Table of Contents
Renin
Renin is one of the main enzymes produced by our kidneys. Also, there is a possibility that it may be excreted by the placenta of the body. This enzyme is an essential part of the entire physiological system and helps regulate blood pressure in the body.
The Renin-angiotensin system is a physiological hormone system involved in regulating arterial blood pressure and sodium concentration in plasma.When renin is released into the bloodstream, it acts on angiotensinogen (a circulating layer) that passes through proteolytic cleavage to form decapeptide angiotensin I. Vascular endothelium contains an enzyme called angiotensin transforming enzyme that separates two amino acids and forms -angiotensin II (AII) and other tissues in the body, including the brain and heart, also form angiotensin II (AII).
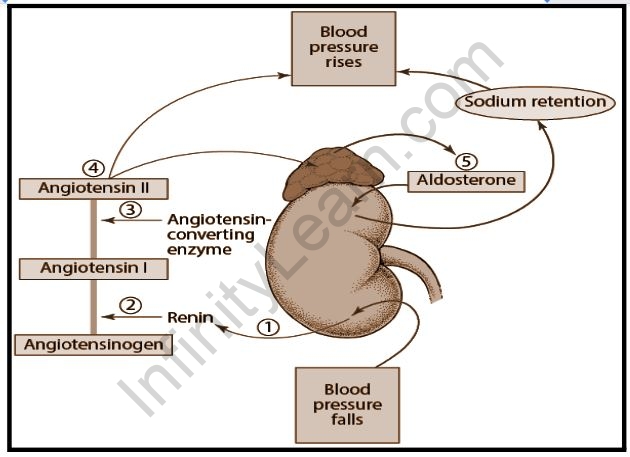
When found in human blood, renin acts on a protein called angiotensinogen and leads to the release of angiotensin I.
Angiotensin I is one of the few products produced with the help of the angiotensin-converting enzyme, which also separates 2 amino acids from all 10-amino-acid chains of angiotensin I. This, in turn, leads to formation. Angiotensin II. Students need to learn more about renin activity and much more. So, we’re here to provide some details on that.
What is Renin Enzyme?
Many readers need to have some idea about the meaning of renin, and that is exactly what we are going to write here. We all know renin is an enzyme that works on angiotensinogen to produce side effects such as high blood pressure and others. It also helps control blood pressure and systolic blood pressure. Angiotensin II is said to be one of the few active and highly potent vasoconstrictors as well. Therefore, there is an increase in the production of aldosterone and cortisol from the direct action that takes place in the adrenal cortex. The discovery of renin hormone activity occurred in 1898 by Per Bergman and Robert Tigerstedt.
What is a Renin Structure?
Renin has a basic structure that contains approximately 406 amino acids in total. There are pre-and-prose segments that carry about 20 amino acids and 46 amino acids. Mature renin contains about 340 amino acids, and the total weight is 37 kDa. Renin is produced by the kidneys and sometimes the placenta and is responsible for many functions as well. We will learn more about encryption and renin functions right now.
Functions of the Renin-Angiotensin System
Listed below are important functions of the Renin-angiotensin system.
- Build resistant vessels, thereby increasing arterial pressure and systemic vascular resistance.
- It promotes the delivery of sodium to various renal tubular areas and increases water retention in the body.
- It stimulates the release of vasopressin in the posterior pituitary and increases fluid retention by the kidneys.
- It provides the release of norepinephrine from the sensitive arteries and prevents the absorption of norepinephrine, thereby enhancing sympathetic adrenergic function.
- It stimulates vascular hypertrophy and cardiac hypertrophy.
- The renin-angiotensin pathway is not only regulated by mechanisms that promote renin release but is also regulated by the natriuretic peptide released by the human heart, and these peptides serve as an important anti-inflammatory system.
Importance of the Renin-Angiotensin System
The Renin-angiotensin system regulates and maintains blood pressure levels in blood cells. If there is a decrease or increase in blood pressure in a person, this system works faster by releasing renin into the bloodstream.
Deceptive therapies play a major role in treating heart failure and high blood pressure. All receptor blockers and ACE inhibitors are used to reduce arterial blood pressure, blood pressure, ventricular congestion, pre-loading ventricular and vascular hypertrophy and reverse cardiac.
Therapies that aim to completely block the Renin-angiotensin system offer additional clinical benefits to patients with kidney and other heart diseases. These methods may include dual inhibition using a combination of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme I or therapies such as direct renin inhibition by aliskiren which is a recently approved treatment for hypertension.
Also read: Important Topic of Biology: Angiotensin
FAQs:
What is Renin Enzyme?
Renin is considered one of the major enzymes produced by our kidneys and regulates some of the vital functions of the body. Also, there may be a chance that it can be hidden by our body's placenta. Renin enzymes tend to play a very important role in the physiological functions that normally work in the body as well. It is an enzyme that helps regulate blood pressure in the body. When found in the blood of the human body, renin acts on a protein called angiotensinogen, and that results in the release of angiotensin I.
What Are the Main Activities of Renin?
Juxtaglomerular kidney cells are responsible for renin excretion, which senses changes in renal perfusion. This is done by the stretch receptors found in our artery walls. These juxtaglomerular cells are also properly stimulated to provide the release of the enzyme renin by rapid signaling from our macula densa. The main function of the macula densa is to detect certain changes in the delivery of sodium to our distal tubule. It then responds to a sudden decrease in tubular sodium load caused by the stimulation of renin release that occurs in these juxtaglomerular cells.






