Table of Contents
Introduction
Our body is made up of 11 vital organs that control all the vital processes of our body. Without relying on others, these systems can come out of compliance. When one of them does not work well, the others will try to compensate for the loss. All other systems come together to achieve homeostasis i.e. a state of balance within the body.
The integumentary system, skeletal system, muscle system, lymphatic system, respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, excretory system, and reproductive systems are among the 11 organ systems.
The Human Excretory System is one of the systems whose function should be essential for a healthy and happy body.
This program manages to remove metabolic waste and other non-essential substances from the body. Excretory Organs work to maintain a controlled amount of fluid in our body by controlling the amount of water released, regulating electrolyte balance, and maintaining adequate blood pH levels. Nephrosis, bladder cancer, urethritis, urination (enuresis), urinary and kidney stones and diseases, kidney failure, incontinence, blood in the urine, and interstitial cystitis are diseases and diseases of the urinary system.
The excretory system is responsible for removing waste from the body. The system is composed of glomerular capillaries and specific structures that assist with the exit function. The kidneys and their functional unit, the proton, are part of the human excrement system. Special hormones control the amount of absorption inside the nephron, thereby regulating kidney function.
All living things produce waste and have a way of eliminating it. The creation and removal of waste is handled by a disposal system. The classification of the human excretory system has the following components:
- 2 Kidneys
- 2 Ureters
- 1 One is one
- 1 Urethra
All of these structures work together to help our body get rid of waste properly.
Human Excretory System
Definition: The human excrement system is a special set of organs that remove waste from the human body. Urea is a very common waste product produced by the human body. Other toxins are also produced as a result of this process. Kidneys excrete urea in the urine, while the intestines filter out solid waste from the body.
Organs of the Excretory System
The organs of the human excrement system work together to eliminate urea, toxic nitrogen, from our bodies. The main components of the human excrement system are: –
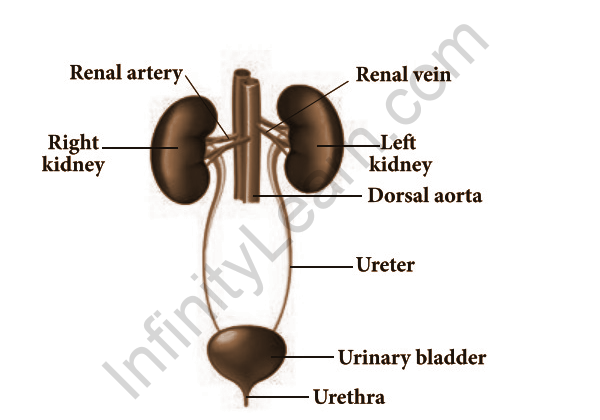
Kidneys
The human kidneys are the major organs in the human excrement system. They are bean-shaped organs that live on each side of the spine, near the abdomen and liver. The arteries carry blood to the kidneys, while the kidney vessels produce blood. Ureters transport waste from one kidney to another, where it is stored or disposed of.
Urine is a liquid that contains waste, salt, organic matter, and two important nitrogen compounds: uric acid and urea, which are produced by the kidneys. Uric acid is produced by the breakdown of nucleic acids, while urea is produced by the breakdown of amino acids in the liver. Both of these nitrogenous compounds are toxic to the human body and must be excreted in the urine.
The unit of kidney function is the nephron. Each kidney is made up of millions of nephrons. Together they work to filter the blood and remove impurities from it. It is made up of the following components:
- Bowman capsule– This is the first part of the nephron. Capillaries are found in this cup-shaped structure. Glomerular filtration occurs within this structure. Cells and enzymes are still present in the blood.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule– The proximal tubule is composed of a Bowman capsule stretching the floor. Water and other substances that are reused in the blood are re-injected into it.
- Henle’s Loop – The tube leads to the formation of a U-shaped loop known as the Henle’s Loop.
The descending leg, the U-shaped curve, and the ascending leg are three parts of Henle’s Loop. As more water is absorbed by the body, urine is concentrated in this area. Water can pass through a descending organ, but not into an ascending organ. - Distal Convoluted Tubule– Distal convoluted tubule is connected to the Loop of Henle. This is where kidney hormones work.
- Pipe Collection – Each nephron’s Distal Convoluted Tubule connects to collecting channels. The renal pelvis is made up of several kidney tubes. Urine flows into the renal pelvis, enters the ureter, and finally into the bladder.
Ureters
It is an important part of the division of the human excretory system. Each kidney has one ureter, outside the kidney pelvis. It is a muscular tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder and transmits urine.
Urine Bladder
It is another structure similar to a bag. Surrounded by smooth muscles. Urine is stored in this organ. Ureters transport urine to the bladder. The process of urinating in the body is called micturition. Bladder In men and women it is found in different levels of the body.
The urethra
The urethra is a tube that connects the bladder and urine. Its main role is to excrete urine. In addition, it is shorter for women and longer for men. It also works as a means of sperm for men. The entrance to the urethra is controlled by the sphincter.
Other Categories of Human Excretory Organs:
Other organs, in addition to those described above, are also involved in extraction. They are as follows:
Skin
The skin is the largest organ in the body. Its main role is to protect the body’s various internal organs. Sweat is released by the skin. The skin, in particular, removes substances such as sodium chloride and a small amount of urea.
Lungs
The main respiratory organs of the lungs. They help to absorb oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. However, they also release a certain amount of water by evaporation during the respiratory process.
Liver
This organ is responsible for producing waste within the body. It is the first line of defence when it comes to hormones, lipids, alcohol, and drugs. Many drugs go through this organ, known as first-pass metabolism. Too much fat and cholesterol are also eliminated by the liver. This is necessary to keep the body healthy.
FAQ’s
List all the organs of the human excretory system.
The organs of the human excrement system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Describe the Human Excretory System.
A human excrement system is a system within the body of an organism that performs the function of excrement, the waste disposal process.
What is the role of the liver in the human excretory system?
The liver releases toxins and breaks down most of the bloodstream, including toxins. The liver also releases bilirubin, a component of haemoglobin catabolism, which is secreted by the intestines through the large intestine.
Why is it important to get rid of excess water from the body?
It is important to get rid of excess water from the body because the right amount of fluid must be stored to achieve homeostasis throughout the body.









