Table of Contents
Valence electrons are the negatively charged particles in the outermost region of atoms that participate in the formation of chemical bonds. Regardless of the type of chemical connection (ionic, covalent, or metallic) between atoms, changes in atomic structure are confined to the outermost, or valence, electrons. They are less strongly attracted to the positive atomic nucleus than the inner electrons and can thus be shared or transferred with nearby atoms during the bonding process. Valence electrons are also involved in the conduction of electric current in metals and semiconductors. Valence electrons are involved in the majority of chemical processes because they have more energy than electrons in inner orbits. They help us determine an element’s chemical properties, such as its valency or how it forms bonds with other elements. It also tells us how easily atoms can form bonds, how many unpaired electrons exist, and how many atoms can take part.
Overview
Electrons are thought to occupy orbitals in an atom and play a role in chemical bonding. Atoms are most stable after completing their octet, which can be accomplished through electron transfer or sharing. In general, an electron dot diagram is a representation of valence electrons in an atom that uses dots to surround the element’s symbol. The number of dots corresponds to the number of valence electrons in the atom. These dots are positioned to the right and left, above and below the symbol, with no more than two dots on each side.
The Lewis Structure is a really symbolic form of a molecule’s valence shell electrons. It is used to depict how electrons in a molecule are arranged around individual atoms. Electrons are represented as “dots” or as a line between two atoms when they are bonded. The goal is to find the “best” electron configuration, which means that the octet rule and formal charges must be met.
The goal of drawing a Lewis dot structure is to identify lone electron pairs in molecules to aid in chemical bond formation. Lewis structures can be created for molecules with covalent bonds as well as coordination compounds. The possible explanation for this is that electrons in a covalent bond are shared. It’s more like one atom donates an electron to the other atom in an ionic bond. A Lewis structure relies on the octet rule, which states that atoms share electrons in order for each atom to have eight electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis Structure
Lewis structure is a visual portrayal of electron distribution around an atom. The main reason for learning Lewis dot structure is that it aids in predicting the number and type of bonds that can form around an atom. It also aids in predicting the molecule’s geometry.
Lewis dot structures portray the elements’ electronic structures, including how electrons are paired. Lewis structures, which can be thought of as “electron bookkeeping,” are a useful way to summarise certain information about bonding. Every single dot in a Lewis dot structure represents an electron. A bond is represented by a pair of dots between chemical symbols for atoms.
We can say that the Lewis Electron Dot Formula has one dot for each valence electron and the symbol of the element. The stages for articulating the electron dot formula are listed below. Make a skeletal structure with only the element symbols that show a realistic bonding pattern.
The following are the steps that must be taken when drawing a Lewis structure.
- Initially, the overall number of valence electrons in the molecule is determined by adding the valencies of each atom.
- If indeed the molecule is an anion, extra electrons are added to the Lewis dot structure (number of electrons added = magnitude of negative charge).
- To compensate for the positive charge in cationic molecules, electrons are subtracted from the total count.
- The molecule or ion’s central atom is the atom with the least electronegative charge.
- The atoms are now linked together by single bonds.
- The lone pairs of electrons are now assigned to each atom in the molecule. Lone pairs are typically assigned to the most electronegative atoms first.
- If every atom does not have an octet configuration after the lone pairs are assigned, a double or triple bond must be drawn to satisfy the octet valency of each atom.
- To satisfy the octet rule for two atoms, a lone pair can be converted into a bond pair if necessary.
It really is worth noting that when drawing Lewis dot structures, only the valence electrons are considered, and electrons that do not belong to the outermost shell are ignored.
SO2 Lewis Structure
When mixed with water, the colourless inorganic gas (SO2) produces a weak acid solution.
To draw the Lewis Structure of SO2, you must first obtain the total valence electrons on both Sulfur and Oxygen. After that, everything should be arranged on Sulfurs outermost shell. The two, Sulfur and Oxygen, each have six valence electrons, and according to the Octet Rule, if there are lone pairs or nonbonding electrons, it can lose or attain and share atoms till it is fully complete.
The finest Lewis Structure would be one in which the two oxygen atoms have double bonds, resulting in their formal charges being zero and the formal charge of Sulfur being zero.

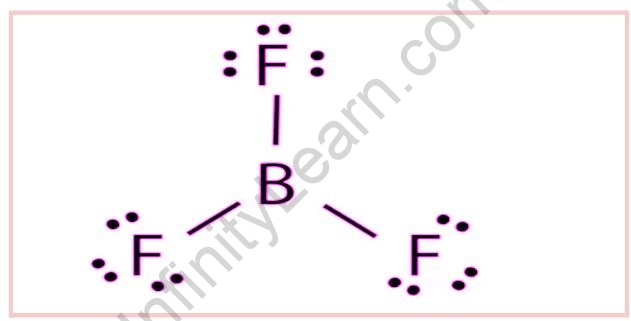
BF3 Lewis Structure
Boron is the least electronegative atom in BF3 and will serve as the central atom. The Lewis Dot Structure depicts one Boron atom with three electrons in its last shell and three Fluorine atoms with seven electrons in its last shell. The calculation will result in 24 total valence electrons, resulting in three B-F bonds.
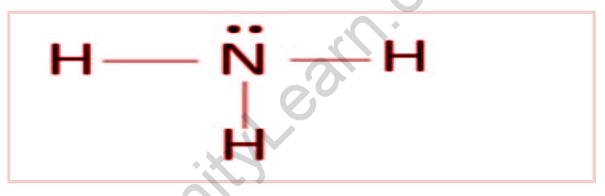
NH3 Lewis Structure
We recognize that nitrogen has five valence electrons in its outer shell, and hydrogen has only one electron.
The Lewis structure of NH3 would be three hydrogen atoms bonded to a nitrogen atom in the centre, with a single pair of electrons on top of the atom. This is why ammonia functions as a Lewis base because it can donate those electrons.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is there any limitation of Lewis Dot Structure?
The Lewis electron dot structure has some limitations or drawbacks. Lewis electron dot structures, which are based on the octet rule of atoms, explain and predict the type and number of bonds formed by elements based on the number of electrons in the outermost cells. However, it fails to explain molecule geometry, is limited to the 2-dimensional representation of molecules through diagrams only, does not accurately describe the magnetic behavior of molecules and bonds, and so on.
Is there any purpose of drawing Lewis Dot Structure?
Clearly, the primary goal of Lewis Dot Structure is to assist students and scientists in making predictions about the most stable structure that a molecule can have while forming bonds with other molecules. There are numerous other uses and benefits to drawing molecular structures with the Lewis Dot technique. It predicts the type and number of bonds, overall formal charge, stability, chemical bond formation, and properties of molecules based on simple graphical representations of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of atoms.
What is the best Lewis structure?
The Lewis structure with nearest formal charges to 0 is best in the sense that it contributes more to the resonance mixture than the other two resonance structures.






