of its progeny – and includes those eukaryotic insects that can be considered animals, plants or fungi such as protozoa. As it is very different it is difficult to divide it into categories, as its members have very little in common.
MONERA KINGDOM:
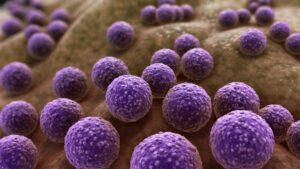
Staphylococcus Bacteria
It is the kingdom of microbiology and combines prokaryotes (archaea and bacteria). This group is present in all habitats and is composed of single-celled organisms that do not have a defined nucleus. Most bacteria are aerobic and heterotrophic, while archaea is usually anaerobic and its metabolism is chemosynthetic.
The fragmentation of the five natural empires is still widely accepted today, although recent advances in genetic research have prompted new revisions and re-opened the debate among experts. This was true of the sixth kingdom of Carl Woese and George Fox, which in 1977 divided the strains into two species (Archaea and Bacteria), and the seventh kingdom of Cavalier-Smith, which added a new group to the last six so-called algae.






