Table of Contents
Gonads: The testes inside the male and the ovaries inside the female are the gonads or primary reproductive organs. These organs are responsible for the development of sperm and eggs, as well as secreting hormones and being classified as endocrine glands. The gonads of vertebrate embryos are remarkable among organs in that they may choose where to develop. Given the necessity of appropriate gonad formation for sexual development and reproduction, extensive study into the genetic and cellular mechanisms of gonad synthesis and sexual differentiation has been done throughout the years. While the genetic trigger for gonadal sex differentiation into the ovary or testis varies from vertebrate to vertebrate, the downstream molecular pathways are mainly consistent.
A brief outline
Gonad definition:
This is a critical stage in embryogenesis, as it determines whether the embryo will develop into a girl or male. Gonads are anatomically identical in both sexes at first (the “bipotential” or “indifferent” stage) and then channeled down the ovarian or testicular paths. Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone are created and given by gonadotrophs of gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland, which controls the gonads. The gonadotropin-releasing hormone generated in the hypothalamus controls this secretion. Gonads begin their development as a common primordium (a developing organ) in the manner of gonadal ridges and are only later differentiated into male or female sex organs.
Important concepts
Function of Gonads
In humans, a gonad supports meiosis, a kind of cell division that produces haploid cells. A diploid cell’s DNA is doubled during meiosis, resulting in 92 chromosomes, that are then split into four cells. Each cell is unique, with 23 chromosomes that are not coupled. These cells will develop into the eggs and sperm that are necessary for sexual reproduction. Even though the number of chromosomes in each species differs, a gonad in another organism acts in the same way.
The gonads are frequently engaged in hormone control in creatures with complicated hormonal systems. In humans, this can be seen. Male testes are involved in the creation and regulation of testosterone, whereas female ovaries generate a range of hormones involved in ovulation and conception, with estrogen being the most important. The gonad is frequently associated with the sexual organ and is involved in the release of gametes. Internal fertilization, or the act of copulating, is exhibited in animals that rely on it. Other animals rely on the environment to disperse their gametes. The gametes are released by the gonads in these species. Flowers are a good example of this.
Example of Gonad
Take, for example, humans. Human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. Your mother gave you 23 chromosomes and your father gave you 23. Because these chromosomes reflect the same DNA segments, the pairs that are similar clump together to form a single chromosome with sister chromatids. As a result, each human cell has 46 chromosomes. This is when the gonad enters the picture. Consider what would happen if two humans reproduced without first splitting their chromosomes. 46 chromosomes plus 46 chromosomes equal 92 chromosomes! While additional copies of the same chromosome may help some species (such as plants), this condition is harmful to humans and many other animals.
As a result, before breeding, an animal must employ germ cells in the gonad to decrease the DNA to 23 non-paired chromosomes. Haploid cells (or gametes) differ from diploid cells in that they have half of their genetic material.
Hormones produced by the female gonads
Progesterone and estrogens are the most important hormones produced by the ovaries.
- Estrogens are a family of female sex hormones that are necessary for reproduction and the growth of the female reproductive system. Estrogens are responsible for vaginal and uterine maturation and growth, enlargement of the pelvis, breast, and uterus changes during the menstrual cycle, and increased hair growth.
- Progesterone is a hormone that prepares the uterus for conception, regulates alterations in the uterus during the menstrual cycle, aids in ovulation, and stimulates gland development for milk production during pregnancy.
Hormones produced by the male gonads
Androgens are hormones that play a big role in how the male reproductive system develops.
- Testosterone is responsible for greater bone and muscle growth, body hair growth, the development of a larger shoulder, voice deepening, and penis enlargement.
- Androstenedione is a hormone that functions as a precursor to estrogen and testosterone.
- Inhibin is a hormone that inhibits the production of FSH and is hypothesized to play a role in sperm cell growth and control.
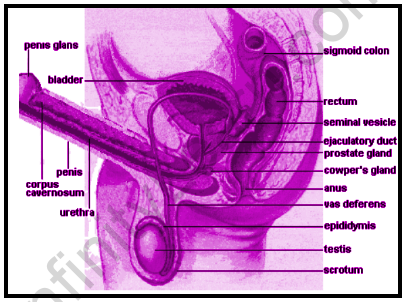

Male sexual differentiation is determined by the existence of the SRY gene, which is found on the Y chromosome and codes for the testis determining factor. The female sex (ovaries rather than testes) will develop if the SRY gene is missing from the Y chromosome. The gonads are formed during the establishment of the urinary and sexual organs.
Significance of Gonads in NEET exam
This course gives students a more in-depth look at the human reproductive process. For extra practice and review for the NEET test, there are questions available. They will have access to error-free answers prepared in a plain and straightforward manner, making it easier for everyone to understand, if they use this study material. Furthermore, our solution material aids a student in achieving a notable Biology grade.
FAQs
What are the functions of the gonads in the human body?
The gonads are the most important hormone-secreting organ in the human body, as they are in charge of functioning the body's basic and secondary sexual characteristics. Not only do these changes affect the sexual organs, but the entire body changes dramatically throughout this time. The individual's height rises in tandem with changes in his or her voice baritone. As a person grows more aware of their body, these changes have a number of mental consequences.
What is the purpose of Gonad?
The most important purpose of the gonads is the generation of gametes and the secretion of sex hormones. Both males and females benefit from the steroid hormones secreted by gonads, which aid in the growth and maturity of sexual organs.
What Hormone Do the Testes Secrete?
Testosterone is a hormone secreted by the testes. It aids in the development of male sexual organs as well as secondary sexual features such as voice deepening, facial hair appearance, and so on.









