Table of Contents
Introduction
Parturition refers to the process of giving birth or expulsion of an adult fetus from the mother’s womb, at the end of pregnancy. This is due to the complex neuroendocrine system. Oxytocin hormone from the mother’s pituitary gland stimulates the strong uterine contractions that lead to the baby being released from the womb.
It is a process of childbirth, and the placenta from the uterus to the vagina is called parturition. It is also called the intermediate stage of cesarean section. The process of giving birth or delivery is called parturition, which occurs about 38 weeks after fertilization. This process has three different stages of work. The first, the stretching phase, begins with the onset of normal, firm uterine contractions and ends with the full opening of the cervix.
Maternity Stages
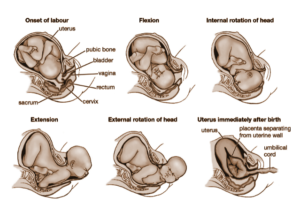
The reproductive process usually occurs in 3 stages
1) Dilation
Stretching is defined as the uterus begins to grow and rupture the membrane. It also starts bleeding continuously. Stretching is often the first stage of the reproductive process. It starts when the closed cervix is enlarged by 3 cm. Although it differs from women and they may have never experienced active access before reaching this stage. During this procedure, the cervix is integrated into the lower part of the uterus. Parturition shortens mussels and upper parts. It pulls up and down the segment during the catch, and slowly releases the movement upwards.
When the cervix has matured, the part of the baby that is introduced allows it to go down enough to allow the baby’s head to pass. About 10 cm of full-time baby, here the stretching process is over. The actual duration of the staff process varies slightly, although the average length of the working phase can be up to 20 hours.
During labor, the cervix will open at a rate of about 1 cm per hour for a woman who is giving birth for the first time. For a woman who has given birth in the vagina, the rate is usually 2 cm/h. This concept has been explained with the help of Friedman’s Curve, which focuses on the average rate of fetal decline and cervical dilation during active childbirth.
2) Expulsion
This second stage of reproduction begins in adulthood and continues until birth. This reproductive process begins when cervical pressure increases, and, in turn, the Ferguson reflex increases uterine contractions. Initially, the upper part is completely involved within the pelvis, that is, the full pinnacle width exceeds the pelvic penetration value. Afterward, the baby’s head continues down to the waist, below the pubic arch, and finally out of the vagina.
The baby’s head is aided by extra effort to give birth or to push down. The successful birth of marks completes the second stage of reproduction. Important factors, such as weight, fetal size, anesthesia, will cause variability in the second stage of childbirth.
3) Placental
This third stage of reproduction begins after birth and ends with the delivery of the placenta. The average length between childbirth and placenta varies between 10-12 minutes. It is usually administered by giving uterotonic injections, such as oxytocin, as well as proper cord pulling. Basic massage supervised by a trained caregiver helps to deliver the placenta. Otherwise, it allows the placenta to be removed without medical help.
The baby is usually born and the membranes remain intact when the amnios do not rupture during a cut or push. It is often referred to as taking inside the caul. It does not cause any damage, and moreover, the membranes can be easily wiped and dispersed.
Medications During Childbirth
Pain during childbirth can be diagnosed or reduced with systemic drugs, psycho prophylaxis, regional nerve blocker, or a combination of these medications.
Since the 1930s, psycho prophylaxis drugs have gained popularity as they prepare a woman mentally and physically for childbirth thus expecting her to experience pain during the procedure. In addition, a comfortable environment, the support of family and friends, and a competent health care provider can help her reduce the need for pain relief.
Let’s talk about these drugs one by one.
- Systemic drugs – Morphine and meperidine are commonly used intravenous drugs to relieve pain (analgesia) during childbirth. However, other side effects are also associated with vomiting and nausea. When meperidine and promethazine are given together the side effects are reduced. Other side effects of these drugs include drowsiness, hypotension, low blood pressure, etc. These drugs can cross the placenta and cause similar effects on newborns. Buorphanol is another common drug that is prescribed for birth pains and is known to produce mild depression in newborns.
- Barbiturates – These drugs are given to reduce the pain of childbirth. However, they are rarely used during childbirth. They are sedatives that can create a relaxed atmosphere. They cannot provide effects like analgesics to reduce pain. When barbiturates are used during childbirth, they can cause respiratory distress in newborns that can be further reduced by using narcotic analgesics.
- Sedatives – These are used in the early stages of childbirth to relieve a woman against the effects of active contractions.
- Local anesthesia – This medication is one of the systemic drugs. Local anesthetics work by inhibiting nerve conduction. Their actions are limited to the injection site as they can spread short distances. They become only numb with a single organ and allow a woman to have control over her whole body. Local anesthesia does not cause serious side effects for the woman and the newborn.
- Pudendal block – It is a common procedure that causes the perineum to become numb and the birth canal to automatically deliver, vacuum discharge, and forceps delivery. Antiviral drugs such as lidocaine and bupivacaine are used and injected into the pudendal nerve through the vagina. This procedure is effective in reducing pain from perineal distention but not in uterine contractions.
Obstetric Diseases
Most women can have a baby automatically. However, complications before, during, or after the operation can endanger the life of both mother and baby and may require medical intervention.
- Cesarean Section – If the mother is unable to deliver the baby through the vagina, a surgical procedure is performed. In this procedure, surgical incisions are made in the abdomen and uterus. This procedure is only performed in extreme cases where the risk of birth defects in the mother and baby exceeds the risk of miscarriage. Common symptoms include premature birth of medical conditions, progressive birth defects, fetal depression, etc.
- Forceps Delivery – It is a type of assisted vaginal delivery. Sometimes it is necessary for vaginal birth. At birth, the health worker inserts a forceps (a metal-shaped object with large spoons or salad spoons) on the baby’s head to exit the birth canal. This is done during the mating season when the mother voluntarily pushes it.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Lactation
FAQs
Q. What is Parturition?
Ans: To give birth means to give birth. It is the process of moving the uterus, or it is the process of giving birth after the end of a pregnancy. A developed baby is born with cortisol.
During the human reproductive process, the cervix expands and relaxes along with cortisol, oxytocin, and estrogen hormones. It is released to start milk production and processing. The uterus shrinks to push the embryo toward the uterus and continues until the embryo descends through the passageway. During this process, the pinnacle should be the first to return to the outside. The uterus expels the placenta, and it emerges immediately after the birth of the baby. Lactation begins, and the first milk is called colostrum. This milk contains the necessary antibodies, which are needed to protect the baby from infections, allergies, and other diseases.
Q. Explain the Human Reproduction Process.
Ans: The reproductive stages take up the normal range of 9 months of gestation, with severe uterine contractions resulting in fetal birth. It is a neuroendocrine mechanism and started with signals from the fully-grown fetus and placenta, producing a fetal reflex. The developing fetus releases hormones into the adrenal glands.
Birth pains mean that oxytocin causes a strong contraction of the smooth muscles of the myometrium. She pushes the teens slowly through the open cervix and vagina, head forward. This also stimulates oxytocin production through uterine contraceptives. The regenerative reflex between uterine contractions and oxytocin continuous leads to further muscle contraction. We are helped by the reflex and voluntary reach of the abdominal muscles. The baby’s membranes rupture and amniotic fluid come out, but the baby’s lining is left behind. This eviction phase takes approximately 20 minutes to one hour. This is followed by a 10-45 minute placenta procedure in which the umbilical cord, placenta, and fetal membranes are removed and the baby is born. After delivery, the uterus shrinks in size, causing the placenta to rupture.




