Table of Contents
Definition:
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system through growth and contraction. Any condition that affects the heart or its function leads to heart disease. Medically heart disease is called cardiovascular disease.
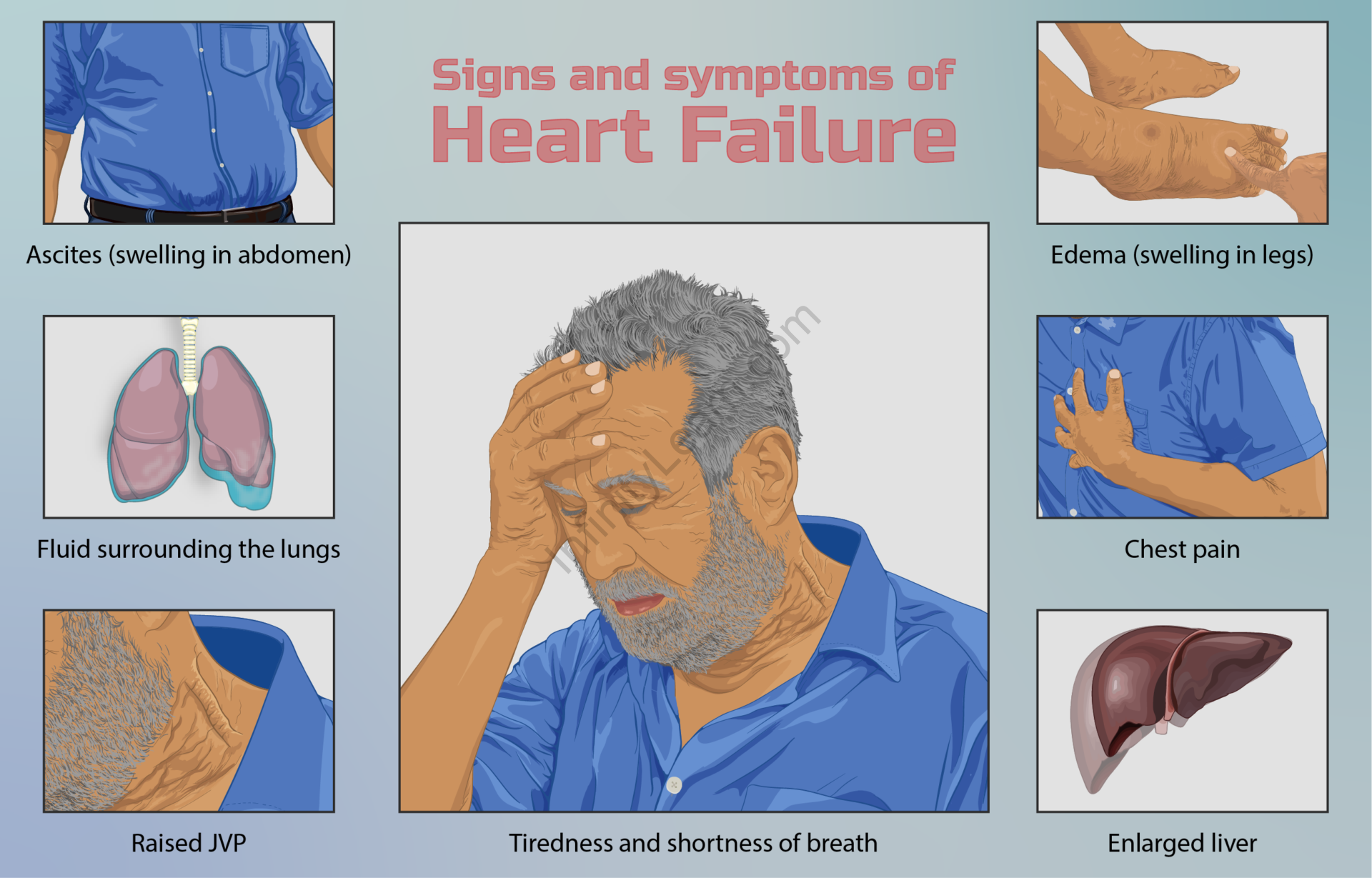
Heart failure is a condition that occurs when your heart does not pump enough blood according to your body’s needs. This can happen if your heart can not be filled with enough blood. It is also possible when your heart is too weak to pump properly. The word “heart failure” does not mean that your heart has stopped.
CHF stands for Congestive Heart Failure. CHF is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump blood properly so the body’s blood supply is affected. The body cannot get the amount of blood it needs.
Classification:
The heart is a four-chambered organ divided by two atria at the top and two ventricles at the bottom. The atria receive blood from different parts of the body as part of the circulation and the ventricles are responsible for pumping oxygenated blood into the body as it reaches the organs and tissues. During CHF, normal circulation is affected and the body fails to receive the required amount of blood because blood and other body fluids begin to fill up around other organs.
CHF Problems:
- CHF occurs when there are health problems involving the cardiovascular system. The first and foremost reason for having high blood pressure.
- Hypertension: This causes a narrowing of the arteries which can increase arterial tension which causes difficulty in blood flow.
- Coronary Artery Disease: There will be a narrowing of the artery walls due to cholesterol suspension thus causing a problem with normal blood flow.
- If there is a disruption of the heart valves and the valves fail to open and close properly that will also impair blood flow.
- Other conditions that can cause CHF are diabetes, thyroid disorders, alcoholism, etc.
Types of Congestive Heart Failure:
As the left side of the heart (oxygenated blood moves from the lungs to the left atrium and then to the left ventricle and is transfused throughout the body) undergoes an additional pumping function, heart failure is said to be similar to the left. – heart failure on the sides. Of course:
Systolic Heart Failure: This occurs when the left ventricles do not reach normally thus failing to push the blood to circulate properly. The heart cannot function normally when the force is not right.
Diastolic Heart Failure: This occurs when the muscles in the left ventricle tighten. The heartbeat includes strength and rest. As the ventricle fails to relax, blood cannot be pumped properly.
The problem starts in the left side of the heart and if left untreated the disease progresses to the right side of the heart.
Diagnosis:
The doctor will take a complete medical history – any past history of diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid problems, chest pain, a heart attack will be carefully monitored. The patient’s surgical history in the past is also considered. This is followed by a physical examination in which the doctor will use a stethoscope to make sure there are no abnormalities in the chest. Physical examination of any signs of congestion, vascular testing, and any accumulation of fluid in the abdominal area is thoroughly evaluated. Once the medical examination has been completed the patient underwent several tests to confirm the diagnosis.
These tests include:
- Blood tests: This is done to make sure the patient is suffering from any disease that can affect the heart condition.
- Chest X-ray: Recognition of any abnormal fluid accumulation near the heart and lungs.
- CT scan: A CT scan provides a clear picture of any abnormalities.
- ECG: Cardiovascular activity is recorded with the help of ECG.
- Treadmill test: This is a type of stress test in which the patient is advised to move to a printing press with cords attached to the chest and these cords are connected to a machine that records heart and lung function during exercise.
- An angiogram was performed to avoid cardiac arrest.
- Myocardial biopsy is one of the tests performed to diagnose heart muscle disorders.
Treatment:
Treatment includes ACE inhibitors to open the arteries, beta-blockers used to lower blood pressure, diuretics are recommended to reduce body fluids leading to excess fluid loss. The surgical aspect includes Angioplasty to open the obstruction of the coronary arteries.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Pancreas
FAQs
Q. What Are The Four Steps To Overcrowding?
Ans: CHF progresses in 4 stages:
- Stage 1– This can be treated with a few lifestyle changes as they do not show any visible symptoms.
- Stage 2– Some exertion can cause breathing, this can also be controlled by lifestyle changes but careful monitoring is required to ensure that symptoms do not get worse.
- Stage 3– Symptoms of respiratory failure and symptoms are worse than stage 2. Consultation with a cardiologist becomes more important and oral treatment is started.
- Stage 4– Shortness of breath is noted because even with rest and symptoms do not go away. Any type of physical activity becomes difficult. This stage is not treatable but medication is recommended to relieve symptoms.
What Is Expected Life With Congestive Heart Failure?
Life expectancy with CHF depends on factors such as size, age, gender, and genetics.








