Table of Contents
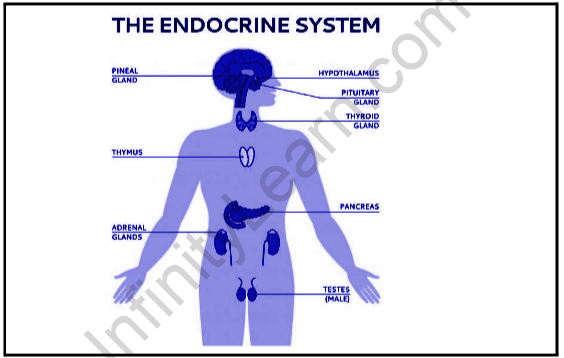
The endocrine system in the human body is a system of glands and organs found in various places. It is like a nervous system because it helps to control and regulate all the functions of the human body. Although the nervous system creates connections with neurotransmitters and nerve impulses, the endocrine system initiates communication through chemical agents such as hormones.
The endocrine system is a complex system of glands and organs that help regulate many bodily functions. This is accomplished by releasing hormones into the endocrine system, or chemical messengers. The endocrine system contains glands that produce and release hormones, which are chemicals produced in the body that regulate cell or organ function. Hormones that regulate body growth, metabolism (physical and chemical processes), and growth and sexual function. Hormones are released into the bloodstream and have the potential to affect one or more organs in the body.
Endocrine System Definition:
Frequently produced hormones in our body directly affect the functioning of the whole body, including hunger, growth, and reproduction. In addition to these small functions, hormones also promote a number of complex functions, including human behavior and emotions. These hormones are produced in our body by the large endocrine glands. These glands, along with other organs, help to provide vital functions that combine to form the endocrine system.
The endocrine system in the human body is responsible for regulating the following functions:
- All human growth and development
- Sexual and reproductive functions
- Conservation of appetite
- Keep a check on the sleep cycle
- It keeps the body temperature in control
- Maintains adequate blood pressure
- Metabolic rate
- It keeps the heartbeat going
The body’s endocrine system performs the following functions:
- It controls how hormones are released into the body
- It makes hormones, which control your emotions, metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, and organs.
- It sends hormones into the bloodstream to ensure that they can travel to different parts of the body.
The endocrine system is controlled by feedback, just as a thermostat controls room temperature. Pituitary gland-regulated hormones receive signals from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland as they release hormones that open the pituitary gland to release circulating hormones for circulation. After that, the hormone will signal the target hunger to release the hormone.
When hormone levels rise in the bloodstream, the pituitary and hypothalamus block the release of hormones. Therefore, it reduces the release of the target gland. It helps with a stable blood concentration of hormones, which are regulated by the pituitary gland.
Endocrine System Hormones
In this section, we will learn about some of the hormones in the human body that are produced by the endocrine glands.
- Adrenaline
Adrenaline is also known as epinephrine is produced by the adrenal gland. The main effects of Adrenaline include increased heart rate, blood pressure, lung enlargement, eye enlargement, redistribution of blood to the muscles, and changes in body function to increase blood sugar levels, especially in the brain.
- Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland. The main function of aldosterone is to regulate salt and water in the body, thereby affecting blood pressure.
- Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland. Cortisol regulates a variety of important functions in the body, including metabolism and the immune response. It also plays an important role in helping the body’s response to stress.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEA)
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA) is produced by the adrenal gland. DHEA is a male sex hormone produced by both men and women. DHEA is needed to produce both the male and female sex hormones testosterone and estrogen. It also contributes to the maturity of male sexual characteristics during puberty.
- Estrogen
Estrogen is produced by the ovaries in women. Estrogens are involved in ovarian function, such as maturation of ovarian follicles, as well as maturation and maintenance of the vaginal and uterus. Estrogens also play an important role in regulating gonadotropin production.
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
The pituitary gland produces Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH). FSH helps regulate the menstrual cycle in women and promotes the development of eggs in the ovaries. Female FSH levels fluctuate during the menstrual cycle, with higher levels occurring before the ovary hatches. This is called ovulation. FSH helps regulate sperm production in males.
- Glucagon
Glucagon is produced by the pancreas. Glucagon stimulates glucose uptake, prevents glucose depletion, and facilitates the conversion of glycogen into glucose in the liver.
- Insulin
Insulin regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the absorption of sugar in cells, regulates carbohydrates, lipids, and protein metabolism, and promotes cell division and growth through its mitogenic effects.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
The pituitary gland produces Luteinizing hormone (LH). LH is important for growth and sexual function. LH helps regulate the menstrual cycle in women. It also causes the egg to be released from the uterus. This is called ovulation.
- Melatonin
Melatonin is produced by the pineal gland. Melatonin is a dark hormone that mediates dark signals and provides nighttime information, rather than a sleeping hormone. It is also thought of as a continuous synchronizer, which stabilizes and strengthens the distinct rhythm of the circadian body.
- Oxytocin
Oxytocin is produced by the pituitary gland. The role of oxytocin in women’s production is well known. It is extracted in vital amounts during childbirth and after breastfeeding. The use of oxytocin as a medicine during childbirth is one of the oldest forms of oxytocin as a medicine.
- Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone is produced by the Parathyroid gland. The parathyroid hormone causes the bones to release calcium from the blood, the intestines absorb calcium from food, and the kidneys store calcium.
- Progesterone
The corpus luteum in the ovary produces the hormone progesterone. Progesterone is essential for maintaining the early stages of pregnancy and the menstrual cycle. It may also contribute to the progression of other cancers.
- Prolactin
Prolactin is produced by the pituitary gland. Prolactin is involved in thousands of physiologic functions, but the two most important are milk production and the growth of mammary glands in the breast tissue. Prolactin promotes the development of the mammary alveoli, which are parts of the mammary gland where milk is produced.
- Testosterone
Testosterone is produced by many glands, ovaries, testes, and adrenal glands. Testosterone is a sex hormone that has many functions in the body. It is thought to regulate libido, bone density, fat distribution, muscle mass and strength, and red blood cell production and sperm production in men. A small amount of testosterone in the blood is converted to estradiol, a substance similar to estrogen.
- Thyroid hormone
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones have an effect on all cells and organs of the body. They contribute to weight loss or gain by controlling their caloric intake. The heartbeat can be reduced or accelerated by thyroid hormone.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Gonads
FAQs
What makes the Endocrine System work?
When the hypothalamus receives a signal from your nervous system, it can release hormones, telling the pituitary gland which hormones to release or produce. The pituitary gland is responsible for releasing hormones into your bloodstream, which travel to cells that need to be blocked or released.
What is an Endocrine System Test?
Endocrine tests are used for a variety of reasons, such as to detect different hormones in the body, to identify the underlying cause of endocrinological problems, and to check whether endocrine glands are functioning properly.
What Stimulates the Endocrine Glands?
There are three ways to stimulate the endocrine glands: neural stimulant, hormonal stimulant, and humoral stimulant.



