Table of Contents
Importance of Polysaccharides: A polysaccharide is a kind of carbohydrate and it is a polymer composed of chains of monosaccharides linked together by glycosidic linkages. Glycans are another name for polysaccharides. A polysaccharide is described as having more than ten monosaccharide units, whereas an oligosaccharide has three to ten linked monosaccharides. Polysaccharides can be straight or branched. Linear polysaccharides, like cellulose in trees, can form rigid polymers. Branched forms, such as gum arabic, are frequently soluble in water. Polysaccharide-derived products are available for ion exchange, gel permeation or gel filtration, affinity and conventional chromatographies, gel media for microbial cultures, electrophoresis, and other applications.
Overview
Polysaccharides serve three primary functions including, structural support, energy storage, and the transmission of cellular communication signals. The function of a carbohydrate is largely determined by its structure. Linear molecules are strong and rigid, such as cellulose and chitin. Plants rely on cellulose as their primary support molecule, whereas fungi and insects rely on chitin. Polysaccharides that are being used for energy storage are typically branched and folded upon themselves. They are usually insoluble in water due to their high concentration of hydrogen bonds. The storage polysaccharides comprises starch in plants and glycogen in animals. Polysaccharides that are used in cellular communication are frequently covalently bonded to lipids or proteins, resulting in glycoconjugates. The carbohydrate acts as a tag, assisting the signal in reaching its intended destination. Glycoproteins, peptidoglycans, glycosides, and glycolipids are examples of glycoconjugates. Plasma proteins, for instance, are glycoproteins. Let us now understand the importance of polysaccharides below:
Importance of polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen)
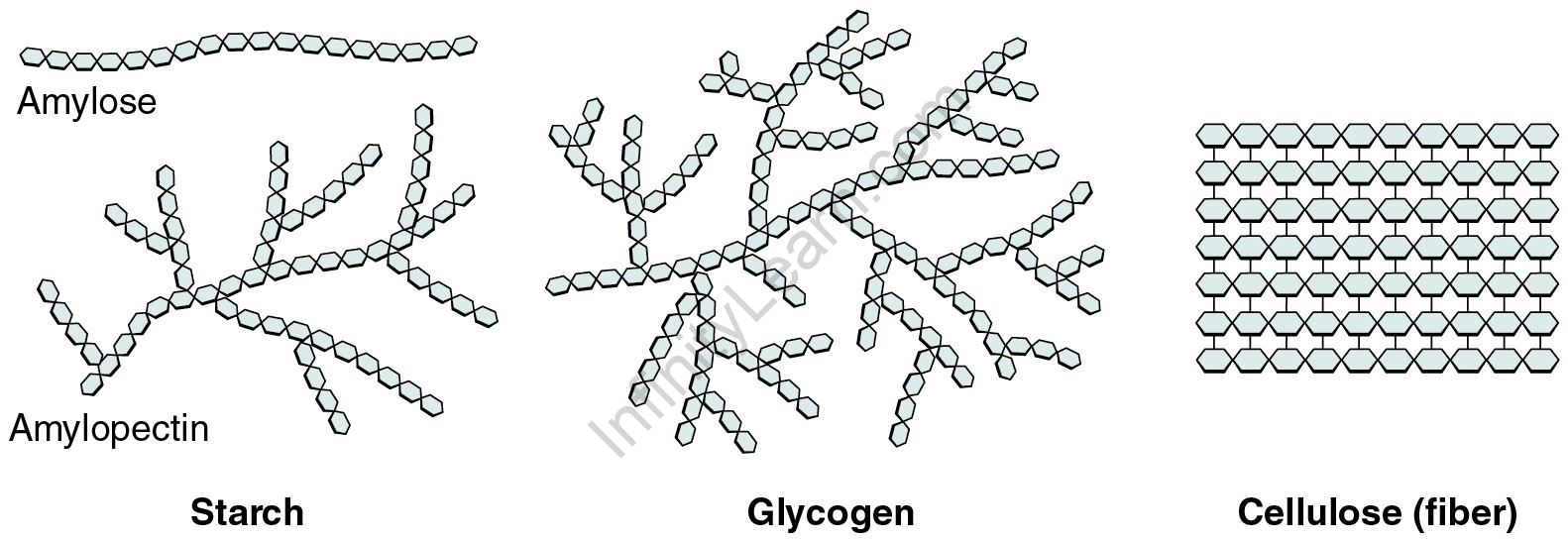
What is the importance of polysaccharides like starch, cellulose and glycogen? Starch is one among the significant important dietary sources for humans, as well as one of the primary plant storage polysaccharides. Cereals, roots, and some vegetables contain a high concentration of starch. It is a -glucose polymer that primarily consists of two components: amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is the most soluble in water and contains about 15-20% starch. Amylose is a long unbranched chain with α-D+ glucose units that range from 200 to 1000 in number and are linked by a C1-C4 glycosidic linkage. Amylopectin contains about 80-85 percent starch, but it is not soluble in water. This is a branched-chain polymer established by C1-C4 linkage followed by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.
Uses:
- Cake and biscuit fillings are examples of bakery products that require starch for elasticity.
- Starch is used in industry to increase mechanical strength, resistance to friction, and resistance to moisture penetration.
- Detergents contain starch.
- Dextrose confectionary energy
- Starch products are frequently used in the production of beer and alcoholic beverages.
- Starch products are required in the production of dry sausages, salamis, brine-cured hams, and other products.
Cellulose is one of most popular organic substances found in the plant kingdom and it is one of the most significant components of plant cells. These are polysaccharides that form a straight chain and are made up of only β-D-glucose units joined by a glycosidic linkage between the first carbon of the glucose unit and the fourth carbon of the next glucose unit.
Carbohydrates are stored in the body of an animal as Glycogen. It is also recognised as animal starch because its structure is similar to amylopectin and has many branches. It can be found in the liver, muscles, and the brain. When the body requires glucose, the enzymes convert glycogen into glucose. Glycogen can also be found in yeast and fungi.
Structural polysaccharides examples
Arabinoxylans seem to be copolymers of two sugars, arabinose and xylose, and are found in both primary and secondary cell walls of plants and they might be useful to human health.
In fact, plants’ structural components are primarily composed of cellulose. Wood is mostly cellulose and lignin, whereas paper and cotton are almost entirely cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer composed of repeated glucose units held together by beta-links. Because humans and many animals lack the enzyme required to break the beta-linkages, cellulose cannot be digested. Termites, for example, can digest cellulose because bacteria containing the enzyme are present in their gut. Water does not dissolve cellulose. When mixed with iodine, it does not change colour. It produces glucose when hydrolyzed. It is the most common carbohydrate found in nature.
Chitin is just one of many polymers found in nature. Many animals, such as exoskeletons, have it as a structural component. It biodegrades in the natural environment over time. Its decomposition may be catalysed by chitinases, which are secreted by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi and produced by some plants. A few of these microorganisms have receptors for simple sugars derived from chitin decomposition. If chitin is detected, enzymes are produced to digest it by cleaving glycosidic bonds and converting it to simple sugars and ammonia.
Pectins are indeed a complex polysaccharide family with 1,4-linked -d-galactosyl uronic acid residues. They can be found in most primary cell walls as well as nonwoody parts of terrestrial plants.
Use of polysaccharides
When we talk about the importance of polysaccharides, we cannot ignore the plenty of benefits they provide. They have multiple uses. Polysaccharides are being used as demulcents, in drug formulations, dental impression materials, dusting powders, hemostatics, and to treat mild intestinal disorders. They are used as plasma substitutes as well as anticoagulants in solution and as a surface treatment on artificial organs. Polysaccharides are converted into bioactive textiles, which are then used to create membranes and hollow fibres for hemofiltration and hemodialysis. They can control drug release by using polymeric carriers or microencapsulation. They were used to speed up healing in surgery and burn therapy.
Polysaccharides play an important role in interstitial fluids and connective tissue, providing mechanical strength and lubrication. Shorter saccharide sequences on soluble proteins and cell surfaces maintain conformation and function as important antigens interacting with soluble and membrane-bound proteins. Similar interactions regulate protein transport and removal from blood serum, are involved in tissue growth control via contact inhibition, and are also involved in blood typing. They can also be used to distinguish between normal and malignant cells, in cell surface studies, radioimmunoassays, and in drug targeting to specific tissues. Similarly, bacteria’s extracellular polysaccharides and surface carbohydrates stimulate the immune system and are used as vaccines and adjuvants.
FAQs
What is the use of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides are being used as demulcents, in drug formulations, dental impression materials, dusting powders, hemostatics, and to treat mild intestinal disorders. They are often used as plasma substitutes as well as anticoagulants in solution and as a surface treatment on artificial organs.
How do polysaccharides affect the body?
Polysaccharides seem to be abundant natural polymers found in plants, animals, and microorganisms. They have exceptional properties and play critical roles in the maintenance of life. They are quite well known for their high nutritive value as well as their beneficial effects on our immune, digestive, and detoxification systems.
Why are polysaccharides considered a good source of energy?
They all seem to be good energy sources because they can be quickly digested to simple sugars like glucose, enter cell respiration, and be used to make ATP (cell energy).
Now you can find answers to all your subject queries & prepare for your Exams on our Ultimate Learning App for Classes 6 to 12 – Infinity Learn.








