Table of Contents
Introduction
Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscles in the human body- some are visceral and cardiovascular muscles. In this study, skeletal muscle, its meaning, structure, structures, functions, and types are described in a simple and detailed manner.
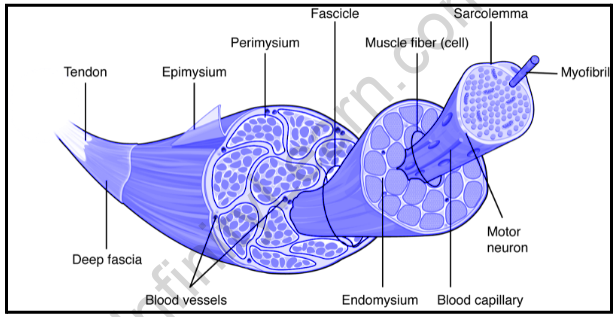
The skeletal muscle is a muscle tissue that attaches to the bones and is involved in the functioning of various parts of the body. These muscles are also called voluntary muscles as they come under the control of the nervous system.
Skeletal fiber muscle structure
Bone marrow cells are fibrous and enormous in size. Each of these muscle fibers is bound to a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma. This membrane is an area where a continuous action may take place, causing muscle contraction.
Each muscle fiber is made up of long cylinders that are joined together by a length inside a fiber. These are called myofibrils. These myofibrils are attached to the sarcolemma at their ends. This causes the contraction of all the fibers when myofibrils become depleted.
The formation of myofibrils
- Myofibrils appear striped or striped due to the arrangement of contractile proteins myosin (dense) and actin (thin).
- Each myofibril has light I-belts and black A-belts.
- Black straps contain a series of thick and thin protein strands.
- Light I bands contain just a few strands of protein fibers.
- I-bands are divided into a dense line called the Z disc or Z line.
- Between the two Z lines is a sarcomere.
- A sarcomere is an active unit of a myofibril.
- It is made up of one black band booked with two halves of I band.
- Myofibril is made up of several sarcomeres and these units interact with myofibril.
Contractile protein definition
Proteins that cause muscle contraction are called contractile proteins.
Contractile Protein Separation
Contractive protein breakdown can be divided into two parts
- thick
- thin
These are dense myosin proteins and a small amount of actin protein.
Contractile Proteins and How They Are Organised
The atomic tail of myosin combines with other myosin molecules to form a middle layer of a thick layer. Some ends of molecules or their heads are located at the junction of tiny filaments. Small filaments are actin proteins. These actin proteins are helical in structure and appear as fibrous pearls. The other two subgroups are tropomyosin and troponin. These both regulate the interaction between myosin and actin and prevent access when the muscles are relaxed.
Muscle contraction and movement
The slide film slide theory proposed by A. F. Huxley and R. Niedergerke (1954), and H. E. Huxley and J. Hanson (1954) described the function of muscles in the human body.
- To touch the muscle the sarcomere should reach
- To reduce sarcoma myosin and actin filaments slide over one another which increases the contrast
- Protein filaments themselves are inaccessible
- But as you increase the range of contracts sarcomere
- This increase in accumulation occurs due to the fact that crossing bridges, the bulbous structures found in myosin, aid in the movement of fibers.
The sarcomere is a distance between two Z-lines. So when the muscle reaches:
- The distance between the Z lines is reduced
- The black center of band A, called the H zone, which contains only dense fibers, shortens
- Light bands also shorten
- The black belt A does not reach
- Tiny strands are pulled in the center of the sarcomere area
- This causes the Z line to get closer to the thick strands
- The area where the thick and thin fibers meet is growing
This is how muscle contraction occurs.
Use of skeletal muscle
- Travel
With flexibility and muscle relaxation, we can move and perform activities such as walking, running, and swimming. Muscles also help us to make good or small movements like writing, speaking, and controlling facial expressions.
- Stability and balance
The muscles attached to the limbs play a key role in keeping our body balanced and stable during rest or movement. Muscles attached to the knees and shoulder joints are essential for this function.In addition, the muscles of the abdomen, pelvis, and back strengthen the body and help lift weights.
- Standing
The skeletal muscles keep the body in good shape while resting, sitting, or standing. Strong and flexible muscles maintain good posture. At the same time, weak and tense muscles lead to poor posture. Standing is important because excessive posture can lead to deterioration of the health of our joints and muscles.
- Urination
Urination involves both the spinal cord and the skeletal system. The nervous system works in conjunction with the muscles in urination.
- Vision
Eye movement is controlled by 6 skeletal muscles all around. It is because of these skeletal tissues that the eye can
- Swivel in socket
- Trace things
- Focus on things
- Protection of organs
The internal organs of the abdominal cavity are protected by the abdominal muscles and back. The bones and joints are also protected by muscles because they absorb shocks and reduce friction.
- Temperature control
Bone marrow produces about 85% of body temperature. Muscle contraction plays an important role in maintaining body temperature. When the body temperature drops, the muscles increase their activity to raise the temperature.
Of the three types of muscles invertebrates, the skeletal muscle is the largest. They are also known as muscles and are attached to the bones with the help of cords. The skeletal muscles are voluntary. That is, they are active and controlled by voluntary action. The brain controls every effort to reach the muscles. A mirror neuron that makes muscle tissue invisible seems to receive electrochemical signals from the brain through the nervous system. Some actions are performed by skeletal muscles and are partially flexible, such as breathing or chewing. In the case of reflexes, signals are usually sent to the spinal cord through a gray-colored information loop. The skeletal muscles attach to the bones and move the body by flexing and resting. This muscle contraction is brought about by complex processes involving muscle fibers made up of specialized proteins. The tissues of the skeletal structure are long and cylindrical, and when viewed through a microscope, they look like a series of strands or strands. This benefit is due to the fact that the fibers are made up of contracted protein that is constantly organized. These proteins bring about muscle movement.
Also read: Important Topic Of Biology: Skeletal System
FAQs
Can you think of any similarities between the heart muscle and the skeletal muscles?
Both skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles are striated muscles.
Name one difference between the skeletal muscles and the heart muscle.
The skeletal muscle is dominated by the somatic nervous system while the heart muscle is not naturally free.








