Table of Contents
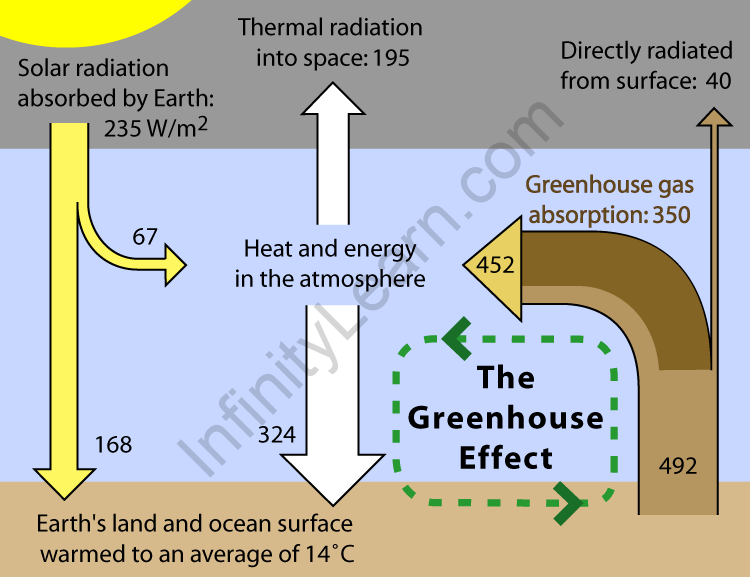
The Greenhouse Effect is the process through which the Earth’s surface heats up until it reaches the troposphere. It occurs as a result of increased concentrations of carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases. Sunlight heats the Earth’s surface, and the energy is then reflected back into space as infrared radiation. The greenhouse effect occurs when concentrated gases absorb energy, raising global temperatures. As a result, the greenhouse effect and global warming are linked.
“The greenhouse effect is the process through which solar energy is absorbed by greenhouse gases rather than reflected out into space.”
A greenhouse is a glass structure that may be used to cultivate plants. The sun’s rays warm the plants as well as the air within the greenhouse. The heat trapped within cannot leave and hence heats the greenhouse, which is necessary for plant development.
The same is true of the earth’s atmosphere. The sun warms the earth’s atmosphere during the day. When the earth cools down at night, the heat is reflected back into the atmosphere. The heat is absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere throughout this process. This is what causes the earth’s surface to warm, allowing living organisms to survive.
However, due to rising amounts of greenhouse gases, the earth’s temperature has risen significantly. This has had a number of far-reaching consequences.
Greenhouse Gases
“Greenhouse gases are gases that absorb infrared light and cause the greenhouse effect.” Carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons are two examples.”
Factories, autos, deforestation, and other key sources of greenhouse gas emissions As the number of manufacturers and vehicles grows, so does the amount of these gases in the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases never allow radiation to escape from the planet and hence raise the earth’s surface temperature. This, in turn, contributes to global warming. “Global warming” is defined as “a progressive increase in the earth’s temperature induced by the greenhouse effect produced by growing amounts of carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants.”
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
The following are the primary causes of the greenhouse effect:
1. Landfills and Industrial Waste
Industries and factories emit toxic pollutants into the environment. Landfills also emit carbon dioxide and methane, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
2. The Use of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels play a significant role in our lives. They are frequently employed in transportation and in the generation of power. Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels are burned. The use of fossil fuels has increased as the world’s population has grown. As a result, the amount of greenhouse gases released into the environment has increased.
3. Deforestation
Plants and trees absorb carbon dioxide and emit oxygen. The chopping of trees causes a significant rise in greenhouse gases, which raises the earth’s temperature. Farming Nitrous oxide, which is utilized in fertilizers, contributes to the greenhouse effect in the environment.
Effects of Greenhouse Effect
The primary consequences of rising greenhouse gas emissions are as follows:
1. Global Warming
It is the progressive rise in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere. The major source of this environmental problem is the growing volume of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane emitted by the combustion of fossil fuels, as well as emissions from automobiles, factories, and other human activities.
2. Water Bodies Acidification
The increase in the overall amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has acidified the majority of the world’s water bodies. The greenhouse gases combine with precipitation and fall to the ground as acid rain. This causes water bodies to become acidic. Furthermore, rainfall takes impurities with it and deposits them in rivers, streams, and lakes, producing acidification.
3. Ozone Depletion
The Ozone Layer shields the planet from the sun’s dangerous UV radiation. It is found in the high stratosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer allows dangerous UV radiation to enter the earth’s surface, which can cause skin cancer and significantly modify the climate. The buildup of natural greenhouse gases such as chlorofluorocarbons, carbon dioxide, methane, and others is the primary source of this phenomenon.
4. Smog and Pollution of the Air
Smog is created when smoke and fog combine. It can be caused by both natural and man-made factors. In general, smog is caused by the buildup of additional greenhouse gases, such as nitrogen and sulfur oxides. Automobile and industrial emissions, agricultural fires, natural forest fires, and the reactivity of these chemicals among themselves are the key contributors to the production of smog.
Runaway Greenhouse Effect
This happens when the planet receives more radiation than it can emit back. As a result, the heat released from the earth’s surface is reduced, and the planet’s temperature continues to rise. Scientists think that this phenomenon occurred billions of years ago on the planet of Venus.
This occurrence is thought to have happened in the following way:
When the temperature of a planet increases to the boiling point of water, a runaway greenhouse effect occurs. As a result, all of the water in the seas condenses into water vapor, trapping more heat from the sun and raising the global temperature. The greenhouse effect is eventually accelerated as a result of this. This is also known as a “positive feedback loop.”
Another possibility giving rise to the runaway greenhouse effect is: Assume that the temperature rise caused by the aforementioned factors reaches such a high degree that chemical reactions begin to occur. Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere as a result of these chemical processes. This would heat the planet’s surface, accelerating the transport of carbon dioxide from the rocks to the atmosphere and causing the runaway greenhouse effect.
Simply said, increasing the greenhouse effect causes a runaway greenhouse effect, which raises the temperature of the Earth to the point where no life will exist in the near future.
Also read: NEET Exam Pattern 2022
FAQs
Name the two gases that have the greatest impact on the greenhouse effect.
CO2 and CH4 are the two gases that contribute the most to the greenhouse effect.
In two lines, explain the Greenhouse Effect.
A greenhouse effect is the trapping of larger amounts of gases, such as carbon dioxide, in the Earth's atmosphere. These gases function as a screen, trapping heat from the sun and generating a significant rise in temperature.
Explain the greenhouse effect and ozone layer depletion in terms of global warming.
The greenhouse effect is the phenomenon that causes the planet to heat up owing to the presence of certain gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases enable solar radiations to enter but hinder heat radiations of longer wavelengths from escaping. When the concentration of these greenhouse gases in the atmosphere rises, global warming occurs.









