Table of Contents
Definition:
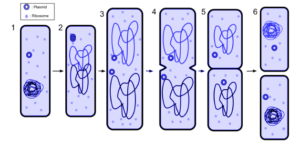
It is a simple & common method of asexual reproduction. In this method, a single-celled organism divides into two daughter cells and then each daughter cell develops into a new individual. This process happens with the division and duplication of the parent’s genetic matter into two parts.
Types of Binary Fission:
- Simple Binary fission
- Longitudinal Binary fission
- Oblique Binary fission
- Transverse Binary fission
Examples:
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are divided by binary fission.
- Most of the bacteria reproduce by this process. The process involves the division by utilizing the FtsZ protein, including chromosomal replication, chromosomal segregation, and cell splitting.
- In protozoans like amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, however, the process might differ in cell splitting and in how the cytoplasm divides.
- Organisms that reproduce by binary fission include Bacillus subtilis, B. cereus, B. pumilus, Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Ceratium, etc.
Additional Information:
- In this process, each daughter cell receives one copy of its parent DNA. It is a primary method of reproduction in prokaryotic organisms.
- Binary Fission occurs without any spindle apparatus formation in the cell. In this process, the single DNA molecule begins replication and then attaches each copy to various parts of the cell membrane. When the cell starts to get drawn apart, the original (actual) and replicated chromosomes get apart.
- The process of binary fission is usually rapid, and its speed varies among species. The time required by organisms to double their number of cells is called doubling time.
- Each species requires specific conditions for its growth. These conditions include pH levels, temperature, oxygen, light, moisture, osmotic pressure. For instance, mesophiles thrive at moderate temperatures ranging from 20 °C to 45 °C. The ambient temperature of the human body is 37 °C, which means many of the disease-causing bacteria are mesophiles.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis in humans. It divides every 15 to 20 hours, which is very slow when compared to other pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, which can divide every 20 minutes.
On the other end of the spectrum are the extremophiles. These bacteria can survive extremely harsh conditions such as high temperatures, high salinity, highly acidic environments, and more. For instance, the Deinococcus radiodurans is an extremophilic bacteria that can survive a thousand times more radiation than a person can. Under normal circumstances, it can divide every 48 hours. However, when exposed to harsh conditions like drought, it can slow down its growth rate until more favorable conditions arise.
Also read: Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
FAQs
What is binary fission?
It is a simple & common method of asexual reproduction. In this method, a single-celled organism divides into two daughter cells, and each daughter cell develops into a new individual. Ex. Euglena, Amoeba, Paramoecium, etc.
Write names of organisms that reproduce by binary fission.
Organisms that reproduce by Binary Fission are:- Bacillus subtilis, B. cereus, B. pumilus, Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Ceratium, etc.
Question: State the types of binary fission.
Answer: Listed below are different types of Binary fission:
- Simple Binary fission
- Longitudinal Binary fission
- Oblique Binary fission
- Transverse Binary fission