Table of Contents
Introduction
The basic theory of molecular biology is the study of the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins. It is understood as a way to turn DNA information into an effective product.
It is thought that the information provided in DNA is needed to build all the proteins and that RNA acts as a messenger, carrying information about ribosomes. Let’s talk about the definition of central doctrine, facts, steps involved, etc.
What is Central Dogma?
Central Dogma is the process by which genetic information contained in DNA is converted into an active product, namely, Proteins. Demonstrates the distribution of genetic information between cells, DNA replication, and RNA coding by writing, followed by RNA coding of proteins by translation. All of this happens in the sequence of interactions. For example, let’s understand the framework of Biopolymers. Proteins, RNA, and DNA are the three major components of biopolymers, which are further subdivided into a normal transfer, unknown transfer, and special transfer.
In the laboratory, special transfers occur in rare cases. Almost all cells are normally transferred. Specifies the normal data flow that occurs as a result of transcription and translation. Anonymous transfers are reported to be very rare.
Facts about the central dogma
- In the master plan, the basic premise of molecular biology is the clarification of how genetic information flows within the biological system.
- It was first clarified by Francis Crick in 1958.
- Once the ‘information’ has entered the protein, it cannot be detected. Specifically, information can be transferred from nucleic acid to nucleic acid or from nucleic acid to proteins, but not from protein to protein or from protein to nucleic acid.
Classification
Reproduction, transcription, and translation are used by all cells to maintain a record of genetic information and to convert coded genetic information into DNA into genetic products, RNA, or genetically based proteins.
Replication and transcription occur in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or cells with a nucleus, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm outside the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells, or cells that do not have a nucleus, enter all three processes in their cytoplasm.
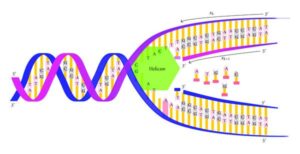
- Transcription process – DNA to RNA
Genetic information is transmitted from a single strand of DNA to RNA through the writing process. The first stage of gene expression occurs in this process, in which DNA strands are translated into RNA. The enzyme RNA Polymerase helps to complete the process. The sequence, gene, and promoter are three categories of single-stranded DNA strands.
The image fiber is one of the two strands of DNA that helps to create RNA, and the writing strand is another. Thereafter, RNA Polymerase binds to the developer. This process is known as polymerization.
Some texts use proteins, while others include regulatory or structural RNA. The written gene produces mRNA or RNA of the message when it encodes a protein code. This mRNA helps in the production of proteins during translation.
- Translation process – RNA to proteins
Messenger RNA is coded and translated by a sequence of proteins or polypeptides during the translation process. This process is activated by the power given to the charged tRNA. This is started by a ribosome, which is made up of two subunits, one large and the other small.
The peptide bond is made up of two tRNA molecules in a large unit close together. The new polypeptide sequence is produced by recording mRNA genetic information. The codon chain in the mRNA strand is translated by tRNA.
TRNA continues to transfer free amino acid cells from the cytoplasm to the growing polypeptide sequence of the ribosome until the chain binds to the codon in mRNA. The ribosome carries protein to the cell when it has finished making it.
- Repetition
It is the first place to find a biological heritage. It has the ability to replicate cell DNA.
The process of converting DNA into RNA is known as transcription. The enzyme RNA polymerase converts the DNA code gene into a coherent RNA molecule. Proteins are produced when mRNA is translated. The ribosome requires mRNA as a template to form a polypeptide shackle of amino acids.
Genetic code
The genetic code is full of the information needed to make an RNA-based protein. Three nucleotides and four nitrogenous bases form a triplet codon, encoding one amino acid. As a result, 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 amino acids are available in total. In nature, there are a total of 20 amino acids.
The genetic code is broken. This was explained by the genetic code, which means that a few amino acids are coded by many codons, causing them to degenerate. Each codon code for one different amino acid and codes are present in all living things.
Three of the 64 codons that stop, stop the typing process and one is the beginner codon, AUG, Methionine cod.
FAQs
What is the significance of core dogma?
Consistent with the basic theory of molecular biology, the DNA code is RNA, encoding protein codes. Significance of messenger RNA, the transmission of R
What does it mean to have a triplet codon?
A triplet codon is a sequence of three nucleotides of DNA or RNA encoding a specific amino acid. More than one base of three codes or cod coders is some amino acids. Represents a number of codon-based three-base variants that encode a specific amino acid.
Is it possible to overthrow Central Dogma?
There is a one really fundamental concept in the heart of Central Dogma, according to Crick. It states that there is no channel for the transmission of retrospective information from proteins to nucleic acids, i.e., no distorted translation.
Where is Central Dogma located?
Nucleus, is known as the basic teaching of molecular biology. Writing and translating are two processes involved in basic teaching.









