Table of Contents
Definition:
The amphibolic pathway is a biochemical process in living organisms in which both catabolic and anabolic processes are included. This process produces energy molecules which are ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate). Catabolism is the process of breaking down complex structures into simple molecules. Anabolism is the process of manufacturing complex molecules from simple molecules. These both are used in amphibolic pathways which are going to be discussed in detail.
Overview:
The amphibolic pathway is a biochemical process in which both catabolic and anabolic processes are included in order to produce ATP molecules during respiration. Catabolic is the breaking down of complex molecules whereas anabolism is the manufacturing of complex molecules.
B.Davis was the scientist who coined this term for the first time in 1961. In respiration, both catabolic and anabolic processes are done. When energy is required proteins and fatty acids are broken down to form acetyl-coenzyme A, when the body requires fatty acids acetyl-coenzyme is utilized to manufacture fatty acids. So, respiration is a process of both catabolism and anabolism. A perfect example for the amphibolic pathway is the Krebs cycle which is also known as the citric acid cycle and TCA. products of the krebs cycle and glycolysis act as a precursor for the synthesis of fats and proteins.
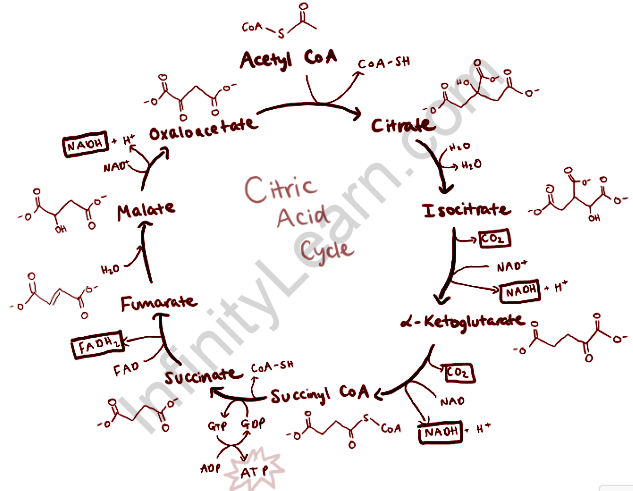
Krebs cycle:
The Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle and also known as TCA (TriCarboxylic Acid cycle).
This cycle is an important part of aerobic respiration and the main source of respiration. Acetyl -CoA is derived from glucose and production by the oxidation of pyruvate as a starting material and in a series of redox reactions most energy is produced in the form of NADH, FADH2, and ATP molecules. NADH and FADH2 which are generated in the TCA cycle and are the reduced electron carriers and pass their electrons through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain and most of the ATP which is produced in cellular respiration will be generated.
This citric acid cycle is done within mitochondria and on the cytosol of bacteria.
The cycle starts from oxaloacetate four-carbon compounds condensing with two carbon compound acetate to form six-carbon citrate compounds which is an anabolic process. The following reaction is the conversion of D-isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate followed by its conversion into succinyl-CoA which is a catabolic process. Carbon dioxide is lost in each step.
In the catabolic process, NAD+ is an oxidizing agent when it is reduced to NADH. In the anabolic process, NADPH is a reducing agent and converted into its oxidized form which is NADP+.
The citric acid cycle first is energy production produced by the oxidative mode as acetyl-CoA is fully oxidized to carbon dioxide. This produces most of the ATP molecules in aerobic heterotrophic metabolism as this energy conversion takes place in membrane structure by oxidative phosphorylation by moving electrons from NADH and FADH2 to the oxygen molecules. Every Krebs cycle gives 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, CO2, and GTP. And also citric acid cycle regenerates oxaloacetate when cycle intermediates are removed in biosynthesis.
Krebs cycle is done in the mitochondrial matrix in eukaryotic organisms whereas in prokaryotic it takes place in the cytoplasm. Krebs’s cycle name suggests that it is a closed-loop in which the molecule used in the first step is again reformed by the last part of the pathway.
Conclusion
We have discussed the amphibolic pathway and its example which is the Krebs cycle. The amphibolic pathway is a biochemical process in which both catabolic and anabolic processes are included in order to produce ATP molecules during respiration. Catabolic is the breaking down of complex molecules whereas anabolism is the manufacturing of complex molecules. A perfect example of the amphibolic pathway is the Krebs cycle which is also known as the citric acid cycle and TCA. Products of the Krebs cycle and glycolysis act as a precursor for the synthesis of fats and proteins. The Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle and also known as TCA (TriCarboxylic Acid cycle). This cycle is an important part of aerobic respiration and the main source of respiration. Acetyl -CoA is derived from glucose and production by the oxidation of pyruvate as a starting material and in a series of redox reactions most energy is produced in the form of NADH, FADH2, and ATP molecules. NADH and FADH2 which are generated in the TCA cycle and are the reduced electron carriers and pass their electrons through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain and most of the ATP which is produced in cellular respiration will be generated. This citric acid cycle is done within mitochondria and on the cytosol of bacteria. Every Krebs cycle gives 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, CO2, and GTP. And also citric acid cycle regenerates oxaloacetate when cycle intermediates are removed in biosynthesis. This is the brief information that we discussed in this article.
Importance of this chapter in NEET:
This is one of the main chapters, we can expect four to five bits from this chapter. Cycles are very important. Questions can be asked from where the cycle takes place, by-products of the cycle, how many ATP molecules are formed from here, and also they can ask enzymes used in the cycle of enzyme breakdown. Focusing on these cycles can guarantee the highest marks in your test. Every year there will be questions from this chapter mainly regarding cycles. If you are aiming for a good score then don’t avoid this chapter.
Also read: Important Topic of Biology: Photoperiodism
FAQs
What is an amphibolic process?
Amphibolic pathway is a biochemical process in which both catabolic and anabolic processes are included in order to produce ATP molecules during respiration. Catabolic is the breaking down of complex molecules whereas anabolism is the manufacturing of complex molecules.
Why is respiration called an amphibolic pathway?
In respiration, both catabolic and anabolic processes are done. When energy is required proteins and fatty acids are broken down to form acetyl-coenzyme A, when the body requires fatty acids acetyl-coenzyme is utilized to manufacture fatty acids. So, respiration is a process of both catabolism and anabolism. A perfect example for the amphibolic pathway is the Krebs cycle which is also known as the citric acid cycle and TCA. products of the Krebs cycle and glycolysis act as a precursor for the synthesis of fats and proteins.
Who coined the term amphibolic pathway?
B.Davis was the scientist who coined the term amphibolic pathway for the first time in 1961.
Q. Write about the amphibolic pathway in the citric acid cycle?
Ans: Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle and also known as TCA (TriCarboxylic Acid cycle).
This cycle is an important part of aerobic respiration and the main source of respiration. Acetyl -CoA is derived from glucose and production by the oxidation of pyruvate as a starting material and in a series of redox reactions most energy is produced in the form of NADH, FADH2, and ATP molecules. NADH and FADH2 which are generated in the TCA cycle and are the reduced electron carriers and pass their electrons through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain and most of the ATP which is produced in cellular respiration will be generated.
This citric acid cycle is done within mitochondria and on the cytosol of bacteria.
The cycle starts from oxaloacetate four-carbon compounds condensing with two carbon compound acetate to form six-carbon citrate compounds which is an anabolic process. The following reaction is the conversion of D-isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate followed by its conversion into succinyl-CoA which is a catabolic process. Carbon dioxide is lost in each step. In the catabolic process, NAD+ is an oxidizing agent when it is reduced to NADH. In the anabolic process, NADPH is a reducing agent and converted into its oxidized form which is NADP+. Every Krebs cycle gives 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, CO2, and GTP. And also citric acid cycle regenerates oxaloacetate when cycle intermediates are removed in biosynthesis.









