Table of Contents
Introduction
A strong electrolyte is a solution/solute that completely or nearly completely ionizes or dissociates in water. In the solution, these ions are excellent conductors of electric current. Originally, a “strong electrolyte” was defined as a chemical that is a good conductor of electricity in an aqueous solution. Its definition was replaced by the current one as we gained a better understanding of the properties of ions in solution. At the same temperature, a concentrated solution of this strong electrolyte has a lower vapour pressure than pure water. Strong electrolytes are strong acids, strong bases, and soluble ionic salts that are not weak acids or weak bases. Electrolytes are substances that, when exposed to electricity, decompose into ions in their aqueous solution or molten state. Electrolytes are chemicals that react with water to form ions. Electrolyte-containing aqueous solutions conduct electricity. Strong electrolytes are made up of strong acids, bases, and salts. In an aqueous solution, these chemicals completely dissociate into ions.
An electrolyte is a chemical compound that dissociates into its respective ions when dissolved in a solvent (usually water). The ions formed in the solution are positively charged, i.e., cations, and negatively charged, i.e., anions, and they are free to move, conducting electricity in the solution. An electrolyte is a liquid or gel that contains ions and can be broken down by electrolysis (Electrolysis is the Chemical decomposition of substances by the passage of electric current). When dissolved in a polar solvent such as water, it forms an electrically conducting solution. When completely dissolved in water, strong electrolytes completely dissociate into ions. Dilution of strong electrolytes causes a slight increase in conductance. They are excellent electrical conductors. At moderate concentrations, they have strong interionic attraction, whereas weak electrolytes do not completely dissociate when dissolved in water. Their conductance rapidly increases with dilution, particularly near-infinite dilution. They are not very good electrical conductors. Even when concentration is extremely high, ionic attractions are weak. Strong electrolytes include strong acids, strong bases, and salts, whereas weak electrolytes include weak acids, weak bases, and salts.
Overview
A strong electrolyte is an electrolyte solute or solution that completely dissociates in solution. The solution will only contain ions and no electrolyte molecules. Strong electrolytes are good electrical conductors, but only in aqueous solutions or molten form. A galvanic cell can be used to determine the relative strength of an electrolyte. The higher the electrolyte concentration, the higher the voltage produced. Strong electrolytes are substances that completely dissociate into ions. Sodium chloride, potassium chloride, lead bromide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and other examples. A strong electrolyte is an electrolyte solute or solution that completely dissociates in solution. The reaction arrow of a strong electrolyte only points toward products, indicating dissociation. A weak electrolyte’s reaction arrow, on the other hand, points in both directions. The strong electrolyte equation has the following general form:
strong electrolyte→ (aq) cation +(aq)+ anion –
The reaction arrow of a strong electrolyte only points toward products, indicating dissociation. A weak electrolyte’s reaction arrow, on the other hand, points in both directions.
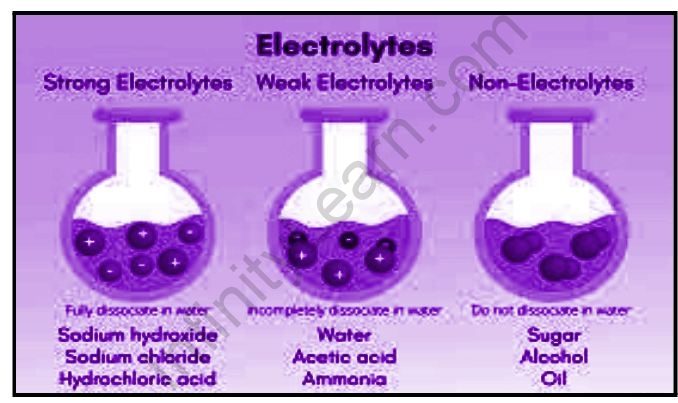
Strong and weak electrolytes
Electrolytes are involved in a variety of vital processes in our bodies. They play an important role in transmitting nerve impulses, contracting muscles, keeping us hydrated, and regulating our body’s pH level. Sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, and bicarbonate are some electrolytes found in our bodies. These electrolytes are required for a variety of bodily processes.
Muscle contraction requires electrolyte calcium. Magnesium is also needed in this process for muscle fibers to slide outwards and muscles to relax after contraction. Water must be kept in the proper amount inside and outside of each cell in our body. Through osmosis, sodium aids in the maintenance of fluid balance. Osmosis is a process in which water moves through cell membranes from a dilute solution (more water and fuel electrolytes) to a concentrated solution (less water and more electrolytes). Cells are prevented from bursting as a result of this.
A weak electrolyte is a molecule that does not completely dissociate in a solution, meaning that the molecule only breaks down into ions in the solvent. These are the electrical current’s poor conductors. Weak electrolytes include weak acids, weak bases, and nitrogen-containing compounds.
A strong electrolyte is a molecule that dissociates completely in solution. In an aqueous solution, these ions are excellent conductors of electricity. At the same temperature, a concentrated solution containing strong electrolytes has a lower vapour pressure than pure water. Strong electrolytes are soluble ionic salts, strong acids, and strong bases.
Weak electrolyte
In an aqueous solution, a weak electrolyte is one that does not completely dissociate. The electrolyte ions and molecules will be present in the solution. Weak electrolytes only partially ionize in water (typically 1% to 10%), whereas strong electrolytes completely ionize (100 percent ). Weak electrolytes include HC2H3O2 (acetic acid), H2CO3 (carbonic acid), NH3 (ammonia), and H3PO4 (phosphoric acid). Weak electrolytes are weak acids and bases. Strong acids, bases, and salts, on the other hand, are strong electrolytes. It is important to note that a salt can have a low water solubility and still be a strong electrolyte because the amount that does dissolve completely ionizes in water.
Weak electrolytes do not dissociate completely into the solvent, whereas strong electrolytes can dissolve in an aqueous solution. The solution contains molecules as well as the ions found in the electrolyte. Weak electrolytes ionize partially in the water, whereas strong electrolytes completely ionize. Weak electrolytes are weak bases and weak acids. Strong electrolytes include strong bases, acids, and salts. Even though salt has low solubility in water, it is considered a strong electrolyte because whatever amount it dissolves in water is completely ionized.
Also read: Le Chatelier’s Principle
FAQs
Q. What exactly is a weak electrolyte? Give a few examples.
Ans: The electrolyte that is not completely dissociated into the solution is referred to as a weak electrolyte. In the case of the weak electrolyte, because the electrolyte is partially dissolved in the solvent, only a small fraction of the ions are present in a dissolved solute. Ammonia (NH3), Carbonic acid (CH2O3), Hydrofluoric acid (HF), Pyridine (C5H5N), Hydrogen cyanide (HCN), and other weak electrolytes
Q. What exactly is a strong electrolyte? Give a few examples.
Ans: Strong electrolytes are electrolytes that have the ability to completely dissociate into the solution. In the case of a strong electrolyte, because the electrolyte is completely dissolved in the solvent, a large fraction of the ions are present in a dissolved solute. Lithium hydroxide (LiOH), barium hydroxide Ba (OH)2, carbonic acid (CH2O3), nitric acid (HNO3), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and other strong electrolytes are examples.







